What Is Fund Of Funds With Example
adminse
Apr 01, 2025 · 9 min read
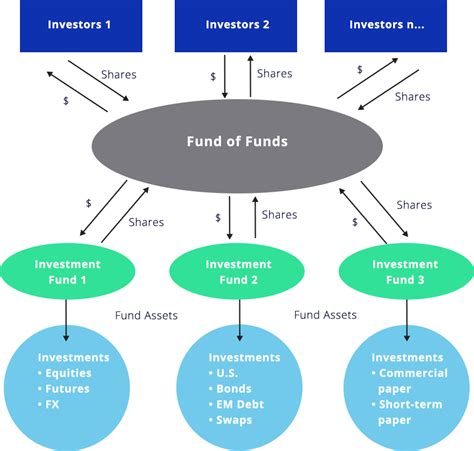
Table of Contents
Unlocking the Potential of Funds of Funds: A Comprehensive Guide
What if accessing diversified investment strategies and expert portfolio management were simpler than ever before? Funds of Funds offer a powerful gateway to sophisticated investment opportunities, mitigating risk and maximizing returns.
Editor’s Note: This article on Funds of Funds provides a comprehensive overview of this investment vehicle, exploring its mechanics, advantages, disadvantages, and real-world examples. Updated for 2024, it offers current insights for investors considering this strategy.
Why Funds of Funds Matter: Relevance, Practical Applications, and Industry Significance
Funds of Funds (FoFs) are investment vehicles that pool capital from multiple investors to invest in a portfolio of other investment funds, rather than directly in individual assets like stocks or bonds. Their significance lies in their ability to provide diversification, professional management, and access to specialized investment strategies otherwise unavailable to individual investors. They are particularly relevant in the context of the growing complexity of global financial markets, requiring sophisticated expertise to navigate successfully. FoFs are used across various asset classes, including hedge funds, private equity, real estate, and even publicly traded mutual funds, catering to a wide range of investor risk tolerances and financial goals.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This article provides a detailed exploration of Funds of Funds, covering their definition, structure, investment strategies, benefits, drawbacks, risk management, regulatory considerations, and real-world examples. Readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of how FoFs work and their role in a diversified investment portfolio.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article draws upon extensive research, including academic literature on investment strategies, regulatory documents pertaining to FoFs, and publicly available information on various FoFs and their underlying investments. Case studies and examples are used to illustrate key concepts and practical applications. The analysis aims to provide readers with a balanced and informed perspective on this complex investment vehicle.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: A clear explanation of what a Fund of Funds is and its fundamental principles.
- Investment Strategies: Examination of different investment strategies employed by FoFs, including active and passive management.
- Advantages and Disadvantages: Weighing the pros and cons of investing in FoFs compared to direct investments.
- Risk Management: Understanding the inherent risks and mitigation strategies employed by FoFs.
- Regulatory Considerations: Overview of the regulatory landscape surrounding FoFs and investor protections.
- Real-World Examples: Case studies and examples of successful and unsuccessful FoFs.
- Selecting a Fund of Funds: Practical guidance for investors considering FoF investments.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
With a foundational understanding of the importance of Funds of Funds, let's delve into a more in-depth analysis of their structure, strategies, and performance.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Funds of Funds
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
A Fund of Funds is essentially a fund that invests in other funds. It acts as an intermediary, allowing investors to access a diversified portfolio of underlying funds managed by different investment professionals. This structure provides diversification across various asset classes, investment strategies, and geographies, reducing overall portfolio risk. The FoF manager selects the underlying funds based on their investment objectives, risk tolerance, and performance track record. Investors in FoFs typically pay fees to both the FoF manager and the underlying fund managers.
2. Investment Strategies:
FoFs employ diverse investment strategies, depending on their investment mandate. Some FoFs may focus on a specific asset class, such as private equity or hedge funds, while others may diversify across multiple asset classes. The investment strategies can be either active or passive. Active management involves selecting underlying funds based on their expected performance and market outlook, while passive management involves investing in a diversified basket of funds according to a predetermined index or benchmark.
3. Advantages of Funds of Funds:
- Diversification: FoFs offer diversification across various asset classes, managers, and investment strategies, reducing overall portfolio risk.
- Professional Management: Investors benefit from the expertise of both the FoF manager and the underlying fund managers.
- Access to Specialized Strategies: FoFs provide access to specialized investment strategies and asset classes that may be difficult or costly for individual investors to access directly.
- Simplified Investment Process: Investing in a single FoF simplifies the investment process compared to managing a portfolio of individual funds.
- Potentially Higher Returns: Skilled FoF managers can potentially generate higher returns than individual investors through strategic fund selection and allocation.
4. Disadvantages of Funds of Funds:
- Higher Fees: FoFs typically charge higher fees than directly investing in individual funds, as investors pay fees to both the FoF manager and the underlying fund managers. This "double layer" of fees can significantly impact returns.
- Lack of Transparency: The complexity of FoFs can make it difficult for investors to understand the underlying investments and their performance.
- Potential for Manager Misalignment: The interests of the FoF manager may not always align with the interests of the investors.
- Liquidity Risk: Some underlying funds may have limited liquidity, making it difficult for the FoF to quickly sell its investments.
- Performance Dependence: The performance of a FoF is heavily dependent on the performance of its underlying funds. Poor performance by the underlying funds can significantly impact the FoF's returns.
5. Risk Management in Funds of Funds:
Effective risk management is crucial for FoFs. This includes thorough due diligence on underlying funds, diversification across various managers and strategies, and regular monitoring of portfolio performance. The FoF manager should also have robust risk management processes in place to identify and mitigate potential risks.
6. Regulatory Considerations:
FoFs are subject to various regulations, depending on their structure and the jurisdiction in which they operate. These regulations aim to protect investors and ensure the transparency and integrity of the market. Compliance with these regulations is essential for FoFs to operate legally and ethically.
Exploring the Connection Between Due Diligence and Funds of Funds
The relationship between thorough due diligence and the success of a Fund of Funds is paramount. Due diligence forms the bedrock of sound investment decisions within this complex structure. Without rigorous scrutiny of underlying funds, the FoF's overall performance and investor protection are severely compromised.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Roles and Real-World Examples: The role of due diligence in selecting high-performing underlying funds is vital. For instance, a FoF focusing on emerging market equities must meticulously vet each fund's country-specific expertise, risk management protocols, and historical performance in diverse economic climates. A failure in this aspect could lead to significant losses.
- Risks and Mitigations: Insufficient due diligence increases the risk of selecting poorly managed or fraudulent underlying funds. Mitigations involve using independent third-party due diligence providers, analyzing fund managers' track records and investment strategies in detail, and examining their compliance records.
- Impact and Implications: The impact of inadequate due diligence can range from underperformance to complete loss of capital. For example, the Madoff scandal highlighted the devastating consequences of failing to conduct proper due diligence, leading to billions of dollars in losses for investors in FoFs that held Madoff's fraudulent funds.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
The interplay between robust due diligence and a successful FoF strategy is undeniable. By prioritizing thorough due diligence, FoFs can mitigate risks, enhance returns, and provide investors with greater confidence in their investments. This systematic process is not merely a compliance exercise; it is an integral part of building a well-diversified and resilient portfolio within the FoF structure.
Further Analysis: Examining Due Diligence in Greater Detail
A closer examination of due diligence reveals its multi-faceted nature. It encompasses not only analyzing the financial performance of underlying funds but also understanding the management team's experience, investment philosophy, and risk management frameworks. This process is iterative and requires ongoing monitoring to adapt to changing market dynamics and evolving risks.
Real-World Examples of Funds of Funds:
Numerous Funds of Funds exist across various asset classes. While specific fund details are often proprietary, analyzing publicly available information about FoFs provides insights into their strategies and performance. Some FoFs focus on specific sectors, like renewable energy or technology, while others diversify across multiple sectors and geographic regions. Examining the performance of various FoFs over time helps illustrate the impact of different investment strategies and market conditions. For instance, comparing FoFs that heavily invested in the tech sector during the dot-com bubble with those that had a more diversified approach would reveal the impact of concentrated investments.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Funds of Funds
- What is a Fund of Funds? A Fund of Funds is an investment vehicle that invests in a portfolio of other investment funds, providing diversification and access to specialized strategies.
- How do Funds of Funds generate returns? FoFs generate returns through the appreciation of the underlying funds’ assets and any distributions received from those funds.
- What are the fees associated with Funds of Funds? FoFs typically charge management fees and performance-based fees. Investors also pay fees to the underlying funds.
- Are Funds of Funds suitable for all investors? No. FoFs are generally more suitable for sophisticated investors with a higher risk tolerance and a long-term investment horizon.
- How can I choose a suitable Fund of Funds? Carefully evaluate the FoF’s investment strategy, fees, risk profile, and track record. Consider consulting with a financial advisor.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Funds of Funds
- Understand the Basics: Before investing, fully grasp the concept, structure, and potential risks associated with FoFs.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Don't over-concentrate your investments in a single FoF. Diversify across multiple FoFs or other asset classes.
- Due Diligence is Key: Thoroughly research and vet any FoF before investing. Examine its track record, management team, fees, and underlying investments.
- Long-Term Perspective: FoFs are typically long-term investments. Avoid making short-term decisions based on market fluctuations.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
Funds of Funds offer a powerful mechanism for accessing diverse investment opportunities and professional management. However, their complexity and potential for higher fees necessitate careful consideration and thorough due diligence. By understanding the intricacies of FoFs and conducting thorough research, investors can leverage these vehicles to potentially enhance returns while mitigating risk within a well-diversified portfolio. The key takeaway remains that while FoFs can offer significant advantages, they are not without risk, and a prudent approach is essential for maximizing their benefits.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do Credit Card Companies Calculate Your Minimum Payment
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Do Credit Card Companies Determine Minimum Payment Due
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Do Credit Card Companies Work Out Minimum Payment
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Does Credit Card Company Calculate Minimum Payment
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Do Credit Card Companies Calculate Minimum Payment Due
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Fund Of Funds With Example . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.