What Is The Typical Late Fee For Late Rent
adminse
Apr 04, 2025 · 8 min read
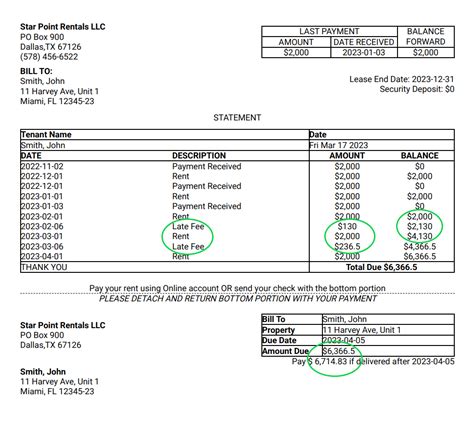
Table of Contents
Decoding Late Rent Fees: A Comprehensive Guide
What if a seemingly small late rent fee could snowball into significant financial hardship? Understanding the nuances of late rent charges is crucial for responsible tenancy and financial stability.
Editor’s Note: This article on late rent fees was published today, providing up-to-date insights into common practices and legal considerations across various jurisdictions. This information is for general guidance only and should not be considered legal advice. Consult with a legal professional for advice specific to your situation.
Why Late Rent Fees Matter: Relevance, Practical Applications, and Industry Significance
Late rent fees are more than just a minor inconvenience; they represent a significant financial burden for tenants and a critical revenue stream for landlords. Understanding these fees is crucial for both parties to navigate the rental agreement effectively and avoid potential legal disputes. This knowledge empowers tenants to budget responsibly and landlords to maintain a stable income flow while adhering to fair practices. The impact extends beyond individual finances, influencing broader economic stability within rental markets.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This article delves into the intricacies of late rent fees, exploring their typical amounts, legal limitations, variations across states and regions, and the best practices for both landlords and tenants. We'll also examine the potential consequences of consistent late payments and strategies for avoiding late fees altogether. Readers will gain actionable insights supported by research and real-world examples.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article draws upon extensive research, including analysis of state and local laws, rental agreements from various regions, and expert opinions from legal professionals specializing in landlord-tenant law. We've consulted reputable sources to ensure accuracy and provide readers with trustworthy information.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: A clear definition of late rent fees and their fundamental components.
- Typical Fee Amounts: An analysis of common late fee structures and their range across different areas.
- Legal Frameworks and Limitations: An exploration of the legal boundaries surrounding late rent fees and tenant protections.
- Variations Across Jurisdictions: A comparison of late fee practices across different states and regions.
- Consequences of Consistent Late Payments: An examination of potential repercussions, including eviction.
- Strategies for Avoiding Late Fees: Practical tips and advice for tenants to avoid late rent payments.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
Now that we've established the importance of understanding late rent fees, let's explore the key aspects in greater detail, beginning with a clear definition and then examining their typical amounts and legal parameters.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Late Rent Fees
Definition and Core Concepts:
A late rent fee is a penalty charged by a landlord to a tenant for failing to pay rent by the agreed-upon due date, as stipulated in the lease agreement. These fees are designed to compensate landlords for the administrative burden and financial losses associated with late payments. The specific amount of the fee is usually outlined in the lease, though regulations often dictate maximum permissible charges.
Typical Fee Amounts:
There's no single "typical" late rent fee. The amount varies considerably depending on several factors:
- Location: State and local laws often regulate the maximum permissible late fee. Some jurisdictions have strict caps, while others allow landlords more flexibility.
- Lease Agreement: The lease itself will specify the amount of the late fee. This amount is usually a fixed dollar amount or a percentage of the monthly rent.
- Lease Type: The type of rental property (apartment, house, etc.) might influence the fee structure.
- Landlord Policies: Some landlords may have more lenient policies, while others might impose stricter penalties.
While there’s no nationwide average, common late fees range from a flat fee of $25 to $100, or a percentage of the monthly rent (typically 5-10%). Some landlords may increase the late fee after a certain grace period. It's crucial to review your lease carefully to understand the specific terms.
Legal Frameworks and Limitations:
Many jurisdictions have laws that regulate the amount of late fees landlords can charge. These laws are in place to protect tenants from excessive charges and ensure fair practices. Excessively high late fees can be challenged legally. The legal framework often dictates:
- Maximum permissible fees: A cap on the total late fee that can be charged.
- Grace periods: A timeframe after the due date before a late fee is applied.
- Notice requirements: The landlord's obligation to provide proper notice about late fees.
It's essential to understand the relevant laws in your area to determine whether a late fee is legally justifiable.
Variations Across Jurisdictions:
Late fee regulations differ significantly across states and even within different cities or counties. Some states have strict caps on late fees, while others allow for greater flexibility. For example, some states may limit the late fee to a percentage of the monthly rent, while others may permit a flat fee or a combination of both. Researching your specific location's laws is crucial.
Consequences of Consistent Late Payments:
Repeated late rent payments can have severe consequences:
- Increased Late Fees: Some leases escalate late fees for repeated offenses.
- Damage to Credit Score: Late rent payments can negatively impact a tenant's credit score, making it more difficult to secure loans or rent in the future.
- Eviction: Consistent late payments can lead to eviction proceedings, resulting in the loss of housing.
- Legal Action: Landlords can pursue legal action to recover unpaid rent and late fees.
Strategies for Avoiding Late Fees:
Avoiding late fees involves proactive financial planning and effective communication:
- Budgeting: Create a budget that accurately reflects monthly expenses, including rent.
- Autopay: Set up automatic payments to ensure rent is paid on time.
- Reminders: Utilize calendar reminders or other tools to stay on top of the rent due date.
- Communication: Contact your landlord promptly if you anticipate difficulty paying rent on time. Many landlords are willing to work with tenants facing temporary financial hardship.
Exploring the Connection Between Grace Periods and Late Rent Fees
The grace period, the time allowed after the rent due date before a late fee is applied, significantly impacts the application of late rent fees. Let's explore this connection:
Roles and Real-World Examples:
A grace period provides a buffer for tenants who might be a few days late due to unforeseen circumstances. For instance, a tenant might have a delayed paycheck or encounter an unexpected expense. Without a grace period, even a minor delay could incur a penalty. Many leases provide a 2-5 day grace period.
Risks and Mitigations:
While a grace period offers some leeway, it's not a guarantee against late fees. Exceeding the grace period invariably results in a late fee. Mitigation strategies include: setting up automatic payments, diligently tracking the due date, and communicating with the landlord about potential delays.
Impact and Implications:
The length of the grace period can significantly affect both tenants and landlords. A longer grace period benefits tenants by providing more flexibility. However, a longer period could also impact landlords' cash flow and financial stability.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
The interplay between grace periods and late fees highlights the need for clear communication and responsible financial planning for both tenants and landlords.
Further Analysis: Examining Grace Periods in Greater Detail
Grace periods are not standardized. Some jurisdictions may require a minimum grace period, while others leave it to the discretion of the landlord and tenant within the lease agreement. Understanding the specific grace period detailed in your lease is critical.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Late Rent Fees
- What is a late rent fee? A late rent fee is a penalty charged for paying rent after the due date.
- How much is a typical late rent fee? There is no typical amount; it varies by location, lease agreement, and landlord policy.
- What happens if I pay rent late repeatedly? Repeated late payments can lead to increased fees, damage to credit score, and even eviction.
- What should I do if I can't pay rent on time? Communicate with your landlord immediately to explore options.
- Are there legal limitations on late fees? Yes, many jurisdictions regulate the maximum amount a landlord can charge.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Understanding Late Rent Fees
- Read Your Lease Carefully: Understand the specific late fee policy in your lease.
- Set Up Autopay: Automate rent payments to ensure timely payments.
- Track Due Dates: Use calendars or reminders to avoid missing deadlines.
- Budget Effectively: Create a budget that includes rent as a priority expense.
- Communicate Proactively: Contact your landlord if you anticipate difficulties.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
Late rent fees represent a significant aspect of the tenant-landlord relationship. Understanding their nuances – including typical amounts, legal limitations, and strategies for avoidance – empowers both parties to navigate this dynamic effectively. Proactive financial management, clear communication, and a thorough understanding of the relevant laws are crucial for maintaining a positive and legally sound rental experience. By embracing responsible practices, tenants can avoid the negative consequences of late rent payments, and landlords can ensure stable cash flow and mitigate risks.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Minimum Payment Due Citi Credit Card
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Do I Know What The Minimum Payment On My Credit Card Is
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Minimum Payment On A Credit Card
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Minimum Credit Score For A Citi Credit Card
Apr 04, 2025
-
Minimum Payment Citi Simplicity
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Typical Late Fee For Late Rent . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.