What Is The Standard Late Fee On An Invoice
adminse
Apr 04, 2025 · 9 min read
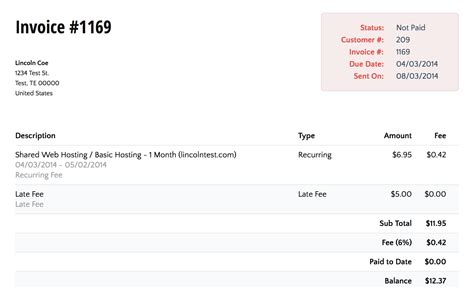
Table of Contents
What are the standard late fees on an invoice?
Late payment penalties are a crucial aspect of effective business management, impacting cash flow and client relationships.
Editor’s Note: This article on standard late fees on invoices was published today, providing current insights into best practices and legal considerations. It's designed to help businesses of all sizes understand how to structure late fees fairly and effectively.
Why Late Fees on Invoices Matter:
Late invoice payments significantly impact a business's financial health. Delayed payments disrupt cash flow, hindering operational efficiency, project timelines, and even employee compensation. Consistent late payments can jeopardize a business's ability to meet its own financial obligations, leading to serious financial repercussions. Establishing and enforcing clear late payment policies is, therefore, critical for maintaining financial stability and promoting timely payments from clients. Furthermore, a well-defined policy demonstrates professionalism and contributes to a positive business image.
Overview: What This Article Covers:
This article explores the complexities of late fees on invoices. We will delve into legal aspects, best practices, industry standards, common late fee structures, considerations for different business types, and strategies for minimizing late payments. Readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of how to establish and manage a late fee policy effectively and legally.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights:
This article is the result of extensive research, drawing upon legal databases, industry reports, accounting practices, and expert opinions from finance professionals. We've examined various state and federal laws governing late fees, analyzed successful late payment policies from diverse industries, and consulted with legal and financial experts to ensure accuracy and practical application.
Key Takeaways:
- Defining Late Fees: A precise definition and legal basis for late fees.
- Legal Frameworks: State and federal laws influencing late fee structures.
- Best Practices: Strategies for designing a fair and effective late fee policy.
- Industry Standards: Common late fee percentages and structures across various sectors.
- Minimizing Late Payments: Proactive measures to encourage prompt payment.
- Negotiating Late Fee Waivers: Considerations for handling exceptional circumstances.
- Collection Practices: Ethical and legal methods for collecting overdue invoices.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
With an understanding of the importance of timely payments, let’s explore the intricacies of establishing and enforcing effective late fee policies.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Late Fees on Invoices:
1. Defining Late Fees and Their Legal Basis:
Late fees are penalties imposed on clients for failing to remit payment by the invoice's due date. The legal enforceability of late fees hinges on the clarity and transparency of the agreement between the business and the client. This typically involves including the late fee policy directly on the invoice itself or in a separate contract signed by both parties. The specific wording should be unambiguous, clearly stating the percentage or fixed amount charged, the grace period (the number of days after the due date before the fee is applied), and the calculation method. Vague language can lead to disputes and legal challenges.
2. Legal Frameworks Governing Late Fees:
Late fee policies must comply with both federal and state laws. Federal regulations, while not directly dictating late fee amounts, govern fair debt collection practices. The Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA) restricts the methods used to collect overdue debts and prevents harassment or abusive tactics. State laws vary significantly. Some states have specific regulations concerning late fees, potentially limiting the amount that can be charged or requiring specific disclosures. Businesses must research and adhere to the relevant laws in their jurisdiction. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines and legal action.
3. Best Practices for Designing a Late Fee Policy:
Creating a fair and effective late fee policy requires careful consideration. The following are key best practices:
- Transparency: Clearly state the late fee policy on the invoice and/or contract. Avoid ambiguous language.
- Reasonableness: Choose a late fee percentage that is reasonable and comparable to industry standards. Exorbitant fees can damage client relationships and create disputes. A common range is 1.5% to 2% per month, but this varies considerably by industry and payment terms.
- Grace Period: Allow a reasonable grace period (e.g., 10-15 days) after the due date before applying the late fee.
- Consistent Application: Apply the late fee consistently to all clients to avoid accusations of bias or unfair treatment.
- Communication: Communicate the late fee policy proactively and clearly. Send reminders before the due date and follow up promptly after the grace period has expired.
- Escalation Process: Establish a clear escalation process for handling persistent late payments, starting with friendly reminders and escalating to more formal methods if necessary.
4. Industry Standards for Late Fees:
While there's no universally standard late fee, certain industries tend to have established norms. For example, the construction industry may have higher late fees due to the large sums involved and project dependencies. Consult industry associations or resources to understand typical late fee practices in your sector. Researching competitors' policies can also provide valuable insights, although direct copying is not advisable; you should adapt these to fit your specific business circumstances.
5. Minimizing Late Payments: Proactive Strategies:
Proactive measures can significantly reduce the incidence of late payments:
- Clear Invoices: Ensure invoices are clear, concise, and easy to understand, including all relevant information (due date, payment terms, contact details).
- Online Payment Options: Offer multiple convenient payment options (e.g., online portals, credit card payments, ACH transfers) to make it easy for clients to pay.
- Automated Reminders: Set up automated email or text message reminders to clients before the due date and again after the grace period.
- Strong Client Relationships: Build strong relationships with clients to foster trust and open communication. Address payment concerns promptly.
- Early Payment Discounts: Consider offering early payment discounts to incentivize prompt payment.
6. Negotiating Late Fee Waivers:
While consistent enforcement of late fees is crucial, there may be exceptional circumstances warranting a waiver. Consider these factors:
- Client History: A long-standing client with a generally good payment history may warrant a one-time waiver for a justifiable reason.
- Economic Hardship: Demonstrated financial hardship on the part of the client might warrant consideration.
- Relationship Value: Weigh the value of the client relationship against the amount of the late fee.
7. Ethical and Legal Debt Collection Practices:
When late payments persist despite reminders, it's crucial to follow ethical and legal debt collection practices. The FDCPA sets strict guidelines to prevent abusive or harassing tactics. These practices include:
- Avoid Threats or Harassment: Refrain from making threats or using abusive language.
- Maintain Professionalism: Keep all communication professional and respectful.
- Accurate Information: Ensure all information conveyed is accurate and truthful.
- Legal Counsel: Consult with legal counsel if necessary, particularly if legal action is being considered.
Exploring the Connection Between Payment Terms and Late Fees:
Payment terms are inextricably linked to late fees. Payment terms define the timeframe given to clients for remitting payment. Common terms include "Net 30" (payment due within 30 days of invoice date), "Net 60," and "Net 90." The length of the payment term directly influences the appropriateness of the late fee. A longer payment term might justify a slightly higher late fee to compensate for the extended credit period. The relationship between payment terms and late fees should be clearly defined and consistently applied.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Roles: The client's role (e.g., large corporation versus sole proprietor) might influence the negotiation of late fees and waivers. Large corporations may have more established payment processes, reducing the frequency of late payments. Smaller businesses might require more flexibility.
- Real-World Examples: A large construction project might have a higher late fee due to the significant financial impact of delayed payment, whereas a small service provider's late fee might be relatively modest.
- Risks and Mitigations: The risk of losing a client due to strict late fee enforcement must be balanced against the need to maintain financial stability. Implementing a tiered late fee system (increasing fees after multiple late payments) can mitigate this risk.
- Impact and Implications: Consistent enforcement of late fees enhances cash flow predictability, reduces financial risk, and fosters a culture of timely payment.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection Between Payment Terms and Late Fees:
The interplay between payment terms and late fees requires careful consideration. Fair and reasonable late fees, clearly communicated within a well-defined policy, protect a business’s financial health while fostering positive client relationships. Businesses must adapt their policies to specific industries and circumstances while remaining compliant with all relevant laws.
Further Analysis: Examining State-Specific Laws in Greater Detail:
A deeper dive into state-specific laws reveals significant variations in regulations regarding late fees. Some states have caps on the amount that can be charged, while others may require specific disclosures. Consulting a legal professional familiar with your state's laws is crucial for ensuring compliance.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Late Fees on Invoices:
Q: What is the average late fee on an invoice?
A: There's no single "average" late fee. The percentage or fixed amount varies considerably by industry, payment terms, and business size. Common ranges include 1.5% to 2% per month, but this can be significantly higher or lower depending on specific circumstances.
Q: Can I charge late fees if it’s not explicitly stated on my invoice?
A: It's strongly recommended to include the late fee policy explicitly on your invoice or in a signed contract. While some jurisdictions may allow late fees even without explicit mention, this can lead to disputes. Clear communication minimizes ambiguity and protects your business.
Q: What if a client disputes a late fee?
A: Address the dispute promptly and professionally. Review your policy and payment records carefully. If the dispute is legitimate (e.g., an invoicing error), resolve the issue fairly. If the dispute is unfounded, maintain a firm but respectful stance, explaining your policy clearly.
Q: What are my options if a client consistently pays late?
A: Implement a tiered system of late fees, increasing the penalty with each late payment. Consider suspending further services until outstanding payments are received. In extreme cases, you may need to consult with legal counsel to explore debt collection options.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Effectiveness of Your Late Fee Policy:
-
Regularly Review Your Policy: Periodically review and update your late fee policy to ensure it remains current, fair, and compliant with all relevant laws.
-
Use Automated Systems: Implement automated invoicing and payment reminder systems to streamline the process and reduce administrative burden.
-
Track Payments Closely: Maintain accurate records of all invoices and payments to ensure timely identification and handling of late payments.
Final Conclusion: A Well-Defined Late Fee Policy is Essential for Business Success:
A well-defined and consistently enforced late fee policy is not just about collecting money; it's about maintaining financial stability, fostering professionalism, and promoting timely payments from clients. By understanding the legal framework, industry standards, and best practices, businesses can establish a system that protects their cash flow while preserving positive client relationships. Remember, proactive communication, clear invoicing, and convenient payment options go a long way in preventing late payments in the first place.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Minimum Monthly Payment For An Irs Installment Plan
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Is The Minimum Irs Payment Plan
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Is The Lowest Payment Plan For Irs
Apr 06, 2025
-
How To Find Minimum Payment Credit Card
Apr 06, 2025
-
Minimum Payment Amount Credit Card
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Standard Late Fee On An Invoice . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.