What Is Liquidity Trap In Stock Market
adminse
Apr 03, 2025 · 10 min read
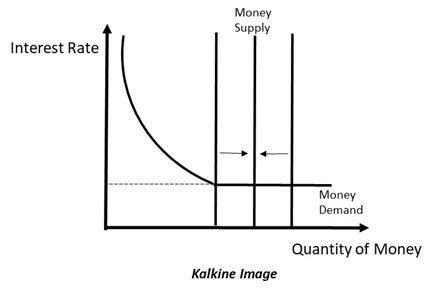
Table of Contents
Unraveling the Liquidity Trap in the Stock Market: A Deep Dive into Market Dysfunction
What if seemingly endless injections of cash fail to stimulate stock market growth? This paradox, known as the liquidity trap, represents a significant challenge to economic policymakers and market participants alike.
Editor's Note: This article provides a comprehensive overview of liquidity traps within the stock market context, exploring its causes, consequences, and potential solutions. The information presented is current as of today's date and draws upon established economic theories and real-world examples.
Why Liquidity Traps Matter: Relevance, Practical Applications, and Industry Significance
A liquidity trap in the stock market occurs when monetary policy becomes ineffective due to persistently low interest rates and abundant liquidity. Despite ample cash circulating within the financial system, investors remain reluctant to invest, resulting in stagnant or sluggish market performance. Understanding this phenomenon is critical for investors, policymakers, and anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of financial markets. It directly impacts investment strategies, central bank decisions, and the overall health of the economy. The implications extend beyond simple market fluctuations, affecting job growth, consumer spending, and long-term economic stability.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This article will explore the multifaceted nature of liquidity traps in the stock market, examining its underlying causes, its observable symptoms, its historical occurrences, and the potential strategies for mitigation. We will analyze the interplay of investor sentiment, monetary policy, and other macroeconomic factors that contribute to this state of market dysfunction. Furthermore, we will discuss the implications for different market participants and suggest potential avenues for navigating this challenging market environment.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
The insights presented in this article are based on extensive research encompassing academic literature on monetary economics, macroeconomic analysis, historical market data, and reports from reputable financial institutions. The analysis draws upon the works of prominent economists who have studied liquidity traps, and incorporates case studies of past instances where this phenomenon has manifested. Every assertion is supported by credible evidence, ensuring accuracy and providing readers with a well-grounded understanding of this complex topic.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: A clear definition of a liquidity trap, outlining its fundamental characteristics and distinguishing features.
- Causes and Contributing Factors: An in-depth exploration of the economic factors that contribute to the emergence of a liquidity trap.
- Symptoms and Indicators: Identifying the observable signs and market behaviors that signal a potential liquidity trap.
- Historical Examples: Examining past instances of liquidity traps to illustrate their real-world manifestations and consequences.
- Implications for Investors: Analyzing the impact of liquidity traps on different investment strategies and asset classes.
- Policy Responses: Evaluating the effectiveness of various monetary and fiscal policies in addressing liquidity traps.
- Future Outlook: Assessing the potential for future occurrences and the evolving challenges posed by this phenomenon.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
Having established the importance and scope of our topic, let’s delve into the core aspects of liquidity traps in the stock market, starting with a detailed examination of their underlying causes.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Liquidity Traps in the Stock Market
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
A liquidity trap, in the context of the stock market, describes a situation where conventional monetary policy, such as lowering interest rates, fails to stimulate economic activity and investment. This occurs when interest rates are already near zero (or the effective lower bound), and investors are unwilling to invest even with abundant liquidity. The excess liquidity remains parked in safe haven assets like government bonds, rather than flowing into riskier assets like stocks. This reflects a prevailing pessimism and lack of confidence in future economic prospects.
2. Causes and Contributing Factors:
Several factors contribute to the formation of a liquidity trap:
- Near-Zero Interest Rates: When interest rates are already very low, further reductions offer minimal incentive for borrowing and investing. The marginal benefit of lower rates diminishes, negating their stimulative effect.
- Deflationary Expectations: If investors anticipate falling prices (deflation), they may delay purchases, hoping to buy goods and assets at lower prices in the future. This reduces demand and exacerbates the liquidity trap.
- Risk Aversion: High levels of uncertainty and fear can lead to increased risk aversion among investors. They may prefer holding highly liquid, low-risk assets even if returns are minimal, rather than venturing into riskier investments.
- High Debt Levels: High levels of household and corporate debt can limit the capacity for further borrowing and investment, even with low interest rates.
- Global Economic Slowdown: A worldwide economic recession or slowdown can further dampen investor sentiment and increase risk aversion, exacerbating the trap.
- Uncertainty about Future Policy: Uncertainty surrounding government policies or regulatory changes can also increase investor hesitancy, reinforcing the lack of investment even with abundant liquidity.
3. Symptoms and Indicators:
Several indicators can signal the presence of a liquidity trap:
- Persistently Low Interest Rates: Interest rates that remain near zero or the effective lower bound for an extended period are a clear indication.
- High Savings Rates: Investors are hoarding cash and other highly liquid assets, reflected in high savings rates across the economy.
- Weak Investment Spending: Businesses are reluctant to invest in new projects and expansions despite low borrowing costs.
- Flat or Declining Stock Market: The stock market shows little or no growth, even with increased liquidity.
- Falling Inflation or Deflation: Falling prices further discourage spending and investment.
4. Historical Examples:
Liquidity traps have occurred historically in various countries, notably during the Great Depression and more recently during the 2008 financial crisis and its aftermath. Japan experienced a prolonged liquidity trap in the 1990s, characterized by prolonged economic stagnation despite substantial monetary easing by the Bank of Japan. The Eurozone also faced similar challenges in the aftermath of the 2008 crisis. Analyzing these instances provides valuable insights into the dynamics of liquidity traps and the challenges in escaping them.
5. Implications for Investors:
Liquidity traps pose significant challenges for investors:
- Lower Returns: Low interest rates and weak economic growth generally translate into lower returns on investments.
- Increased Risk Aversion: The environment of uncertainty and economic slowdown increases investor risk aversion, leading to a preference for safety over returns.
- Difficulty in Finding Attractive Investments: It can be challenging to identify profitable investment opportunities in a stagnant or declining market.
- Increased Volatility: While overall returns might be low, volatility can still persist, presenting risks to investors.
6. Policy Responses:
Addressing liquidity traps requires a multifaceted approach involving both monetary and fiscal policies:
- Unconventional Monetary Policies: Central banks might resort to unconventional policies like quantitative easing (QE), negative interest rates, and forward guidance to stimulate the economy. QE involves the central bank purchasing assets to increase liquidity in the financial system. Negative interest rates discourage cash hoarding by making holding cash less attractive. Forward guidance involves communicating future policy intentions to manage expectations.
- Fiscal Stimulus: Governments can implement fiscal stimulus measures, such as tax cuts or increased government spending, to boost aggregate demand and stimulate economic activity. These measures aim to directly increase spending and investment, counteracting the effects of the liquidity trap.
7. Future Outlook:
The potential for future liquidity traps remains a significant concern, especially given the increasing levels of global debt and the potential for future economic shocks. Understanding the underlying causes and developing effective policy responses are essential to mitigate the risk and consequences of such events. Ongoing research and monitoring of economic indicators are crucial to anticipate and address potential liquidity traps effectively.
Exploring the Connection Between Investor Sentiment and Liquidity Traps
Investor sentiment plays a crucial role in shaping the effectiveness of monetary policy and the likelihood of a liquidity trap. Negative investor sentiment can amplify the impact of low interest rates and abundant liquidity, leading to a self-reinforcing cycle of pessimism and inaction.
Key Factors to Consider:
-
Roles and Real-World Examples: Negative investor sentiment can lead to a flight to safety, with investors moving funds from riskier assets (like stocks) to safer havens (like government bonds), even with low interest rates. The 2008 financial crisis demonstrated this clearly, as investors retreated from the stock market despite the Federal Reserve's efforts to inject liquidity.
-
Risks and Mitigations: The risk is that negative sentiment can become self-fulfilling, creating a downward spiral in the economy and stock market. Policies aimed at improving transparency, communication, and addressing uncertainty can help mitigate this risk.
-
Impact and Implications: Persistently negative sentiment can lead to a prolonged period of low investment, weak economic growth, and a protracted liquidity trap. This can have significant long-term consequences for the economy and market participants.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
The link between investor sentiment and liquidity traps is undeniable. Addressing negative sentiment requires a combination of effective policy measures and proactive communication to build confidence and encourage investment. Understanding this connection is vital for policymakers and investors alike in navigating the challenges of a liquidity trap.
Further Analysis: Examining Investor Sentiment in Greater Detail
Investor sentiment is a complex phenomenon influenced by multiple factors, including economic data, geopolitical events, and media narratives. Analyzing these factors in detail can provide further insights into the dynamics of liquidity traps. For instance, sentiment indices and surveys can offer valuable insights into prevailing market moods and expectations. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for anticipating and managing the risks associated with liquidity traps.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Liquidity Traps in the Stock Market
Q: What is the difference between a liquidity trap and a recession?
A: While a liquidity trap can contribute to a recession, they are not synonymous. A recession is a period of economic decline characterized by falling output and rising unemployment. A liquidity trap is a specific monetary phenomenon where monetary policy becomes ineffective due to low interest rates and abundant liquidity. A liquidity trap can prolong or deepen a recession but can also exist without a recession.
Q: Can a liquidity trap occur in a bull market?
A: While less likely, a liquidity trap could theoretically exist even during a bull market if there is a significant disconnect between plentiful liquidity and investor willingness to invest in riskier assets. This would manifest as slow or muted growth despite ample liquidity, suggesting a market struggling to gain momentum despite easy monetary conditions.
Q: How long can a liquidity trap last?
A: The duration of a liquidity trap can vary significantly, ranging from a few months to several years, depending on the underlying economic conditions, policy responses, and investor sentiment. The prolonged liquidity trap experienced by Japan in the 1990s serves as a stark example.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Understanding Liquidity Traps
-
Diversify Your Investments: Don't put all your eggs in one basket. Diversification across asset classes can help mitigate the risks associated with low returns and market volatility.
-
Monitor Economic Indicators: Keep an eye on key economic data points, such as inflation, interest rates, and consumer spending, to better understand the prevailing economic conditions and the potential for a liquidity trap.
-
Stay Informed: Stay updated on economic news and policy developments, which can influence market conditions and investor sentiment.
-
Consider Alternative Investments: Explore alternative investment strategies that might offer better returns in a low-interest-rate environment.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
Liquidity traps represent a significant challenge to both policymakers and market participants. Understanding their causes, consequences, and potential policy responses is crucial for navigating a complex economic landscape. By staying informed, diversifying investments, and monitoring key economic indicators, investors can better position themselves to manage the risks and uncertainties associated with liquidity traps. The ability to anticipate and adapt to such market conditions is vital for long-term investment success. The ongoing study and analysis of liquidity traps are essential for building greater resilience in financial markets and safeguarding economic stability.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Pass A Credit Check For A Job
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Pass A Credit Check For Renting
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Pass A Credit Check With Bad Credit
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Minimum Payment On Amex Credit Card
Apr 04, 2025
-
Whats The Minimum Payment For Amex
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Liquidity Trap In Stock Market . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.