What Does Grace Period Mean For Loans
adminse
Apr 01, 2025 · 8 min read
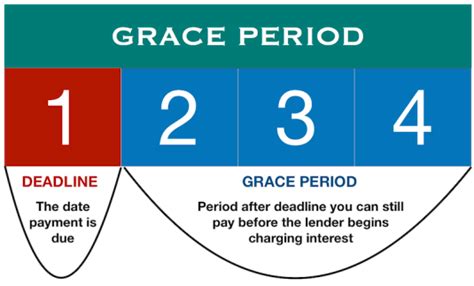
Table of Contents
Unlocking the Secrets of Loan Grace Periods: A Comprehensive Guide
What if navigating the complexities of loan repayments was easier than you think? Understanding the grace period is key to responsible borrowing and avoiding financial pitfalls.
Editor’s Note: This article on loan grace periods was published today, providing you with the most up-to-date information and insights to help you manage your loans effectively.
Why Loan Grace Periods Matter: Relevance, Practical Applications, and Financial Implications
A loan grace period is a crucial aspect of borrowing money. It represents a temporary reprieve, a period where borrowers are not required to make regular loan payments. Understanding its nuances is vital for both responsible borrowing and effective financial management. This period significantly impacts a borrower's financial well-being, influencing their credit score, overall debt burden, and future borrowing capabilities. Failing to grasp its implications can lead to late payment fees, damaged credit, and even default.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This article delves into the core aspects of loan grace periods, exploring their different types, eligibility criteria, implications for various loan types, and potential pitfalls. Readers will gain actionable insights, backed by illustrative examples and practical advice, enabling informed decision-making regarding personal loan management.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article is the result of extensive research, drawing upon information from reputable financial institutions, government agencies, and consumer protection organizations. It synthesizes established financial principles with real-world examples to provide a comprehensive and accessible understanding of loan grace periods.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Types of Grace Periods: A detailed explanation of what constitutes a grace period and the various forms it can take.
- Grace Periods Across Loan Types: How grace periods are applied to different loans (student loans, mortgages, personal loans, etc.).
- Eligibility Criteria and Application Process: Understanding the requirements to qualify for a grace period and how to request one.
- Implications of Grace Periods: The impact on credit scores, interest accrual, and future borrowing capacity.
- Potential Pitfalls and Avoiding Problems: Common misconceptions and strategies to prevent negative consequences.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
With a foundational understanding of the importance of grace periods, let's explore their key aspects in detail, examining their application across different loan types and the implications for borrowers.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Loan Grace Periods
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
A loan grace period is a predefined period after the loan disbursement date (or a specific event, like graduation for student loans) during which the borrower is not obligated to make regular loan repayments. However, this doesn't mean it's a free pass. In most cases, interest will continue to accrue during the grace period. This accumulated interest can significantly impact the total repayment amount. The length of a grace period varies widely depending on the type of loan and the lender's policies.
2. Grace Periods Across Loan Types:
- Student Loans: Federal student loans typically offer a grace period of six months after graduation, leaving school, or dropping below half-time enrollment. Private student loans may have shorter grace periods or no grace period at all.
- Mortgages: Mortgages rarely offer a grace period in the traditional sense. However, some lenders may work with borrowers facing temporary financial hardship to create a forbearance plan, which temporarily modifies payment terms. This is not a grace period, but a similar concept.
- Personal Loans: Personal loans generally do not have built-in grace periods. If a borrower experiences difficulty making payments, they should contact the lender immediately to explore options such as repayment plans or hardship programs.
- Auto Loans: Similar to personal loans, auto loans typically don't include grace periods. Missed payments will negatively impact the credit score and could lead to repossession of the vehicle.
3. Eligibility Criteria and Application Process:
Eligibility for a grace period is primarily determined by the loan agreement and the specific terms set by the lender. For student loans, eligibility is often tied to graduation status, enrollment status, or completion of a degree program. For other loan types, eligibility for hardship programs (which can provide temporary relief similar to a grace period) is generally based on documented financial difficulties. The application process varies by lender but usually involves providing proof of hardship, such as job loss documentation or medical bills.
4. Implications of Grace Periods:
- Interest Accrual: Even though payments aren't due during a grace period, interest typically continues to accrue on the loan principal. This can lead to a significantly larger loan balance at the end of the grace period, increasing the total repayment amount.
- Credit Score Impact: While a grace period itself doesn't directly affect your credit score, missing payments after the grace period ends will severely damage your credit rating. Late payments are reported to credit bureaus and can significantly reduce your credit score, making it harder to obtain loans or credit in the future.
- Future Borrowing Capacity: A lower credit score due to missed payments can severely impact your ability to secure future loans. Lenders often view borrowers with poor credit history as higher risk, resulting in higher interest rates or loan denials.
5. Potential Pitfalls and Avoiding Problems:
- Misunderstanding Interest Accrual: Many borrowers mistakenly believe that a grace period means they don't owe any money during that time. Understanding that interest continues to accumulate is crucial for responsible financial management.
- Failing to Plan for Repayment: The grace period is temporary. Borrowers need to develop a robust repayment plan before the grace period ends to avoid late payments and credit damage.
- Ignoring Communication with Lenders: If facing financial difficulties, proactive communication with the lender is crucial. They may offer solutions like repayment plans or hardship programs to avoid default.
Closing Insights: Summarizing the Core Discussion
Loan grace periods offer temporary relief from loan repayments, but they are not a free pass. Understanding the implications of interest accrual and the importance of timely repayment after the grace period is crucial for maintaining good credit and responsible financial management. Proactive communication with lenders is essential in navigating potential financial challenges.
Exploring the Connection Between Financial Literacy and Grace Periods
The relationship between financial literacy and effectively utilizing grace periods is significant. A lack of financial understanding can lead borrowers to misinterpret grace periods, leading to missed payments and credit damage. Strong financial literacy empowers borrowers to use grace periods strategically, giving them time to adjust their finances and create a solid repayment plan.
Key Factors to Consider:
Roles and Real-World Examples: Lack of financial literacy can result in borrowers failing to plan for repayment after the grace period, leading to late payments. For example, a student might assume that the six-month grace period on their student loans is sufficient and fail to budget for repayment, resulting in a damaged credit score. Conversely, financially literate borrowers will use the grace period to create a budget, explore repayment options, and prepare for consistent payments.
Risks and Mitigations: The primary risk associated with a lack of financial literacy regarding grace periods is missed payments, leading to penalties, late fees, and a damaged credit score. Mitigation involves educating oneself on loan terms, budgeting effectively, and actively communicating with lenders when facing financial hardship.
Impact and Implications: The long-term impact of financial illiteracy regarding grace periods can be severe. It can lead to a cycle of debt, difficulty securing future loans, and long-term financial instability. Financial literacy empowers borrowers to make informed decisions, avoid these pitfalls, and build a strong financial future.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
The connection between financial literacy and navigating grace periods underscores the importance of financial education. By understanding the nuances of grace periods and possessing strong financial literacy, borrowers can effectively utilize this temporary reprieve to manage their loans responsibly and build a solid financial foundation.
Further Analysis: Examining Financial Literacy in Greater Detail
Financial literacy encompasses a wide range of skills and knowledge, including budgeting, saving, investing, and understanding debt management. It's a crucial life skill that empowers individuals to make sound financial decisions, avoid debt traps, and achieve their financial goals. Improving financial literacy can be achieved through various resources, including online courses, workshops, and financial counseling services.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Loan Grace Periods
Q: What is a grace period on a loan? A: A grace period is a temporary period after a loan is disbursed (or a specific event occurs) during which regular loan payments are not required. However, interest usually still accrues.
Q: How long are grace periods typically? A: Grace period lengths vary depending on the loan type and lender. Federal student loans often have six-month grace periods, while other loans may have shorter periods or none at all.
Q: Does interest accrue during a grace period? A: Generally, yes. While payments are not due, interest continues to accumulate, increasing the total loan balance.
Q: What happens if I miss payments after the grace period? A: Missing payments after the grace period ends will negatively impact your credit score, potentially leading to late fees, further penalties, and even default on the loan.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Loan Grace Periods
- Understand the Terms: Carefully review your loan agreement to understand the exact terms of your grace period, including its length and whether interest accrues.
- Budget and Plan: Use the grace period to create a realistic budget and develop a comprehensive repayment plan before the grace period ends.
- Communicate with Lenders: If you anticipate difficulty making payments, contact your lender proactively to explore options like repayment plans or hardship programs.
- Seek Financial Counseling: If you need help managing your finances, consider seeking guidance from a financial counselor or credit counselor.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
Loan grace periods can be valuable tools for managing debt, but only when understood and used responsibly. By educating yourself on the terms of your loan, budgeting effectively, and communicating openly with lenders, you can utilize grace periods to your advantage and avoid the pitfalls of missed payments and damaged credit. Remember, responsible financial management is key to long-term financial well-being.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do Credit Cards Calculate Minimum Payment
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Do Credit Card Companies Most Typically Calculate The Minimum Payment Due
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Do Credit Card Companies Determine Your Minimum Payment
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Do Credit Card Companies Calculate Your Minimum Payment
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Do Credit Card Companies Determine Minimum Payment Due
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Does Grace Period Mean For Loans . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.