How To Calculate Late Fees On Invoices
adminse
Apr 03, 2025 · 8 min read
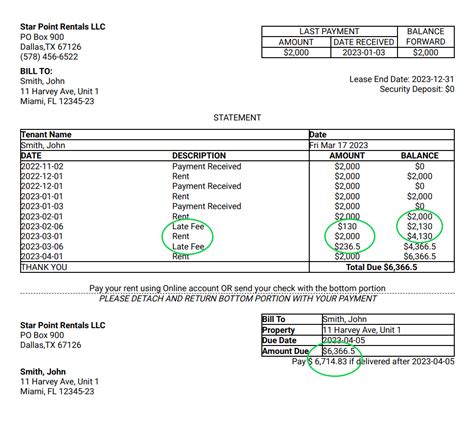
Table of Contents
Decoding Late Fees: A Comprehensive Guide to Calculating Invoice Penalties
What if seemingly simple late fees on invoices could significantly impact your business's cash flow and profitability? Mastering the art of calculating and implementing these fees is crucial for maintaining financial health and fostering timely payments.
Editor’s Note: This article on calculating late fees on invoices was published today, providing you with the most up-to-date information and best practices to manage your accounts receivables effectively.
Why Calculating Late Fees Matters:
Late payments are a pervasive issue for businesses of all sizes. The cost of chasing overdue invoices, the strain on cash flow, and the potential impact on business growth are significant. Implementing a clear and legally sound late fee policy is essential for:
- Improving Cash Flow: Consistent and timely payments are crucial for maintaining healthy cash flow, allowing for smoother operations and strategic investments.
- Reducing Administrative Burden: A well-defined late fee policy minimizes the time and resources spent on chasing overdue payments.
- Enforcing Payment Terms: Clearly stating and enforcing late fees reinforces the agreed-upon payment terms, encouraging clients to prioritize timely payments.
- Protecting Profitability: Unpaid invoices directly impact profitability. Late fees help compensate for the financial losses incurred due to delayed payments.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This article will delve into the intricacies of calculating late fees on invoices. We'll explore different methods of calculation, legal considerations, best practices for implementing a late fee policy, and how to avoid potential disputes. You'll gain actionable insights to manage your invoicing process more effectively and protect your financial well-being.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This guide is the product of extensive research, incorporating legal precedents, accounting best practices, and real-world examples. We've consulted various legal and financial resources to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information presented. Every recommendation is supported by evidence, offering you a trustworthy and actionable framework.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the Fundamentals: Defining late fees, their legal implications, and the importance of clear communication.
- Methods of Calculation: Exploring various approaches to calculating late fees, including flat fees, percentage-based fees, and tiered systems.
- Legal Compliance: Ensuring your late fee policy adheres to relevant state and federal laws.
- Best Practices: Implementing a robust late fee policy that is both effective and fair.
- Dispute Resolution: Strategies for handling disputes and maintaining positive client relationships.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
With a clear understanding of why effectively calculating late fees is crucial, let's now delve into the specifics of how to do it correctly and legally.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Calculating Late Fees
1. Defining Late Fees and Payment Terms:
Before calculating late fees, establish clear payment terms on your invoices. This includes specifying the due date, the acceptable payment methods, and the consequences of late payment. Clearly state the late fee amount and the calculation method. Ambiguity can lead to disputes. For example:
- "Payment is due within 30 days of invoice date. A late fee of 1.5% of the invoice total will be added for payments received after the due date."
2. Methods of Calculating Late Fees:
Several methods exist for calculating late fees, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
-
Flat Fee: A fixed amount is charged for late payment, regardless of the invoice total. This method is simple to implement but might not be proportional to larger invoices. For example, a $25 late fee.
-
Percentage-Based Fee: A percentage of the outstanding invoice amount is charged as a late fee. This method is often considered more equitable, as it scales with the invoice amount. For example, 1.5% of the invoice total.
-
Tiered System: This combines elements of both flat and percentage-based fees, using increasing late fees based on the number of days overdue. This method can be more effective in incentivizing timely payment. For example:
- 0-15 days late: 1% late fee
- 16-30 days late: 2% late fee
- 31+ days late: 5% late fee + potential collection agency referral.
3. Legal Compliance:
The legality of late fees varies by state and country. Some jurisdictions have specific laws regulating the amount and calculation of late fees. It's crucial to research and comply with the relevant regulations to avoid legal issues. Factors to consider include:
- State Laws: Some states have specific laws limiting the maximum allowable late fee percentage or requiring specific disclosures.
- Contract Law: Your late fee policy should be clearly stated in your contract or terms and conditions, making it a legally binding agreement.
- Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (FDCPA): If you outsource collections, ensure the collection agency adheres to the FDCPA to avoid legal repercussions.
4. Best Practices for Implementing a Late Fee Policy:
- Clear Communication: Clearly communicate your late fee policy on your invoices, website, and contracts. Avoid ambiguity.
- Consistent Application: Apply the late fee policy consistently to all clients to avoid accusations of bias.
- Grace Period: Consider offering a short grace period (e.g., a few days) before imposing late fees. This allows for minor delays without immediate penalties.
- Reminder Notices: Send polite reminder notices before applying late fees to give clients an opportunity to pay on time.
- Transparent Processes: Clearly outline the process for calculating and applying late fees.
- Professionalism: Maintain a professional and courteous demeanor when dealing with late payments.
5. Handling Disputes and Maintaining Relationships:
Even with a clear late fee policy, disputes may arise. Handle these situations professionally and transparently:
- Open Communication: Listen to the client's concerns and attempt to find a mutually agreeable solution.
- Documentation: Keep detailed records of all communications and payment transactions.
- Negotiation: Explore options like payment plans or extensions if the circumstances warrant it.
- Escalation: If a resolution cannot be reached, consider escalating the matter to a collections agency or legal counsel.
Exploring the Connection Between Clear Communication and Effective Late Fee Implementation
Clear communication is paramount to successful late fee implementation. Vague or poorly communicated policies can lead to confusion, disputes, and damaged client relationships. The connection between clear communication and effective late fee implementation is undeniable.
Key Factors to Consider:
-
Roles and Real-World Examples: Effective communication involves clearly stating the late fee policy on invoices, contracts, and website terms of service. Using examples clarifies expectations, reducing potential misunderstandings. For instance, a sample invoice with a highlighted late fee section.
-
Risks and Mitigations: Poor communication risks client dissatisfaction, disputes, and negative reviews. Mitigating this requires clear, concise language, multiple communication channels (email, mail, phone), and readily available contact information for questions.
-
Impact and Implications: Successful communication strengthens client relationships, improves cash flow, and reduces administrative burdens. Conversely, poor communication hurts client relationships, impacts profitability, and increases administrative costs.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
The interplay between clear communication and effective late fee implementation underscores the importance of transparency and professionalism in business dealings. By proactively communicating the policy and handling disputes fairly, businesses can successfully implement late fees while maintaining positive client relationships and improving financial health.
Further Analysis: Examining Clear Communication in Greater Detail
Effective communication goes beyond simply stating the late fee; it requires understanding the client's perspective. This involves tailoring communication to suit different client needs, offering multiple communication channels, and employing a proactive approach.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Calculating Late Fees on Invoices
-
Q: What is the best method for calculating late fees?
- A: The optimal method depends on your business's specific needs and the nature of your client relationships. Consider a percentage-based fee for larger invoices or a tiered system for greater flexibility.
-
Q: How do I ensure my late fee policy is legally compliant?
- A: Research your state's specific regulations on late fees. Consult with a legal professional if you have concerns about compliance.
-
Q: What should I do if a client disputes a late fee?
- A: Review your documentation, listen to the client's concerns, and try to negotiate a solution. If negotiation fails, consider escalating the matter.
-
Q: Can I charge interest on late payments in addition to late fees?
- A: The legality of charging interest on late payments in addition to late fees depends on state laws and contract terms. Review relevant regulations before implementing this practice.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Late Fee Policies
- Automate your invoicing and payment reminders: Use accounting software to automate the process, ensuring timely invoice delivery and payment reminders.
- Offer multiple payment options: Providing clients with various payment options (e.g., credit card, ACH transfer, online payment portals) can improve payment efficiency.
- Regularly review and update your late fee policy: Ensure your policy remains current and complies with relevant laws.
- Train your staff on the proper application of the late fee policy: Consistent application is essential to avoid disputes.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
Implementing a robust late fee policy is crucial for maintaining financial health and fostering timely payments. By understanding the different calculation methods, legal considerations, and best practices, businesses can protect their profitability and streamline their invoicing processes. Remember, clear communication and professional handling of disputes are key to building strong client relationships while enforcing your payment terms effectively. Through diligent application and careful consideration of the points discussed, you can transform your invoicing practices and foster a healthy financial foundation for your business.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Total Minimum Payment Due Bank Of America
Apr 04, 2025
-
Minimum Payment On Bank Of America Credit Card
Apr 04, 2025
-
Bank Of America What Is The Minimum Balance On Checking Account
Apr 04, 2025
-
Minimum Pay Bank Of America
Apr 04, 2025
-
Can You Lower Minimum Payment On Credit Card
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Calculate Late Fees On Invoices . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.