How Many Days Is Grace Period
adminse
Apr 02, 2025 · 9 min read
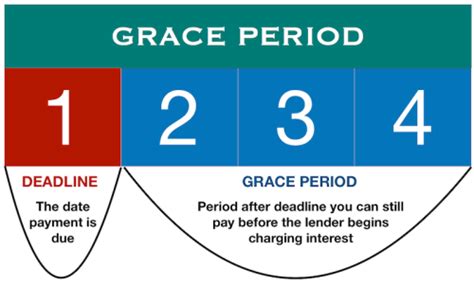
Table of Contents
Decoding the Grace Period: How Many Days Do You Really Have?
What if the seemingly simple question of "how many days is a grace period?" hides a complex web of regulations and industry practices? Understanding grace periods is crucial for avoiding late fees, penalties, and even legal repercussions.
Editor’s Note: This article on grace periods was published today, providing you with the most up-to-date information available on this important topic. We've compiled information from various sources to offer a comprehensive understanding of grace periods across different contexts.
Why Understanding Grace Periods Matters:
Grace periods are crucial because they offer a buffer between missing a deadline and facing negative consequences. Whether it's a credit card payment, a loan repayment, a subscription renewal, or a tax filing, understanding the length of the grace period – and what happens after it expires – is vital for maintaining good financial standing and avoiding penalties. The consequences of missing a deadline without a clear understanding of the grace period can range from minor inconveniences like late fees to significant financial penalties and even legal action in some cases. This knowledge empowers individuals and businesses to manage their financial obligations effectively and avoid unnecessary stress.
Overview: What This Article Covers:
This article provides a comprehensive overview of grace periods, exploring their definition, variations across different contexts (credit cards, loans, insurance, subscriptions, taxes, etc.), the factors influencing their length, and the implications of exceeding them. We will also delve into the legal aspects of grace periods and offer practical advice on how to effectively manage deadlines and avoid late payments.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights:
This article is the product of extensive research, drawing from legal documents, financial institution websites, industry reports, and consumer protection agencies' publications. We've meticulously cross-referenced information to ensure accuracy and provide readers with a reliable and up-to-date understanding of grace periods. The information presented here is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered legal or financial advice. Consult with a qualified professional for personalized guidance.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: A clear definition of a grace period and its foundational principles.
- Variations Across Contexts: Exploration of grace period lengths in different financial and non-financial situations.
- Factors Influencing Length: Identification of variables that determine the duration of a grace period.
- Consequences of Exceeding Grace Periods: Understanding the penalties and repercussions for late payments.
- Legal Aspects of Grace Periods: Examination of legal protections and regulations surrounding grace periods.
- Practical Tips for Managing Deadlines: Actionable advice for avoiding late payments and maximizing the benefits of grace periods.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
Now that we've established the importance of understanding grace periods, let's delve into the specifics, exploring their variations across different contexts and the implications of exceeding them.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Grace Periods:
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
A grace period is a designated timeframe after a payment due date during which a payment can still be made without incurring penalties or late fees. The length of this period varies significantly depending on the type of payment, the provider, and sometimes, even the individual's payment history. The core principle behind a grace period is to provide a degree of flexibility and understanding, acknowledging that unforeseen circumstances can sometimes lead to delayed payments.
2. Variations Across Industries and Contexts:
The length of a grace period varies considerably depending on the type of obligation:
-
Credit Cards: Credit card grace periods typically range from 21 to 25 days. This is the time between the statement closing date and the payment due date. Importantly, the grace period only applies if the previous balance is paid in full. Carrying a balance eliminates the grace period, and interest charges begin accruing immediately.
-
Loans (Mortgages, Auto Loans, Personal Loans): Grace periods on loans are less common and usually only apply in very specific circumstances, such as during periods of hardship documented through a formal process with the lender. Most loans do not offer a grace period for missed payments. Late fees and potentially increased interest rates will apply promptly after the due date.
-
Insurance Premiums: Insurance policies often have a grace period, usually ranging from 15 to 30 days, during which a missed payment can be made without the policy being canceled. However, this grace period is not universal and varies by insurer and policy type.
-
Subscriptions (Streaming Services, Software, etc.): Grace periods for subscriptions are less standardized. Some services might offer a short grace period before suspending access, while others may cancel immediately upon non-payment. It’s essential to check the terms and conditions of each subscription service.
-
Taxes: Tax filing deadlines have no grace periods in most jurisdictions. Extensions might be granted under specific circumstances, but these are not grace periods; they simply delay the deadline. Penalties for late filing and unpaid taxes accumulate from the official deadline.
3. Factors Influencing the Length of Grace Periods:
Several factors can influence the length of a grace period:
- Industry Regulations: Some industries have regulations dictating minimum grace periods (e.g., credit cards in some jurisdictions).
- Company Policies: Individual companies set their grace period policies, often reflecting their risk assessment and customer service approach.
- Payment History: Some lenders may offer extended grace periods to customers with a consistently good payment history.
- Specific Circumstances: Hardship situations might justify extended grace periods, though this is typically a negotiated process with the creditor.
4. Consequences of Exceeding Grace Periods:
The consequences of failing to make a payment within the grace period can be severe:
- Late Fees: Most creditors charge late fees for payments made after the due date, even within a grace period.
- Increased Interest Rates: For loans and credit cards, late payments can result in higher interest rates, significantly increasing the overall cost of borrowing.
- Negative Impact on Credit Score: Late payments are reported to credit bureaus and negatively impact credit scores, making it harder to obtain future loans or credit at favorable rates.
- Account Suspension or Closure: For subscriptions and some loans, missed payments can lead to account suspension or closure.
- Legal Action: In extreme cases, particularly with loans, creditors may take legal action to recover unpaid amounts.
5. Legal Aspects of Grace Periods:
Grace periods are not always legally mandated. While certain industries may have regulations regarding minimum grace periods (e.g., credit card legislation), the specific length and conditions are largely determined by the creditor's policies. It's crucial to understand the terms and conditions of any agreement before entering into it. Consumer protection laws vary by jurisdiction, providing different levels of protection against unfair practices related to late payments and grace periods.
Exploring the Connection Between Payment History and Grace Periods:
The relationship between payment history and grace periods is significant. A consistent history of on-time payments often translates to a more favorable treatment by lenders and service providers. Lenders may be more inclined to offer extended grace periods or show greater leniency in case of occasional missed payments to loyal customers. Conversely, a history of late payments can lead to shorter or non-existent grace periods, stricter enforcement of late fees, and potentially even denial of future credit.
Key Factors to Consider:
-
Roles and Real-World Examples: Individuals with excellent payment histories often benefit from implicit or explicit grace period extensions, perhaps through a more lenient approach from service providers. Businesses with proven financial stability may also negotiate better terms, including potential grace periods, with their lenders.
-
Risks and Mitigations: The primary risk is the accumulation of late fees and a negative impact on credit scores. Mitigation strategies include setting up automatic payments, setting reminders, and proactively communicating with creditors in case of anticipated delays.
-
Impact and Implications: Long-term consequences include diminished creditworthiness, increased borrowing costs, and potential legal ramifications. Responsible financial management minimizes these risks.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection:
The connection between payment history and grace periods is undeniable. Maintaining a strong payment record strengthens one's financial standing and can lead to greater flexibility and leniency from creditors. Conversely, neglecting payments can severely impact financial health.
Further Analysis: Examining Payment History in Greater Detail:
A closer examination of payment history reveals its predictive power in assessing creditworthiness. Credit scoring models heavily rely on payment history to evaluate the likelihood of future defaults. Consistent on-time payments build trust and demonstrate responsible financial behavior, while a pattern of late payments signals increased risk.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Grace Periods:
Q: What happens if I miss a payment during the grace period?
A: Even within a grace period, late fees typically apply. The severity of the consequences depends on the specific agreement and the creditor's policies.
Q: Can I negotiate an extension beyond the grace period?
A: In some cases, you can contact your creditor to explain your situation and request an extension. The likelihood of success depends on your payment history and the creditor's policies.
Q: Are grace periods legally mandated?
A: Not universally. While some regulations might require minimum grace periods for certain types of debt, many grace periods are set by company policy.
Q: How do grace periods affect my credit score?
A: Missing payments, even within the grace period, can negatively impact your credit score, affecting your ability to get loans and credit in the future.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Grace Periods:
-
Understand your deadlines: Note all due dates and grace periods for all your financial obligations.
-
Set up automatic payments: This eliminates the risk of forgetting to make a payment on time.
-
Use payment reminders: Set calendar alerts or use reminder apps to avoid missing deadlines.
-
Review your statements carefully: Ensure you understand the terms and conditions of your accounts.
-
Communicate proactively: If you anticipate a difficulty making a payment, contact your creditor immediately to discuss possible solutions.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights:
Understanding grace periods is crucial for managing personal and business finances effectively. While their length and application vary widely, recognizing the implications of missed payments is paramount. Proactive financial planning, combined with clear communication with creditors, helps individuals and businesses navigate financial obligations successfully. Remember, responsible financial management prevents many issues stemming from missed deadlines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Quickbooks Late Fees
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Set Up Automatic Late Fees In Quickbooks Desktop
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Charge Late Fees In Quickbooks
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Apply Late Fees In Quickbooks
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Set Up Automatic Late Fees In Quickbooks Online
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Days Is Grace Period . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.