What Is Minimum Amount Due In Credit Card Sbi
adminse
Apr 04, 2025 · 8 min read
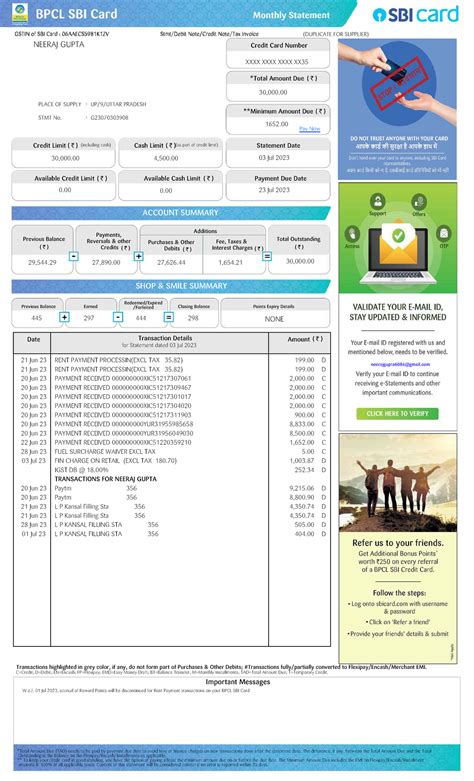
Table of Contents
Decoding the SBI Credit Card Minimum Amount Due: A Comprehensive Guide
What if managing your SBI credit card payments was simpler than you think? Understanding the minimum amount due is key to avoiding late fees and building a strong credit history.
Editor’s Note: This article on the SBI credit card minimum amount due was published today, providing readers with up-to-date information and practical strategies for managing their credit card accounts effectively. This guide aims to demystify the concept and help you navigate your SBI credit card statement with confidence.
Why Understanding Your SBI Credit Card Minimum Amount Due Matters:
Ignoring or misunderstanding your minimum amount due can have serious consequences. Failing to pay at least this amount by the due date results in late payment fees, negatively impacts your credit score, and can ultimately lead to account suspension or even debt collection actions. Furthermore, focusing solely on the minimum payment can lead to accumulating high interest charges and prolonging the repayment period, costing you significantly more in the long run. Understanding this figure empowers you to make informed financial decisions and manage your credit responsibly.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This article will comprehensively explore the SBI credit card minimum amount due. We'll define the term, explain how it's calculated, discuss factors influencing its amount, address common misconceptions, and offer practical tips for effective credit card management. We'll also delve into the implications of only paying the minimum amount and explore alternative strategies for debt repayment.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights:
The information presented here is based on a thorough review of SBI credit card statements, terms and conditions, official SBI website documentation, and widely accepted best practices in credit card management. We have also incorporated insights gleaned from financial experts and consumer reports to provide a balanced and accurate perspective.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: A clear explanation of the minimum amount due and its significance.
- Calculation Methodology: How SBI determines the minimum amount due on your statement.
- Factors Influencing the Amount: Variables affecting the minimum due, such as outstanding balance, credit limit, and payment history.
- Common Misconceptions: Debunking common myths surrounding minimum payments.
- Consequences of Only Paying the Minimum: The long-term financial implications of this strategy.
- Strategic Debt Repayment Options: Alternative methods for efficiently repaying your credit card debt.
- Practical Tips for Effective Credit Card Management: Actionable advice for responsible credit use.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
Now that we’ve established the importance of understanding your SBI credit card minimum amount due, let's delve into the specifics.
Exploring the Key Aspects of the SBI Credit Card Minimum Amount Due:
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
The minimum amount due on your SBI credit card statement is the smallest payment you can make to avoid late payment fees and maintain your account in good standing. It’s crucial to understand that this is not the total amount you owe; it’s merely a portion of your outstanding balance. Paying only the minimum amount does not mean you are debt-free; it simply postpones the repayment of the larger outstanding amount.
2. Calculation Methodology:
SBI's calculation of the minimum amount due isn't publicly disclosed as a precise formula. However, it generally takes into account several factors:
- Outstanding Balance: The primary factor is the total amount you owe on your card at the statement closing date. A higher outstanding balance generally results in a higher minimum amount due.
- Credit Limit: Your credit limit influences the minimum amount due, although the relationship isn't directly proportional. Individuals with higher credit limits might see a higher minimum amount, even with a similar outstanding balance.
- Payment History: Consistent and timely payments generally lead to a lower minimum amount due as SBI might offer some leeway to loyal customers with good repayment behavior.
- Pre-defined Percentage: SBI likely uses a pre-defined percentage of the outstanding balance (often between 5% and 10%, but this can vary) to determine the minimum amount due. This percentage can vary based on your credit history and card type.
- Interest Accrued: The minimum amount due usually does not include the interest accrued on the outstanding balance. This interest is added to your next billing cycle, increasing your outstanding balance and consequently impacting the minimum amount due.
- Fees and Charges: Any outstanding fees or charges (like late payment fees from previous cycles) will also be included in the calculation of the minimum amount due.
3. Factors Influencing the Minimum Amount Due:
Several factors beyond the outstanding balance and credit limit can influence the amount you're required to pay:
- Type of Credit Card: Different SBI credit cards may have varying minimum payment requirements. Premium cards might have higher minimum amounts compared to basic cards.
- Promotional Offers: Promotional periods with 0% interest rates might not significantly alter the minimum payment, although they could decrease the total amount owed over the promotional period.
- Credit Score: A good credit history can influence the minimum amount due, although this influence is subtle.
4. Common Misconceptions:
- Myth 1: Paying the minimum is a good long-term strategy. This is false. Paying only the minimum keeps you in debt for longer, accumulating significant interest charges.
- Myth 2: The minimum amount due covers all interest charges. Incorrect. Interest is added to your next billing cycle, increasing your overall debt.
- Myth 3: My minimum amount due is fixed. It's usually calculated on your outstanding balance each month.
5. Consequences of Only Paying the Minimum:
Paying only the minimum amount due has several drawbacks:
- High Interest Accumulation: You’ll pay significantly more in interest over time.
- Lengthened Repayment Period: It takes much longer to pay off your debt.
- Damaged Credit Score: Consistent minimum payments can negatively impact your creditworthiness.
- Increased Financial Burden: You'll be paying more in total due to the added interest.
6. Strategic Debt Repayment Options:
Instead of solely relying on minimum payments, consider these strategies:
- Debt Snowball Method: Prioritize paying off the smallest debts first for motivation, then move on to larger ones.
- Debt Avalanche Method: Focus on paying off the debt with the highest interest rate first.
- Balance Transfer: Transfer your balance to a card with a lower interest rate.
7. Practical Tips for Effective Credit Card Management:
- Pay More Than the Minimum: Aim to pay at least the full interest charged in addition to a portion of your principal balance.
- Track Your Spending: Monitor your expenses closely to avoid exceeding your credit limit.
- Set Up Autopay: Automate your payments to avoid late fees.
- Read Your Statement Carefully: Understand all charges and fees.
- Contact SBI Customer Service: If you anticipate trouble making your payment, contact them to discuss options.
Exploring the Connection Between Credit Utilization Ratio and Minimum Amount Due:
The credit utilization ratio (the percentage of your available credit that you're using) indirectly influences your minimum amount due. A higher utilization ratio (closer to your credit limit) often leads to a higher minimum amount due because of the larger outstanding balance. Keeping your credit utilization low (ideally below 30%) demonstrates responsible credit management and might lead to a lower minimum payment requirement in the long term.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Roles and Real-World Examples: A high credit utilization ratio, even with on-time payments, might trigger a higher minimum payment to encourage faster debt reduction. For instance, if you consistently use 80% of your credit limit, the minimum payment will likely be higher than if you only use 20%.
- Risks and Mitigations: High credit utilization can negatively impact your credit score, making it harder to get loans or credit in the future. Mitigation involves paying down your balance to lower your utilization ratio.
- Impact and Implications: The long-term impact of high credit utilization includes higher interest payments, limited borrowing options, and potential difficulties in obtaining favorable credit terms.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection:
The relationship between credit utilization and the minimum amount due highlights the importance of responsible credit card usage. By managing your spending habits and keeping your credit utilization low, you can reduce your minimum amount due, avoid excessive interest charges, and build a strong credit history.
Further Analysis: Examining Credit Utilization in Greater Detail:
Maintaining a low credit utilization ratio is crucial for long-term financial health. This ratio is a significant factor in credit scoring models. Regularly reviewing your credit report and addressing any discrepancies are vital for ensuring accurate credit information.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About SBI Credit Card Minimum Amount Due:
Q: What happens if I don't pay the minimum amount due?
A: You will incur late payment fees, and it will negatively impact your credit score. Your account might be suspended, and debt collection agencies could be involved.
Q: Can I negotiate the minimum amount due?
A: It's generally not possible to negotiate the minimum amount due. However, you can contact SBI customer service to discuss payment options if you're facing financial hardship.
Q: Where can I find the minimum amount due on my statement?
A: It's clearly stated on your SBI credit card statement, typically prominently displayed near the payment due date.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Understanding Your Minimum Amount Due:
- Step 1: Understand the calculation method and factors influencing it.
- Step 2: Track your spending and utilization ratio.
- Step 3: Aim to pay more than the minimum amount due consistently.
- Step 4: Explore alternative debt repayment strategies if necessary.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights:
Understanding your SBI credit card minimum amount due is not just about avoiding late fees; it's about responsible financial management. By actively monitoring your spending, paying more than the minimum, and strategically managing your debt, you can build a strong financial foundation and avoid the pitfalls of excessive credit card debt. Consistent responsible credit behavior leads to better credit scores, improved financial well-being, and ultimately, more financial freedom.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Is It More Difficult To Get Out Of Debt When Only Paying The Minimum Payment Edpuzzle
Apr 05, 2025
-
Why Is It More Difficult To Get Out Of Debt When Only Paying The Minimum Payment Quizlet
Apr 05, 2025
-
Minimum Payment Home Depot Card
Apr 05, 2025
-
Does Home Depot Do Monthly Payments
Apr 05, 2025
-
What Is A Minimum Monthly Payment
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Minimum Amount Due In Credit Card Sbi . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.