What Is A Decile Definition Formula To Calculate And Example
adminse
Mar 25, 2025 · 8 min read
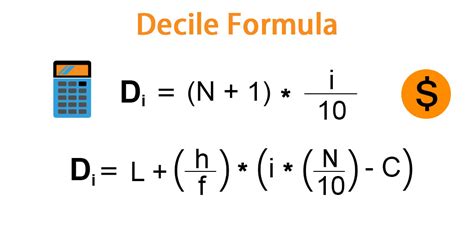
Table of Contents
Understanding Deciles: Definition, Formula, Calculation, and Examples
What if decile analysis unlocked deeper insights into your data than ever before? This powerful statistical tool provides a nuanced understanding of data distribution, revealing patterns often missed by simpler measures.
Editor’s Note: This article on decile definition, formula, calculation, and examples was published today, providing readers with the latest insights and practical applications of this crucial statistical concept.
Why Deciles Matter: Relevance, Practical Applications, and Industry Significance
Deciles are a fundamental tool in descriptive statistics, offering a more granular view of data distribution than simpler measures like the median or quartiles. Instead of dividing data into two (median) or four (quartiles) groups, deciles partition a dataset into ten equal parts. This allows for a more refined analysis, revealing subtle shifts and trends that might otherwise be obscured. Deciles are used extensively across various fields, including:
- Finance: Assessing investment risk, analyzing portfolio performance, and understanding income distribution.
- Healthcare: Studying disease prevalence, analyzing patient outcomes, and evaluating the effectiveness of treatments.
- Education: Comparing student performance across different schools or districts, identifying areas needing improvement.
- Business Analytics: Understanding customer segmentation, identifying key market trends, and optimizing business strategies.
- Social Sciences: Analyzing socioeconomic disparities, studying population demographics, and researching social phenomena.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This article provides a comprehensive guide to deciles, covering their definition, the formula for their calculation, various methods for computation, and illustrative examples. Readers will gain a practical understanding of how to interpret decile results and apply this knowledge to real-world datasets.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article draws upon established statistical principles and incorporates examples from various fields to illustrate the practical application of decile analysis. The explanations are designed to be accessible to a broad audience, requiring no prior advanced statistical knowledge.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: A precise definition of deciles and their significance in data analysis.
- Calculation Methods: Different methods for calculating deciles and their respective advantages and disadvantages.
- Practical Applications: Examples of decile applications in diverse fields, showcasing their versatility.
- Interpretation of Results: How to interpret decile values and draw meaningful conclusions from the analysis.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion
Now that the importance of decile analysis has been established, let's delve into the specifics, beginning with a precise definition and moving on to the methods of calculation and interpretation.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Deciles
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
A decile is a statistical measure that divides a dataset into ten equal parts. Each decile represents the value below which a certain percentage of the data falls. For example, the first decile (D1) represents the value below which 10% of the data lies, the second decile (D2) represents the value below which 20% of the data lies, and so on, until the tenth decile (D10), which represents the value below which 100% of the data lies (the maximum value).
2. Calculation Methods:
There isn't one universally accepted method for calculating deciles. The method chosen often depends on the size and characteristics of the dataset and the specific software used. Several common approaches exist:
-
Method 1: Using the formula: This method uses a formula to calculate the position of each decile within the ordered dataset. The formula is:
Di = (i/10) * (n + 1)Where:
Direpresents the position of the ith decile.iis the decile number (1, 2, 3,..., 10).nis the total number of data points.
If the result is a whole number, that data point is the decile. If the result is a decimal, the decile is found by interpolation between the two nearest data points.
-
Method 2: Linear Interpolation: This method is used when the formula above results in a decimal value. Linear interpolation estimates the decile value by weighting the two adjacent data points based on their proximity to the calculated position.
-
Method 3: Using Software Packages: Statistical software like R, SPSS, Excel, and Python's various libraries (NumPy, Pandas) offer built-in functions to calculate deciles, often employing slightly different algorithms. These software packages usually handle interpolation automatically.
3. Applications Across Industries:
The versatility of deciles extends across numerous sectors. Here are a few examples:
-
Income Inequality: Deciles are frequently used to analyze income distribution within a population, illustrating the gap between the richest and poorest segments. The difference between the 9th and 1st decile can highlight the level of income inequality.
-
Sales Performance: A company can use deciles to segment its sales team, identifying top performers (above the 9th decile) and those needing additional support (below the 1st decile).
-
Risk Assessment: In finance, decile analysis helps in evaluating the risk associated with different investment options. Securities with returns consistently below the 1st decile might be considered high-risk.
-
Quality Control: Manufacturing processes can use decile analysis to monitor product quality. If a significant portion of products falls below a certain decile, it indicates a potential quality issue.
4. Impact on Innovation:
Decile analysis doesn't directly drive innovation but provides a crucial data-driven foundation for informed decision-making. By understanding the distribution of data through deciles, businesses can target specific market segments, tailor products and services, and optimize resource allocation, indirectly fostering innovation.
Closing Insights: Summarizing the Core Discussion
Deciles offer a valuable tool for analyzing data distributions, providing a more detailed picture than simpler measures. The choice of calculation method depends on the specific context and dataset, but all methods aim to divide the data into ten equal parts, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of the data's spread and characteristics.
Exploring the Connection Between Interpolation and Decile Calculation
Interpolation plays a crucial role in decile calculation, particularly when the formula yields a non-integer value for the decile position. This section explores the importance of interpolation in ensuring accurate decile determination.
Key Factors to Consider:
-
Roles and Real-World Examples: Linear interpolation is frequently used in decile calculations to estimate the decile value when the formula produces a decimal. For example, if the formula gives a decile position of 7.3, interpolation weighs the 7th and 8th data points to approximate the 7.3rd position.
-
Risks and Mitigations: Inaccurate interpolation can lead to misinterpretations. Using appropriate interpolation methods and ensuring the data is correctly ordered are crucial to mitigate this risk.
-
Impact and Implications: The accuracy of decile analysis directly depends on the accuracy of interpolation. Incorrect interpolation can skew the results and lead to flawed conclusions.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
Interpolation is not merely a supplementary technique but an integral part of decile calculation, ensuring accuracy and precision in determining decile values, especially when dealing with datasets with a large number of data points or those where the decile positions are not whole numbers.
Further Analysis: Examining Interpolation in Greater Detail
Different interpolation methods exist, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Linear interpolation is the most common, but other methods such as polynomial interpolation might be used in specific situations. The choice of method depends on the nature of the data and the desired level of accuracy.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Deciles
Q: What is the difference between deciles and percentiles? A: Deciles divide data into ten equal parts, while percentiles divide data into 100 equal parts. Deciles are a subset of percentiles. For instance, the 1st decile is equivalent to the 10th percentile, the 2nd decile to the 20th percentile, and so on.
Q: Can deciles be used with non-numerical data? A: Deciles are primarily used with numerical data. However, you can apply them to ordinal data (data with a clear order, like rankings) after assigning numerical values to the categories.
Q: How do I interpret decile values? A: Decile values represent the data points below which a certain percentage of the data falls. For example, if the 3rd decile is 25, then 30% of the data is less than or equal to 25. The difference between deciles shows the distribution of data.
Q: What software can I use to calculate deciles? A: Most statistical software packages, including R, SPSS, SAS, and Excel, have built-in functions to calculate deciles. Python libraries like NumPy and Pandas also provide the necessary tools.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Decile Analysis
-
Data Preparation: Ensure the data is clean, accurate, and appropriately ordered before commencing any decile calculation.
-
Method Selection: Choose the appropriate calculation method based on the dataset's size and characteristics. Consider the trade-off between accuracy and computational complexity.
-
Interpretation Context: Always interpret decile values within the context of the data and the research question. Do not solely rely on decile values without considering other relevant factors.
-
Visualization: Use visual aids like box plots or histograms to represent the decile analysis results effectively. This aids in understanding data distribution and identifying patterns.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
Decile analysis is a powerful tool offering a detailed insight into data distribution, exceeding the granularity of simpler descriptive statistics like the median or quartiles. By understanding its definition, calculation methods, and various applications across different fields, researchers and practitioners can leverage deciles to gain a more nuanced understanding of their data, thereby making better-informed decisions and driving meaningful insights. The careful application of interpolation ensures the accuracy and reliability of decile calculations, ultimately enhancing the value derived from this fundamental statistical technique.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Decile Definition Formula To Calculate And Example . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.