What Does Credit Transfer Mean In College
adminse
Mar 31, 2025 · 9 min read
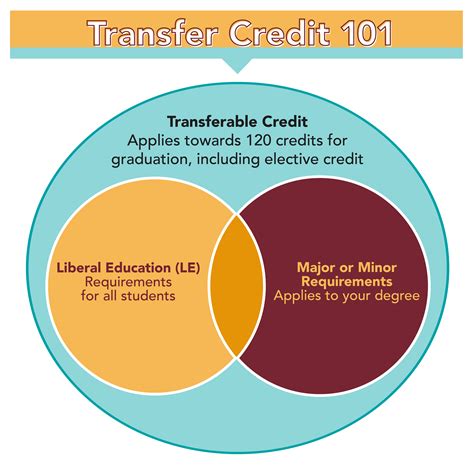
Table of Contents
Unlocking Academic Potential: A Deep Dive into College Credit Transfer
What if your past academic efforts could significantly shorten your path to a college degree? Credit transfer is a powerful tool that allows students to leverage previously earned college-level credits towards a new degree or certificate program, saving time and money.
Editor’s Note: This comprehensive article on college credit transfer was published today to provide students with the most up-to-date information and strategies for maximizing their academic achievements. We've included practical tips and real-world examples to help you navigate the sometimes complex process of transferring credits.
Why Credit Transfer Matters: Time, Money, and Academic Flexibility
Credit transfer is more than just a convenient option; it's a vital strategy for many college students. The potential benefits are substantial, affecting both personal finances and academic timelines. For students who have taken college courses at another institution, whether a community college, a different university, or even through online learning platforms, transferring credits can dramatically reduce the overall time and cost of completing a degree. It also offers flexibility for students who need to adjust their academic paths due to changing career goals or personal circumstances. The ability to transfer credits seamlessly allows for a more personalized and efficient educational journey. Search terms like "credit transfer," "course equivalency," "articulation agreement," and "transfer credit policy" all point to the significance of this process in the higher education landscape.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This article provides a thorough exploration of college credit transfer. We will define key terms, delve into the various types of credit transfer, explain the process, address common challenges, and offer practical advice to maximize your chances of a successful transfer. We will also explore the role of articulation agreements, the impact on financial aid, and the potential benefits beyond just saving time and money.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article is the culmination of extensive research, drawing on information from official college websites, government resources (such as the U.S. Department of Education), and expert opinions from academic advisors and admissions officers. Data on credit transfer success rates and common challenges have been analyzed to provide readers with accurate and trustworthy information. We have also included real-world examples and case studies to illustrate the complexities and benefits of the credit transfer process.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: A comprehensive understanding of credit transfer terminology and foundational principles.
- Types of Credit Transfer: Exploring various methods, including direct transfer, equivalency evaluations, and articulation agreements.
- The Transfer Process: A step-by-step guide to navigating the procedures involved.
- Challenges and Solutions: Identifying potential obstacles and strategies to overcome them.
- Financial Aid Implications: Understanding how credit transfer affects financial aid eligibility.
- Maximizing Transfer Credit: Tips and strategies to maximize the number of transferable credits.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
Now that we understand the importance of credit transfer, let's delve into the specifics. We'll start by defining key terms and exploring different types of credit transfer available to students.
Exploring the Key Aspects of College Credit Transfer
Definition and Core Concepts:
Credit transfer refers to the process of applying college-level courses completed at one institution toward the requirements of a degree or certificate program at another institution. A crucial aspect is the assessment of "course equivalency," which determines whether a course taken at the previous institution satisfies the requirements of a similar course at the new institution. Not all credits are created equal; some institutions may have stricter transfer policies than others. It's vital to understand the receiving institution's policies and procedures before embarking on the transfer process. Key terms to understand include:
- Transfer Credits: College credits that are accepted by a new institution.
- Articulation Agreement: A formal agreement between two or more institutions outlining which courses will transfer.
- Course Equivalency: Determining if a course taken at a previous institution is equivalent to a course offered at the new institution.
- Transfer Policy: The specific rules and regulations of an institution governing credit transfer.
- Transcript: An official record of a student's academic performance.
Types of Credit Transfer:
There are several ways to transfer credits:
- Direct Transfer: The most straightforward method. Credits from one institution are directly applied to the new institution's degree requirements. This usually requires both institutions to be regionally accredited.
- Equivalency Evaluation: If there's no direct equivalent course, the receiving institution evaluates the course content and determines if it meets their requirements. This process can vary in rigor and timeframe.
- Articulation Agreements: Formal agreements between institutions guaranteeing the transferability of specific courses or programs. These agreements often streamline the transfer process. Community colleges frequently have articulation agreements with four-year universities, making the transfer process smoother for students who begin their education at a community college.
- CLEP/DSST Exams: College-Level Examination Program (CLEP) and DANTES Subject Standardized Tests (DSST) exams allow students to earn college credit by demonstrating proficiency in specific subjects, regardless of prior coursework. This can be particularly useful for students who lack formal college credit or wish to accelerate their progress.
The Transfer Process:
The credit transfer process generally involves these steps:
- Research: Identify potential transfer institutions and carefully review their transfer policies.
- Request Transcripts: Order official transcripts from all previous institutions attended.
- Submit Application: Apply to the receiving institution and submit your transcripts.
- Credit Evaluation: The receiving institution will evaluate your transcripts to determine which credits will transfer. This can take several weeks or even months.
- Course Selection: Once credits are evaluated, you'll work with an academic advisor to create a course plan that incorporates your transferred credits.
Challenges and Solutions:
Several challenges can arise during the credit transfer process:
- Strict Transfer Policies: Some institutions have stringent transfer policies, limiting the number of transferable credits.
- Course Equivalency Issues: Finding equivalent courses can be difficult, especially with specialized or unique courses.
- Time Constraints: The credit evaluation process can be lengthy, potentially delaying enrollment.
- Lack of Communication: Poor communication between institutions can lead to delays and frustration.
Solutions include:
- Thorough Research: Research transfer policies upfront.
- Contacting Admissions: Reach out to admissions or academic advisors to discuss your situation.
- Articulation Agreements: Utilize articulation agreements whenever possible.
- Planning Ahead: Begin the transfer process well in advance of the desired enrollment date.
Financial Aid Implications:
Transferring credits can impact financial aid eligibility. The receiving institution will assess your overall academic history and recalculate your financial aid package based on the number of transferred credits and remaining coursework. It's crucial to contact the financial aid office at the receiving institution to understand how your financial aid will be affected.
Maximizing Transfer Credit:
Strategies for maximizing transferable credits include:
- Choosing Accredited Institutions: Ensure your previous and new institutions are regionally accredited.
- Understanding Transfer Policies: Thoroughly review the transfer policies of the receiving institution.
- Selecting Courses Wisely: Choose courses that are likely to transfer and align with your degree requirements.
- Maintaining a High GPA: A higher GPA increases your chances of successful credit transfer.
- Communicating with Advisors: Regularly communicate with academic advisors at both institutions.
Exploring the Connection Between Articulation Agreements and Credit Transfer
Articulation agreements are a cornerstone of successful credit transfer. They are formal agreements between institutions that guarantee the acceptance of credits from one institution to another. These agreements simplify the transfer process, often providing a clear roadmap for students transferring between specific programs. Community colleges frequently have extensive articulation agreements with four-year universities, ensuring a smoother transition for students pursuing bachelor's degrees after completing associate's degrees.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Roles and Real-World Examples: Articulation agreements define which courses will transfer, eliminating uncertainty and streamlining the process. For instance, an agreement between a community college and a state university might specify that all credits earned in an associate's degree program in business administration will transfer directly to the university's bachelor's degree program in business.
- Risks and Mitigations: Even with articulation agreements, unforeseen changes in curriculum or program requirements could affect transferability. Regular communication between the institutions and the student is crucial to mitigate these risks.
- Impact and Implications: Articulation agreements reduce stress and improve the efficiency of the transfer process, contributing to higher student success rates and potentially reducing overall time and cost of education.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
The existence of articulation agreements significantly enhances the credit transfer process, making it more transparent, reliable, and efficient. Students should actively seek institutions with strong articulation agreements to simplify their academic journey.
Further Analysis: Examining Articulation Agreements in Greater Detail
Articulation agreements are not one-size-fits-all. They can vary in scope and detail, ranging from agreements covering specific courses to comprehensive agreements encompassing entire programs. Some agreements might only guarantee the transfer of credit; others may specify how the transferred credits will be applied to the new degree program. The level of detail and the specific terms of the agreement should be carefully reviewed by students before making any decisions.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About College Credit Transfer
-
What is a transfer credit? A transfer credit is a college-level course credit earned at one institution that is accepted by another institution towards a degree or certificate program.
-
How do I find out which credits will transfer? Contact the admissions or academic advising office at the receiving institution and provide them with official transcripts from your previous institution(s).
-
What is an articulation agreement? An articulation agreement is a formal agreement between two or more institutions guaranteeing the transferability of certain courses or programs.
-
What if my previous institution is not accredited? Unaccredited institutions' credits are less likely to be transferred.
-
How long does the credit evaluation process take? The evaluation process can vary, typically taking several weeks or months.
-
Can I transfer credits from a foreign institution? Yes, but the process is often more complex and may require additional documentation and evaluation.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Credit Transfer
- Plan Ahead: Start researching transfer options early in your academic career.
- Maintain Good Grades: A strong GPA significantly increases your chances of successful credit transfer.
- Choose Courses Wisely: Select courses that align with your degree requirements at the receiving institution.
- Communicate Regularly: Keep in touch with admissions and academic advisors at both institutions.
- Review Transfer Policies: Carefully review the transfer policies of the receiving institution before enrolling.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
Credit transfer is a valuable tool for students seeking to streamline their educational journey and save time and money. By understanding the process, navigating potential challenges, and utilizing available resources such as articulation agreements, students can maximize their chances of a successful transfer and achieve their academic goals more efficiently. The strategic use of credit transfer empowers students to design a personalized path to their degree, maximizing their past efforts and shaping a more efficient and fulfilling college experience.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Carry In Private Equity
Apr 29, 2025
-
What Is An Independent Sponsor In Private Equity
Apr 29, 2025
-
Rule 144a Definition What It Allows And Criticism
Apr 29, 2025
-
Rule 10b5 1 Definition How It Works Sec Requirements
Apr 29, 2025
-
How To Get Into Private Equity From Consulting
Apr 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Does Credit Transfer Mean In College . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.