Late Payment Fee On Rent
adminse
Apr 03, 2025 · 8 min read
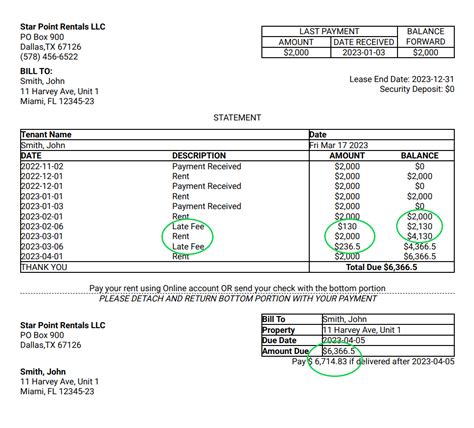
Table of Contents
Late Payment Fees on Rent: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding, Avoiding, and Navigating Them
What if the seemingly small late rent fee could snowball into significant financial hardship? Late payment fees, while seemingly insignificant, represent a crucial aspect of the landlord-tenant relationship, impacting both parties significantly.
Editor’s Note: This article on late payment fees on rent was published today, providing up-to-date insights and legal considerations for both landlords and tenants. This guide aims to clarify the complexities surrounding late fees, offering practical advice and solutions for all involved.
Why Late Rent Fees Matter: Relevance, Practical Applications, and Industry Significance
Late rent fees are a cornerstone of the rental agreement, designed to incentivize timely payments and compensate landlords for the financial and administrative burdens associated with late rent. For landlords, consistent late payments disrupt cash flow, potentially impacting their ability to cover mortgage payments, property maintenance, and other operational expenses. For tenants, late fees can quickly escalate, leading to debt, damaged credit scores, and even eviction. Understanding these fees' implications is crucial for maintaining a healthy landlord-tenant relationship and avoiding costly consequences. This understanding applies across all rental sectors, from residential apartments and single-family homes to commercial properties.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This article provides a comprehensive exploration of late payment fees on rent. It will delve into the legal frameworks governing these fees, examine common practices across different jurisdictions, discuss strategies for avoiding late fees, analyze the potential consequences of non-payment, and offer advice for both landlords and tenants navigating this critical aspect of rental agreements. We will also explore the ethical considerations surrounding late fees and analyze how technology is impacting their implementation and management.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article is the result of extensive research, incorporating legal analysis of various state and local laws, review of numerous landlord-tenant agreements, and analysis of data related to rental payment trends and eviction rates. The information presented is intended to be informative and should not be considered legal advice. Consult with legal professionals for specific guidance related to your situation.
Key Takeaways:
- Legal Framework: A detailed understanding of state and local laws regarding late fees, including permissible amounts and notification requirements.
- Avoiding Late Fees: Practical strategies and techniques for ensuring timely rent payments.
- Consequences of Non-Payment: Exploring the potential repercussions of consistently late payments, including eviction and damage to credit scores.
- Landlord Responsibilities: Clarification of landlords' obligations concerning late fee implementation and communication.
- Tenant Rights: Understanding tenant rights and protections related to late fees and potential disputes.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
With a clear understanding of the importance of addressing late rent fees, let's now examine the key aspects influencing their application and impact.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Late Payment Fees on Rent
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
A late payment fee is a penalty charged to a tenant for submitting their rent payment after the agreed-upon due date specified in the lease agreement. These fees are intended to compensate landlords for the administrative burden and potential financial losses associated with late rent. The specific amount of the late fee, the grace period allowed before the fee is applied, and the process for applying the fee are usually detailed within the lease agreement.
2. Applications Across Industries:
Late payment fees are prevalent across various rental sectors. Residential rentals (apartments, houses, townhouses) generally have standardized late fee policies, often dictated by local laws or industry best practices. Commercial rentals (office spaces, retail stores, warehouses) might have more flexible fee structures, often negotiated individually as part of the lease agreement and can be substantially higher than residential fees, reflecting the larger financial stakes involved.
3. Challenges and Solutions:
One common challenge is the lack of clear communication regarding late fees. Lease agreements often contain complex language, making it difficult for tenants to understand their rights and obligations. To address this, landlords should provide clear, concise explanations of late fee policies in easily understandable language, possibly using visual aids or frequently asked questions (FAQs). Tenants, in turn, should actively read and understand their lease agreements before signing. Another challenge is inconsistency in fee enforcement. Some landlords may be more lenient than others, leading to unfairness and potential disputes. Standardized procedures and consistent application of policies are crucial for fairness.
4. Impact on Innovation:
Technological advancements have significantly impacted rent payment methods and late fee management. Online payment platforms, automated payment reminders, and tenant portals are streamlining rent collection and minimizing late payments. These technological innovations have also allowed for more transparent and efficient communication between landlords and tenants regarding late payment fees.
Closing Insights: Summarizing the Core Discussion
Late rent fees are an integral part of the landlord-tenant relationship. While they serve a legitimate purpose in incentivizing timely payments and compensating landlords for administrative costs, they must be implemented fairly and transparently. Clear communication, easily understood lease agreements, and consistent enforcement are crucial for minimizing disputes and ensuring a positive experience for both parties.
Exploring the Connection Between Lease Agreements and Late Payment Fees
The lease agreement forms the cornerstone of the relationship between landlord and tenant, explicitly outlining the terms and conditions governing the rental property, including the details of late payment fees. This connection is vital because the lease serves as the legally binding document defining the rights and responsibilities of both parties.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Roles and Real-World Examples: The lease agreement explicitly states the amount of the late fee, the grace period, and the method for calculating and applying the fee. For example, a lease might specify a $50 late fee after a three-day grace period.
- Risks and Mitigations: A poorly drafted lease agreement regarding late fees can lead to legal disputes. To mitigate this risk, both landlords and tenants should consult with legal counsel to ensure the lease accurately reflects the applicable laws and industry best practices.
- Impact and Implications: A clearly defined and legally compliant late fee policy minimizes potential conflicts and promotes a healthy landlord-tenant relationship. Conversely, ambiguous or overly punitive late fee clauses can lead to frustration and legal challenges.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
The relationship between the lease agreement and late payment fees is inextricably linked. The lease agreement is the legal document that governs the terms of the tenancy and defines the penalties for late rent. Thoroughly understanding and agreeing upon these terms is crucial for avoiding disputes and fostering a positive relationship between landlord and tenant.
Further Analysis: Examining Grace Periods in Greater Detail
The grace period, a crucial element in lease agreements, represents the timeframe after the rent due date during which a tenant can make a payment without incurring a late fee. The length of the grace period varies across jurisdictions and individual lease agreements, often ranging from a few days to a week.
State-Specific Variations: Many states have laws governing the permissible length of grace periods and whether landlords are required to provide written notice before applying late fees. For instance, some states mandate a specific grace period, while others allow landlords and tenants to negotiate the length.
Impact on Tenant Rights: The grace period provides a buffer for tenants experiencing unexpected financial difficulties or logistical delays. This buffer allows for timely resolution of payment issues without immediate penalty.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Late Payment Fees on Rent
Q: What is a reasonable late payment fee?
A: The "reasonableness" of a late fee depends on several factors, including local laws, industry standards, and the terms of the lease agreement. While there is no universally accepted standard, many jurisdictions impose limits on how high a late fee can be. Fees that are excessively high compared to the rent amount may be deemed unenforceable.
Q: Can a landlord change the late payment fee during the lease term?
A: Generally, a landlord cannot unilaterally change the late fee stipulated in a signed lease agreement. Any change to the fee would need to be negotiated and agreed upon by both parties, typically requiring a formal amendment to the lease.
Q: What happens if I consistently pay rent late?
A: Consistent late rent payments can have significant consequences, potentially including damage to credit scores, eviction notices, and legal action by the landlord.
Q: What are my rights if I believe a late fee is unfair?
A: If you believe a late fee is unfairly applied or excessive, consult your lease agreement and the laws in your jurisdiction. You may have grounds to dispute the fee. You may wish to seek legal counsel.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of a Clear Late Fee Policy (For Landlords)
- Clearly Define Fees in the Lease: Ensure the lease agreement explicitly details the late fee amount, the grace period, and the method of calculation.
- Use Automated Payment Systems: Implement online payment platforms and automated reminders to reduce late payments.
- Communicate Effectively: Provide tenants with clear and accessible communication channels, such as email or text messaging, for rent inquiries.
- Maintain Consistent Enforcement: Apply late fees consistently to all tenants to avoid accusations of unfair treatment.
- Review Local Laws: Ensure the late fee policy complies with all applicable state and local regulations.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
Late payment fees, though often viewed as a minor detail, play a significant role in the landlord-tenant relationship. For landlords, they are a crucial tool for mitigating financial risks and incentivizing timely rent payments. For tenants, understanding these fees, and having a plan to pay rent on time, is essential for avoiding negative financial and legal consequences. By fostering open communication, clearly defined policies, and adherence to applicable laws, both parties can navigate the complexities of late payment fees to maintain a healthy and productive rental relationship.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Impact Does Only Paying The Minimum Payment Have On A Consumer
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Impact Of Only Paying The Minimum Payment On A Credit Card
Apr 04, 2025
-
Minimum Payment Of Student Loans
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Do Institutions Calculate The Minimum Payment
Apr 04, 2025
-
How To Find Minimum Payment On Student Loans
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Late Payment Fee On Rent . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.