Cost Of Work Done Definition
adminse
Mar 28, 2025 · 8 min read
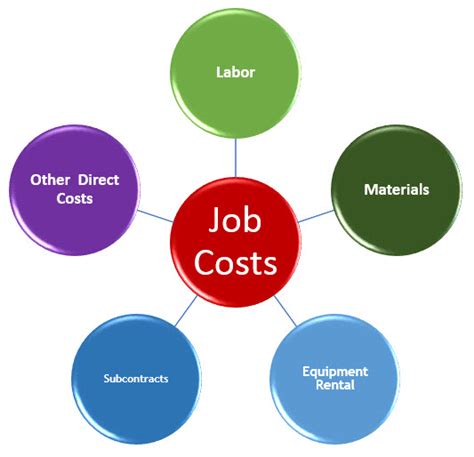
Table of Contents
Decoding the Cost of Work Done: A Comprehensive Guide
What if accurate cost accounting is the key to unlocking sustainable profitability? Understanding the precise definition and calculation of the cost of work done (COWD) is paramount for businesses striving for financial success.
Editor’s Note: This article provides an in-depth exploration of the cost of work done, updated for today's business landscape. We cover the definition, calculation methods, practical applications, and potential pitfalls to help businesses gain a clearer understanding of their true costs.
Why "Cost of Work Done" Matters:
In the dynamic world of business, knowing precisely what each project or task costs is not merely beneficial—it's essential. The cost of work done (COWD) is a crucial metric that reveals the actual expenses incurred in completing a specific job or project. This information is critical for:
- Accurate Pricing: Knowing your true costs enables businesses to set realistic prices that cover all expenses and generate profit. Underpricing due to inaccurate cost estimations can lead to financial losses.
- Profitability Analysis: COWD allows for a detailed analysis of project profitability, highlighting areas for improvement and identifying underperforming projects.
- Resource Allocation: Understanding the cost of past projects helps businesses optimize resource allocation for future endeavors, minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency.
- Improved Budgeting and Forecasting: Precise COWD data significantly enhances budgeting and forecasting accuracy, improving financial planning and management.
- Compliance and Auditing: Accurate cost accounting is crucial for compliance with financial regulations and simplifies the audit process.
Overview: What This Article Covers:
This article will delve into the intricacies of the cost of work done, offering a comprehensive guide to its definition, calculation, applications, and challenges. We will explore different costing methods, address common misconceptions, and provide practical strategies for effective COWD management. Readers will gain actionable insights to improve their cost accounting practices and make informed business decisions.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights:
This article synthesizes information from accounting standards, industry best practices, and real-world examples. The insights are supported by extensive research across various accounting and management literature, ensuring accuracy and relevance for businesses of all sizes.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: A precise definition of COWD and its core components.
- Calculation Methods: Various methods for calculating COWD, including job order costing, process costing, and activity-based costing.
- Practical Applications: Examples of how COWD is used in different industries.
- Challenges and Solutions: Common challenges associated with COWD calculation and strategies for overcoming them.
- Impact on Business Decisions: How accurate COWD data can improve pricing, resource allocation, and profitability.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
Now that we understand the importance of COWD, let's explore its key aspects in more detail.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Cost of Work Done:
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
The cost of work done refers to the total cost incurred in completing a specific project or job. It encompasses all direct and indirect costs associated with the work. Direct costs are easily attributable to a specific project (e.g., materials, labor directly involved). Indirect costs are not directly attributable and are allocated based on predetermined methods (e.g., overhead, administrative expenses).
2. Calculation Methods:
Several methods exist for calculating COWD, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
-
Job Order Costing: This method is best suited for projects with unique characteristics, where costs can be easily traced to individual jobs. Each job is treated as a separate cost center, and all costs associated with that job are accumulated. This is common in construction, custom manufacturing, and consulting.
-
Process Costing: This method is used for mass production where identical or similar products are manufactured in large quantities. Costs are averaged across the entire production run, making it less precise for individual units but efficient for large-scale operations.
-
Activity-Based Costing (ABC): ABC is a more sophisticated method that assigns costs based on activities that consume resources. It provides a more granular view of costs, attributing them to specific activities rather than just products or projects. This method is beneficial for complex projects with multiple activities.
3. Applications Across Industries:
COWD is relevant across various industries:
- Construction: Determining the cost of building a house or a commercial structure.
- Manufacturing: Calculating the cost of producing a specific batch of goods.
- IT Services: Estimating the cost of developing a software application or providing consulting services.
- Consulting: Calculating the total cost of a consulting project, including consultant fees, travel expenses, and research costs.
- Healthcare: Determining the cost of a specific surgical procedure or treatment plan.
4. Challenges and Solutions:
Calculating COWD accurately can be challenging:
-
Allocating Indirect Costs: Accurately allocating indirect costs to specific projects can be complex and requires careful consideration. Using appropriate allocation methods (e.g., machine hours, direct labor costs) is crucial.
-
Tracking Costs: Maintaining detailed records of all costs associated with a project is vital. Robust cost accounting systems and procedures are necessary.
-
Estimating Costs: Accurately estimating costs for future projects is difficult. Using historical data, industry benchmarks, and expert opinions can improve accuracy.
-
Dealing with Changes: Project changes can impact costs. Having a system to track and manage change orders is essential.
Closing Insights: Summarizing the Core Discussion:
Accurate calculation of the cost of work done is fundamental to sound financial management. By understanding the different costing methods and addressing potential challenges, businesses can gain valuable insights into their operations, improve profitability, and make well-informed decisions.
Exploring the Connection Between Overheads and Cost of Work Done:
Overhead costs represent a significant portion of the total cost of work done in many businesses. Understanding their impact and how they are allocated is critical.
Key Factors to Consider:
-
Roles and Real-World Examples: Overhead costs include rent, utilities, administrative salaries, and depreciation. For example, in a manufacturing setting, factory rent and machinery depreciation are overhead costs allocated to products.
-
Risks and Mitigations: Inaccurate allocation of overheads can distort the true cost of a project, leading to mispricing and profitability issues. Using appropriate allocation bases (e.g., direct labor hours, machine hours) and regularly reviewing the overhead allocation method can mitigate these risks.
-
Impact and Implications: Overlooking or underestimating overheads can significantly impact profitability. Accurate overhead allocation ensures realistic pricing and allows for informed decision-making regarding project acceptance and resource allocation.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection:
The relationship between overheads and the cost of work done is intricate yet crucial. Effective management of overheads and their accurate allocation are essential for accurate cost accounting and informed business decisions.
Further Analysis: Examining Overhead Allocation in Greater Detail:
Different overhead allocation methods exist, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The chosen method should align with the nature of the business and the complexity of its operations. Common methods include the direct labor hour method, the machine hour method, and activity-based costing.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Cost of Work Done:
-
Q: What is the difference between cost of work done and cost of goods sold?
- A: Cost of goods sold (COGS) refers to the direct costs associated with producing goods sold during a specific period. COWD is broader, encompassing the cost of completing a specific project or job, including both direct and indirect costs, regardless of whether the project resulted in a saleable good.
-
Q: How often should COWD be calculated?
- A: The frequency of COWD calculation depends on the nature of the business and the project timeline. For short-term projects, it might be calculated upon completion. For long-term projects, it might be calculated periodically (e.g., monthly or quarterly) to monitor progress and costs.
-
Q: What software can help with COWD calculation?
- A: Numerous accounting software packages, such as QuickBooks, Xero, and SAP, offer features for tracking and calculating costs, aiding in COWD calculation.
-
Q: How can I improve the accuracy of my COWD calculations?
- A: Implement a robust cost accounting system, regularly review and update your cost allocation methods, utilize technology for cost tracking, and conduct regular cost analysis to identify areas for improvement.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Accurate COWD Calculation:
-
Implement a robust cost accounting system: This system should track all costs associated with projects, including direct and indirect costs.
-
Use a consistent costing method: Choose a costing method that best suits your business operations and stick to it consistently.
-
Regularly review and update cost drivers: Analyze your cost drivers periodically to ensure they accurately reflect current operations.
-
Analyze variances: Regularly compare actual costs to budgeted costs to identify and address any discrepancies.
-
Invest in cost accounting software: Technology can streamline cost tracking and reporting, improving accuracy and efficiency.
-
Train employees on cost accounting principles: Ensure that employees understand the importance of accurate cost tracking and the procedures for recording costs.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights:
The cost of work done is not merely a number; it's a critical piece of information that provides crucial insights into business performance. By understanding its definition, calculation methods, and practical applications, businesses can make data-driven decisions, optimize resource allocation, and ultimately achieve sustainable profitability. Accurate COWD calculation is not just good accounting practice; it’s a strategic advantage in today’s competitive landscape.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Indicated Dividend Definition
Apr 24, 2025
-
India Etf Definition
Apr 24, 2025
-
Indexing Definition And Uses In Economics And Investing
Apr 24, 2025
-
Indexed Earnings Definition
Apr 24, 2025
-
Indexed Annuity Definition How It Works Yields And Caps
Apr 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Cost Of Work Done Definition . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.