Working Age Population Importance Explain
adminse
Apr 02, 2025 · 9 min read
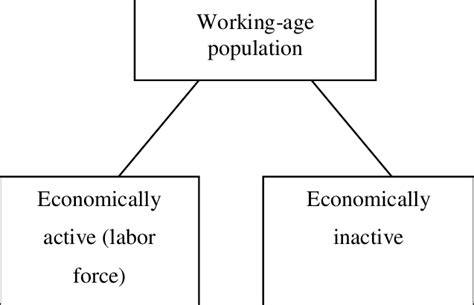
Table of Contents
The Crucial Role of the Working-Age Population: Fueling Economic Growth and Societal Well-being
What if the future of global prosperity hinges on understanding the dynamics of the working-age population? This critical demographic segment is the engine of economic growth, driving innovation, and shaping the very fabric of society.
Editor’s Note: This article on the importance of the working-age population provides an up-to-date analysis of this crucial demographic group, examining its impact on economic growth, social welfare, and future societal challenges. The insights presented are drawn from extensive research and data analysis, offering a comprehensive understanding of this vital subject.
Why the Working-Age Population Matters:
The working-age population, typically defined as individuals aged 15 to 64, represents the core workforce of any nation. Its size, characteristics, and productivity directly influence a country's economic output, technological advancement, and overall societal well-being. This demographic group is responsible for producing goods and services, paying taxes, contributing to social security systems, and driving innovation. A healthy and productive working-age population is essential for sustainable economic growth, improved living standards, and the provision of crucial public services. Conversely, a shrinking or less productive working-age population can lead to economic stagnation, increased social burdens, and a decline in overall quality of life. Understanding the dynamics of this population is paramount for effective policymaking and long-term planning.
Overview: What This Article Covers:
This article will delve into the multifaceted importance of the working-age population. We will explore its role in economic growth, examining key indicators like labor force participation rates, productivity, and human capital development. We will then analyze the societal impact of this demographic, considering its influence on social security systems, healthcare, and the overall well-being of communities. Furthermore, we'll discuss the challenges posed by demographic shifts, such as aging populations and declining birth rates, and explore potential solutions and policy recommendations for ensuring a thriving working-age population in the future. Finally, we’ll consider the interplay between technological advancements and the workforce, examining how automation and innovation are reshaping the landscape of work.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights:
This article is based on extensive research drawn from reputable sources including the World Bank, the International Labour Organization (ILO), national statistical agencies, academic publications, and reports from leading think tanks. Data analysis, comparative studies, and expert opinions have been carefully considered to ensure accuracy and provide readers with robust and reliable information. The structured approach aims to offer clear, actionable insights that can inform policymakers, businesses, and individuals alike.
Key Takeaways:
- Economic Engine: The working-age population is the primary driver of economic growth, contributing significantly to GDP through production and consumption.
- Social Security & Welfare: This group fuels social security systems and contributes to the provision of essential public services like healthcare and education.
- Innovation and Technological Advancement: A dynamic and skilled workforce is crucial for technological innovation and economic competitiveness.
- Demographic Challenges: Aging populations and declining birth rates pose significant challenges to economic growth and social welfare.
- Policy Implications: Effective policies are needed to address these challenges, focusing on areas such as education, healthcare, and labor market reforms.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
Having established the crucial role of the working-age population, let’s now explore its key contributions to economic prosperity and societal well-being in greater detail.
Exploring the Key Aspects of the Working-Age Population's Importance:
1. Economic Growth and Productivity:
The size and productivity of the working-age population are directly correlated with a nation's economic output. A larger working-age population, coupled with high labor force participation rates and strong productivity, translates into higher GDP growth. Productivity, measured as output per worker, is influenced by factors such as education levels, technological advancements, and investment in human capital. Countries with well-educated and highly skilled workforces tend to experience greater economic prosperity. Conversely, a shrinking working-age population or low productivity can lead to slower economic growth and potentially economic decline.
2. Social Security and Public Services:
The working-age population is the primary contributor to social security systems, funding pensions, healthcare, and other social welfare programs. As populations age and the ratio of retirees to workers increases, the sustainability of these systems becomes a significant concern. Maintaining a healthy and productive working-age population is essential for ensuring the long-term viability of social security and the provision of essential public services. This also includes supporting the education system which creates future generations of workers.
3. Innovation and Technological Advancement:
A dynamic and skilled working-age population is crucial for driving innovation and technological advancement. A workforce with strong STEM skills (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) is essential for developing new technologies, improving productivity, and fostering economic competitiveness in a globalized world. Investment in education and training is vital for ensuring that the workforce possesses the necessary skills and knowledge to adapt to changing technological landscapes and meet the demands of a rapidly evolving economy.
4. Demographic Shifts and Challenges:
Many developed nations face the challenge of aging populations and declining birth rates, leading to a shrinking working-age population. This demographic shift has profound implications for economic growth, social security systems, and the provision of public services. The shrinking workforce can lead to labor shortages, increased pressure on social security systems, and a potential decline in economic output. Addressing these challenges requires proactive policy interventions, including measures to encourage higher birth rates, attract skilled immigrants, and promote longer working lives.
Closing Insights: Summarizing the Core Discussion:
The working-age population is the cornerstone of economic prosperity and societal well-being. Its size, skills, and productivity are critical determinants of a nation's economic growth, social welfare, and overall development trajectory. Understanding the dynamics of this demographic is crucial for effective policymaking and long-term planning.
Exploring the Connection Between Technological Advancements and the Working-Age Population:
Technological advancements significantly impact the working-age population, presenting both opportunities and challenges. Automation and artificial intelligence are transforming the nature of work, leading to the displacement of some jobs while creating new opportunities in other sectors. This necessitates a focus on reskilling and upskilling the workforce to adapt to these changes. The working-age population needs to develop adaptability, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills to thrive in this evolving landscape. Furthermore, the integration of technology into the workplace can lead to increased productivity and efficiency, benefiting both businesses and workers. However, the ethical implications of automation and the potential for increased inequality need careful consideration and proactive policy interventions.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Roles and Real-World Examples: Automation is already impacting sectors like manufacturing, transportation, and customer service, leading to job displacement in some areas and job creation in others. For example, the rise of e-commerce has created jobs in logistics and online retail, while simultaneously reducing employment in traditional brick-and-mortar stores.
- Risks and Mitigations: The risk of increased income inequality and job displacement can be mitigated through investments in education and training, promoting lifelong learning, and providing social safety nets for workers affected by automation. Government policies can play a crucial role in supporting this transition.
- Impact and Implications: The long-term impact of technological advancements on the working-age population will depend on how effectively societies adapt to these changes. A focus on human capital development, innovation, and inclusive growth will be essential for harnessing the benefits of technology while mitigating its potential negative consequences.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection:
The interplay between technological advancements and the working-age population is a defining feature of the 21st-century economy. By investing in human capital, fostering innovation, and implementing effective social safety nets, societies can ensure that the working-age population thrives in an increasingly automated world.
Further Analysis: Examining Education and Skills Development in Greater Detail:
Education and skills development are crucial for preparing the working-age population for the challenges and opportunities of the future. Investment in quality education, from early childhood to higher education, is essential for building a skilled and adaptable workforce. Curriculum reforms that emphasize critical thinking, problem-solving, and digital literacy are particularly important in the context of technological advancements. Lifelong learning initiatives, providing opportunities for reskilling and upskilling throughout an individual's career, are also essential for ensuring that the workforce remains competitive and adaptable to evolving job market demands.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About the Working-Age Population:
Q: What is the significance of the working-age population's size?
A: The size of the working-age population directly impacts a nation's economic potential. A larger working-age population generally translates to a larger potential workforce, leading to higher production and economic growth. However, a rapidly growing population without adequate infrastructure and resources may also lead to challenges.
Q: How does the working-age population contribute to social security?
A: The working-age population is the primary contributor to social security systems through taxation and contributions. These contributions fund pensions, healthcare, and other social welfare programs for retirees and other vulnerable populations.
Q: What are the key challenges posed by an aging working-age population?
A: An aging working-age population may lead to labor shortages, increased strain on social security systems, and slower economic growth. It may also result in a higher dependency ratio (the ratio of non-working individuals to working individuals), potentially impacting the sustainability of social welfare programs.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of a Thriving Working-Age Population:
- Invest in education and skills development: Prioritize quality education and training programs that equip individuals with the skills needed for the modern workforce.
- Promote lifelong learning: Encourage continuous learning and upskilling to adapt to evolving job market demands.
- Support inclusive growth: Implement policies that promote equitable access to opportunities and resources for all members of the working-age population.
- Encourage active aging: Promote policies that support longer working lives and active participation of older workers in the labor force.
- Invest in infrastructure and technology: Ensure that the infrastructure and technology are in place to support a productive and efficient workforce.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights:
The working-age population is not merely a demographic statistic; it is the driving force behind economic growth, social progress, and national development. By understanding its significance, addressing its challenges, and investing in its potential, nations can build a more prosperous and equitable future for all. The strategic management of this vital demographic segment will be essential for navigating the complexities of the 21st century and ensuring sustainable development for generations to come.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Lower Minimum Payment On Credit Card
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is Minimum Payment Credit Card Rbc
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is Minimum Payment For 10000 Credit Card
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Minimum Payment For A Visa Credit Card
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Minimum Payment For A 1000 Credit Card
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Working Age Population Importance Explain . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.