Work Control Process
adminse
Apr 01, 2025 · 9 min read
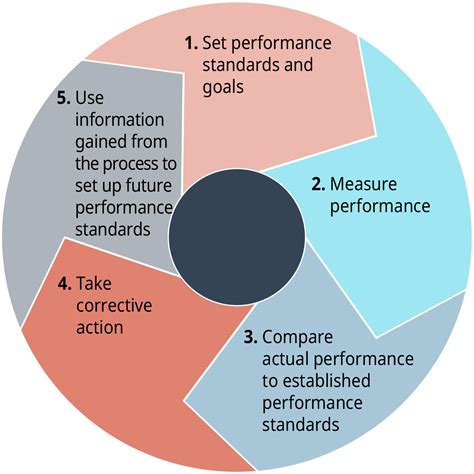
Table of Contents
Mastering the Work Control Process: A Comprehensive Guide to Safety and Efficiency
What if a robust work control process is the key to unlocking peak operational efficiency and unwavering safety? This critical system is not merely a set of procedures; it's the bedrock upon which reliable and risk-managed operations are built.
Editor’s Note: This article on the Work Control Process was published today, providing readers with the latest insights and best practices for implementing and maintaining a robust system. This guide is designed for safety professionals, operations managers, and anyone seeking to improve workplace safety and efficiency.
Why Work Control Matters: Relevance, Practical Applications, and Industry Significance
The Work Control Process (WCP), often referred to as a Permit-to-Work system in certain industries, is a formalized system designed to manage potentially hazardous work activities. It's not just a box to check; it's a proactive approach to risk mitigation, ensuring that work is planned, executed, and completed safely and efficiently. Its significance transcends specific industries, impacting everything from manufacturing and energy to healthcare and construction. The implementation of a thorough WCP directly translates to reduced accidents, minimized downtime, improved regulatory compliance, and ultimately, a safer and more productive work environment. Failure to implement a robust WCP, conversely, can lead to costly incidents, regulatory penalties, reputational damage, and even fatalities. The increasing emphasis on safety and regulatory compliance across various sectors makes a well-defined WCP not just desirable but essential.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the Work Control Process. We will delve into its core components, explore practical applications across diverse industries, analyze potential challenges and solutions, and discuss its future implications in an increasingly automated and interconnected world. Readers will gain a practical understanding of how to implement, maintain, and optimize a WCP to achieve significant improvements in safety and operational efficiency.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article draws upon extensive research, including industry best practices, regulatory guidelines (such as OSHA and ISO standards), case studies of successful WCP implementations, and expert opinions from safety professionals across multiple sectors. The information provided is supported by evidence-based research and aims to provide readers with accurate and reliable guidance. A structured approach has been employed to ensure clarity and ensure that actionable insights are readily accessible.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: Understanding the fundamental principles of a WCP and its various components.
- Practical Applications: Exploring how the WCP is implemented across various industries to mitigate risks.
- Challenges and Solutions: Identifying common obstacles in WCP implementation and strategies to overcome them.
- Future Implications: Analyzing the evolving landscape of WCPs in light of technological advancements and changing regulatory requirements.
- The Role of Technology: How digital tools enhance WCP efficiency and safety.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion
Having established the importance of a robust Work Control Process, let’s now delve into its key aspects, examining its practical implementation, common challenges, and its transformative potential.
Exploring the Key Aspects of the Work Control Process
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
The Work Control Process is a systematic approach to managing high-risk work activities. It involves a series of steps designed to identify hazards, assess risks, implement control measures, and authorize work only when it's safe to proceed. Key elements typically include:
- Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment: A thorough analysis of potential hazards associated with the specific task. This often involves job safety analyses (JSAs) and other risk assessment techniques.
- Permit Issuance: Formal authorization to commence work, typically issued by a competent authority after all necessary precautions have been verified.
- Pre-Job Briefing: A meeting between the work crew and the authorizing authority to review the task, risks, and control measures.
- Work Execution: Performing the task according to the established procedures and control measures.
- Post-Job Inspection: A final check to ensure that the work area is safe and that all equipment is properly secured.
- Permit Closure: Formal documentation that the work has been completed safely and the permit is no longer valid.
2. Applications Across Industries:
The WCP is applicable across a vast range of industries. Specific implementations may vary based on industry-specific regulations and hazards. Examples include:
- Oil and Gas: Managing potentially explosive or hazardous materials during maintenance and repair activities.
- Manufacturing: Controlling lockout/tagout procedures during equipment maintenance.
- Construction: Managing work at height, confined spaces, and other high-risk environments.
- Healthcare: Managing procedures involving hazardous materials or complex medical equipment.
- Utilities: Controlling work near energized electrical equipment or high-pressure pipelines.
3. Challenges and Solutions:
Implementing and maintaining an effective WCP can present challenges:
- Complexity: The process can be complex, requiring thorough training and understanding. Solution: Simplified procedures, user-friendly documentation, and comprehensive training programs.
- Resistance to Change: Some workers may resist the additional paperwork and procedures. Solution: Emphasize the benefits of the WCP in terms of safety and efficiency, provide adequate training, and involve workers in the process development.
- Inconsistent Application: The process may not be consistently followed across all teams and locations. Solution: Regular audits, clear accountability, and robust monitoring systems.
- Technological Limitations: Manual systems can be inefficient and error-prone. Solution: Implementing digital work management systems to streamline the process and reduce paperwork.
4. Impact on Innovation:
The WCP itself is constantly evolving to incorporate new technologies and address emerging challenges. Innovation in this area is crucial for maintaining a safe and efficient workplace. The integration of digital tools like mobile applications and cloud-based platforms enhances data management, tracking, and communication, further boosting efficiency and safety.
Closing Insights: Summarizing the Core Discussion
The Work Control Process is not a mere checklist; it's a dynamic system for managing high-risk work, ensuring the safety and efficiency of operations. Its successful implementation hinges on commitment, clear procedures, comprehensive training, and robust monitoring. By proactively addressing potential challenges and integrating new technologies, organizations can leverage the WCP to create a safer and more productive environment for all.
Exploring the Connection Between Technology and the Work Control Process
The relationship between technology and the WCP is increasingly vital. Technology offers tools to significantly improve the efficiency, accuracy, and overall effectiveness of the process.
Roles and Real-World Examples:
- Digital Permitting Systems: Mobile apps and software solutions allow for electronic permit creation, approval, and tracking, eliminating paperwork and improving communication. Examples include systems used in oil and gas facilities, streamlining maintenance procedures and reducing errors.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Sensors and IoT devices can monitor environmental conditions and equipment status, providing real-time data to enhance risk assessment and decision-making. This is particularly useful in hazardous environments where immediate intervention might be crucial.
- Data Analytics: Analyzing historical WCP data can identify trends and areas for improvement, leading to proactive risk mitigation and optimized procedures.
Risks and Mitigations:
- System Dependence: Over-reliance on technology can create single points of failure. Mitigation: Developing robust backup systems and ensuring adequate training for both manual and digital processes.
- Data Security: Protecting sensitive data related to permits and work activities is paramount. Mitigation: Implementing strong cybersecurity measures, including encryption and access controls.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating new technology with existing systems can be complex and time-consuming. Mitigation: Careful planning, phased implementation, and selecting compatible software solutions.
Impact and Implications:
The integration of technology into the WCP signifies a move towards a more proactive, data-driven approach to safety management. It improves communication, reduces errors, and enables real-time risk assessment, ultimately leading to a safer and more efficient workplace.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
The synergy between technology and the Work Control Process is transformative. By effectively leveraging technological advancements, organizations can significantly enhance their WCP, optimizing safety, boosting efficiency, and promoting a more proactive safety culture.
Further Analysis: Examining Digitalization in Greater Detail
Digitalization is revolutionizing the WCP by streamlining processes, enhancing data management, and fostering better communication. The shift towards digital platforms offers opportunities to reduce paperwork, improve accuracy, and facilitate real-time collaboration. This includes the use of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) for training and simulations, improving worker preparedness and reducing on-site errors.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About the Work Control Process
Q: What is a Work Control Process?
A: A Work Control Process (WCP) is a systematic approach to managing high-risk work activities to minimize hazards and ensure safety. It involves a series of steps from hazard identification and risk assessment to permit issuance, execution, and post-job inspection.
Q: Why is a WCP important?
A: A WCP is crucial for preventing accidents, minimizing downtime, improving regulatory compliance, and creating a safer work environment. It provides a structured framework for managing risks, ensuring that work is performed safely and efficiently.
Q: Who is responsible for implementing and maintaining a WCP?
A: Responsibility for implementing and maintaining a WCP typically rests with management, but it requires the active participation of all employees. Dedicated safety professionals often play a key role in the design, implementation, and oversight of the system.
Q: How can I improve the effectiveness of my organization's WCP?
A: Regularly review and update the WCP, provide thorough training, use technology to enhance efficiency, and consistently monitor and audit its application. Engaging workers in the process and encouraging feedback are crucial for continuous improvement.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of the Work Control Process
- Start with a thorough risk assessment: Identify all potential hazards and assess the associated risks before developing your WCP.
- Develop clear and concise procedures: Ensure all procedures are easy to understand and follow.
- Provide comprehensive training: Train all personnel on the WCP and its procedures.
- Implement a robust monitoring system: Track permit issuance, work execution, and post-job inspections to ensure compliance.
- Regularly review and update the WCP: Stay current with best practices and regulatory requirements.
- Encourage feedback and continuous improvement: Solicit input from employees to identify areas for improvement.
- Use technology to enhance efficiency: Consider implementing digital work management systems to streamline the process.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
The Work Control Process represents a foundational element of any robust safety management system. By understanding its core principles, embracing technological advancements, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, organizations can effectively manage high-risk activities, creating a safer, more efficient, and ultimately, more successful work environment. A well-implemented WCP is not just a compliance requirement; it's a strategic investment in the well-being of employees and the long-term success of the organization.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Minimum Salary For A Credit Card In Qatar
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Minimum Salary For A Credit Card In Pakistan
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Minimum Salary For A Credit Card
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Average Minimum Payment For A Credit Card
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is A Minimum Payment On A Credit Card Chase
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Work Control Process . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.