What Is The Minimum Amount Of Social Security At Age 62
adminse
Apr 05, 2025 · 7 min read
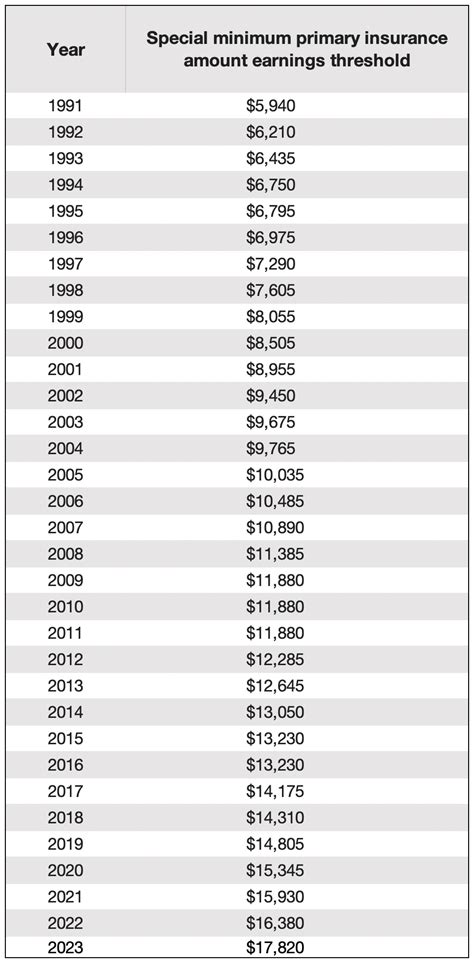
Table of Contents
What's the lowest possible Social Security retirement benefit at age 62?
Claiming Social Security at 62 guarantees a smaller monthly check, but it's not always the lowest possible amount.
Editor’s Note: This article on minimum Social Security retirement benefits at age 62 was published today, [Date]. This information is for general understanding and does not constitute financial advice. Consult a qualified financial advisor for personalized guidance.
Why Minimum Social Security Benefits at 62 Matter:
The decision of when to start receiving Social Security retirement benefits is a crucial one, impacting a retiree's financial well-being for years to come. While many focus on maximizing their benefits, understanding the minimum possible amount received at age 62 – the earliest possible claiming age – provides valuable context. Knowing the lowest potential payout allows individuals to better plan their retirement finances and understand the trade-offs associated with early retirement. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their retirement income strategy.
Overview: What This Article Covers:
This article will comprehensively explore the factors influencing the minimum Social Security retirement benefit at age 62. We'll examine the calculation methods, the impact of earnings history, the role of spousal benefits, and the potential for receiving a zero benefit. Furthermore, we will discuss the implications of claiming early and offer strategies for maximizing benefits despite an initially lower payout.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights:
The information presented here is based on extensive research utilizing official data from the Social Security Administration (SSA), analysis of benefit calculation formulas, and consideration of various scenarios affecting benefit amounts. The goal is to provide accurate, reliable, and easily understandable information to assist individuals in making informed decisions about their retirement.
Key Takeaways:
- Minimum Benefit Calculation: Understanding how the SSA computes minimum benefits.
- Impact of Earnings History: How low lifetime earnings affect Social Security payments.
- Spousal Benefits: The role of spousal benefits in supplementing low individual retirement payments.
- Zero Benefits: Circumstances where a retiree might receive no Social Security retirement benefits.
- Early Claiming Strategies: Methods for mitigating the impact of a lower benefit.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
While there isn't a single definitive "minimum" in the traditional sense, several factors interact to drastically reduce, or even eliminate, Social Security benefits received at age 62. Let's delve into these critical elements.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Minimum Social Security Benefits at 62:
Definition and Core Concepts: The SSA calculates retirement benefits based on an individual's earnings history over their working life. These earnings are indexed to account for inflation, and the highest 35 years of earnings are used in the calculation. A lower average indexed monthly earnings (AIME) will result in a lower benefit. Furthermore, claiming benefits at age 62 significantly reduces the monthly amount compared to waiting until full retirement age (FRA) or age 70.
Applications Across Industries: The minimum benefit scenario affects individuals across all industries. Those with lower lifetime earnings, intermittent work histories, or careers predominantly in low-paying sectors are particularly susceptible to receiving a lower-than-average benefit at age 62.
Challenges and Solutions: The primary challenge is the inherent reduction in benefits for early claiming. While the solution isn't simple – increasing earnings throughout one's career is ideal – strategies like delaying claiming and maximizing spousal or survivor benefits can help mitigate the impact of low individual benefits.
Impact on Innovation: The minimum benefit situation doesn't directly relate to innovation, but it highlights the need for innovative financial planning strategies for individuals facing low retirement income projections. This can lead to an increased demand for financial planning services and tools tailored to assist those facing such challenges.
Closing Insights: Summarizing the Core Discussion:
The minimum Social Security benefit at 62 is not a fixed amount. Instead, it's the result of a complex calculation influenced by an individual's work history and the timing of their benefit claim. Low lifetime earnings are the primary driver of lower payouts.
Exploring the Connection Between Low Lifetime Earnings and Minimum Social Security Benefits at Age 62:
The relationship between low lifetime earnings and minimum Social Security benefits at age 62 is direct and significant. The SSA uses the average indexed monthly earnings (AIME) from the 35 highest-earning years to calculate retirement benefits. Individuals with low earnings throughout their working lives will have a low AIME, leading to a proportionally low benefit, even more so when claimed early at age 62.
Key Factors to Consider:
Roles and Real-World Examples: Someone who worked part-time jobs with low wages throughout their career would likely have a substantially lower AIME than someone with a consistent, high-earning career. This translates directly into a much smaller monthly benefit at age 62.
Risks and Mitigations: The primary risk is inadequate retirement income. Mitigating this involves working longer to increase earnings, actively saving and investing for retirement, and considering part-time work during retirement.
Impact and Implications: Low Social Security benefits significantly impact financial security in retirement, potentially leading to financial hardship, reduced healthcare access, and limited opportunities for travel or leisure activities.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection:
The link between low lifetime earnings and the minimum Social Security benefit at age 62 is undeniable. Planning for retirement requires a realistic assessment of one's earnings history and the potential for a lower benefit. Strategies to mitigate the risks must be implemented well in advance of retirement.
Further Analysis: Examining Low AIME in Greater Detail:
A low AIME is the fundamental cause of low Social Security benefits. This is determined by several factors, including the length of one's work history, periods of unemployment, low wages, and gaps in employment. Understanding how these elements affect the AIME calculation provides insight into planning for a secure retirement. Individuals with low AIME should seriously consider working longer to boost their earnings and potentially increase their Social Security benefits.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Minimum Social Security Benefits at Age 62:
What is the absolute minimum Social Security benefit at age 62? There is no guaranteed minimum dollar amount. The benefit calculation depends entirely on your earnings history. It’s possible to receive a very small benefit or even zero.
How is a zero Social Security benefit possible? A person with very limited work history or very low earnings in those years might not have enough credited work to receive any retirement benefit.
How can I increase my Social Security benefit if I have low lifetime earnings? Working longer, even part-time, can significantly increase your benefit. Delaying your claim until full retirement age or beyond will also result in a higher monthly payment.
Can I supplement my low Social Security benefit with other sources of income? Absolutely. A combination of savings, investments, pensions, and part-time work can provide a more secure retirement.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Social Security Despite Low Lifetime Earnings:
Understand the Basics: Learn how the SSA calculates benefits and how your earnings history affects the outcome.
Identify Practical Applications: Explore potential strategies for increasing your AIME and optimizing your benefit claim timing.
Plan Ahead: Start saving and investing early to supplement your Social Security income. Consider part-time work during retirement to bolster your financial security. Consult a financial advisor to develop a personalized plan.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights:
The minimum Social Security benefit at age 62 is not a fixed number, but rather a consequence of an individual's work history. Low lifetime earnings significantly impact the amount received. However, by understanding the benefit calculation and implementing effective strategies, individuals can mitigate the impact of lower payouts and plan for a more secure retirement, even with a lower initial Social Security benefit. Proactive planning, including saving, investing, and considering the timing of your Social Security claim, is vital for financial well-being in retirement.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Investment Landscape
Apr 05, 2025
-
Navigating Between China And Japan Indonesia And Economic Hedging
Apr 05, 2025
-
What Is Amazon Pay On My Credit Card
Apr 05, 2025
-
Whats Minimum Payment On A Credit Card
Apr 05, 2025
-
Chase Amazon Credit Card Minimum Payment
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Minimum Amount Of Social Security At Age 62 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.