What Is The Grace Period To Pay Your Mortgage
adminse
Apr 02, 2025 · 8 min read
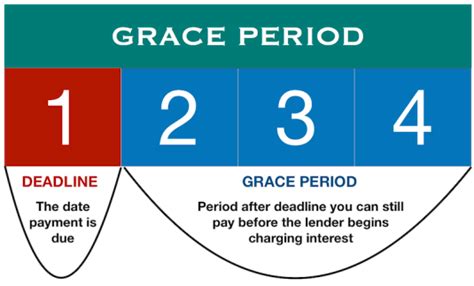
Table of Contents
Understanding the Grace Period for Mortgage Payments: Avoiding Late Fees and Protecting Your Credit
What happens if you miss a mortgage payment? Is there a safety net?
Missing a mortgage payment can have serious consequences, but understanding the grace period can help you navigate financial difficulties and avoid costly penalties.
Editor’s Note: This article on mortgage grace periods was published today, providing up-to-date information on this crucial aspect of homeownership. We've consulted multiple reputable sources to ensure accuracy and clarity.
Why Understanding Your Mortgage Grace Period Matters:
A mortgage is likely the largest financial commitment most people will ever make. Understanding the terms of your mortgage, particularly the grace period for payments, is paramount to maintaining a healthy financial standing and protecting your credit score. Failing to meet your payment obligations can lead to late fees, damage to your credit history, and even foreclosure. Conversely, knowledge of your grace period provides a crucial buffer, allowing time to address unexpected financial setbacks without immediate dire consequences.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This comprehensive article explores the concept of a mortgage grace period, detailing its definition, variations among lenders, implications for late payments, and strategies for avoiding late payments altogether. We will also examine the differences between a grace period and a cure period, and address frequently asked questions to ensure a complete understanding of this vital topic.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article draws upon extensive research, including analysis of lender websites, legal documents, and financial expert opinions. We have consulted various reputable sources to ensure the information provided is accurate, up-to-date, and relevant to a broad audience of homeowners and prospective homebuyers.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition of a Grace Period: A grace period is the short timeframe after the official due date of your mortgage payment during which you can still make a payment without incurring late fees.
- Length of Grace Periods: Grace periods vary, typically ranging from a few days to 15 days, depending on your lender and the specific terms of your mortgage agreement.
- Consequences of Missing the Grace Period: Failing to make your payment within the grace period results in late fees, potentially impacting your credit score and increasing the overall cost of your mortgage.
- Cure Periods: Separate from the grace period, a cure period provides additional time to rectify a late payment before more serious actions, such as foreclosure proceedings, are initiated.
- Strategies for Avoiding Late Payments: Proactive financial planning, budgeting, and automated payment systems can help prevent missed payments.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion
Now that we've established the importance of understanding your mortgage grace period, let's delve into the details, examining its definition, variations, and implications.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Mortgage Grace Periods
Definition and Core Concepts: A mortgage grace period is a short window of time, typically a few days to two weeks, after your mortgage payment's due date, during which you can make your payment without penalty. This period offers a buffer for minor delays, such as forgetting the due date or experiencing a slight delay in receiving your paycheck. It's crucial to note that the existence and length of this grace period are explicitly defined within your mortgage agreement.
Variations Among Lenders: While the existence of a grace period is common, the specific length varies significantly between lenders. Some lenders may offer a grace period of only a few days, while others may extend it to as long as 15 days. This variance highlights the importance of carefully reviewing your mortgage documents to understand your specific terms. The grace period is not a standardized industry practice, and it's never implicitly assumed.
Consequences of Missing the Grace Period: Once the grace period expires, your mortgage payment is considered late. This triggers several consequences:
- Late Fees: Lenders typically charge late fees for payments made after the grace period ends. These fees can vary significantly, ranging from a small fixed amount to a percentage of your missed payment.
- Credit Score Damage: Late mortgage payments are reported to credit bureaus, negatively impacting your credit score. A lower credit score can make it more difficult to secure future loans, rent an apartment, or even obtain certain jobs.
- Escalating Penalties: Continued late payments can lead to more severe consequences, including further late fees, increased interest rates, and ultimately, foreclosure proceedings.
Cure Periods: A Separate Safety Net: While a grace period prevents immediate late fees, a cure period offers a more extended window to rectify a missed payment. A cure period typically comes into play after the grace period has lapsed. It gives the borrower a more extended period – usually 30 to 60 days – to bring their account current. However, during a cure period, late fees still apply, and the lender may initiate collection efforts.
Impact on Homeownership: Understanding the grace period is vital to responsible homeownership. It enables you to address unforeseen financial issues without immediately jeopardizing your home. By understanding your specific grace period, you can take proactive steps to avoid late fees and maintain a positive credit history.
Exploring the Connection Between Financial Planning and Grace Periods
The relationship between diligent financial planning and effective grace period utilization is crucial. Effective financial planning mitigates the risk of needing to rely on the grace period in the first place.
Roles and Real-World Examples: A well-structured budget, factoring in mortgage payments alongside other essential expenses, prevents surprises. For example, setting up automatic payments ensures timely mortgage payments, eliminating the risk of missed deadlines. This proactive approach reduces reliance on the grace period's buffer, safeguarding your credit score and avoiding unnecessary fees.
Risks and Mitigations: Unexpected financial emergencies, such as job loss or medical expenses, can disrupt even the most meticulous budget. Having emergency savings mitigates these risks. Even a small emergency fund provides a safety net to cover a missed payment without resorting to relying solely on the grace period.
Impact and Implications: Proactive financial planning minimizes the need to utilize the grace period, preserving your credit rating and reducing financial stress. Ignoring financial planning increases the likelihood of missed payments, impacting your creditworthiness and potentially leading to serious financial consequences, including foreclosure.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
The connection between financial planning and effectively utilizing grace periods is undeniable. Responsible financial management drastically reduces the likelihood of needing a grace period and offers a buffer in case of unexpected events. Proactive planning protects your credit, minimizes financial stress, and ultimately secures your homeownership.
Further Analysis: Examining Budgeting in Greater Detail
Effective budgeting is the cornerstone of responsible homeownership. It's a systematic process of tracking income and expenses to ensure adequate funds for mortgage payments and other essential expenditures. Budgeting methodologies vary, from simple spreadsheets to sophisticated financial software, but the core principle remains consistent: understanding your financial inflows and outflows to make informed decisions.
Types of Budgeting Methods:
- Zero-Based Budgeting: This method allocates every dollar of your income to a specific expense category, ensuring a balanced budget where income equals expenditures.
- 50/30/20 Rule: This popular approach divides your after-tax income into three categories: 50% for needs, 30% for wants, and 20% for savings and debt repayment.
- Envelope System: This cash-based method involves allocating cash to different envelopes representing specific expense categories. Once the cash in an envelope is depleted, spending in that category is halted until the next budget cycle.
Importance of Regular Review: A budget is not a static document. Regular review and adjustments are necessary to reflect changing circumstances, such as unexpected expenses or income fluctuations. Consistent monitoring allows for timely adjustments, preventing overspending and ensuring timely mortgage payments.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Mortgage Grace Periods
Q: What happens if I miss my mortgage payment, even within the grace period?
A: While some lenders might not charge late fees if you pay within the grace period, it's still advisable to pay on time to avoid any potential issues and maintain a positive payment history. Confirm with your lender their specific policy.
Q: Is the grace period the same as the cure period?
A: No. The grace period is a short window to pay without late fees. The cure period, typically longer, follows the grace period and offers a chance to rectify a late payment before further action is taken.
Q: Can I negotiate a longer grace period with my lender?
A: While it's unlikely that a lender will extend the grace period explicitly defined in your agreement, you can contact your lender to discuss your financial situation if you anticipate difficulty making a payment. They might offer alternative solutions, such as a forbearance plan or loan modification.
Q: What happens if I consistently miss mortgage payments?
A: Consistent missed payments can lead to serious consequences, including escalating late fees, a severely damaged credit score, foreclosure proceedings, and ultimately, the loss of your home.
Q: How can I prevent missed mortgage payments?
A: Set up automatic payments, create a comprehensive budget, and maintain an emergency fund to cover unforeseen expenses.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Understanding Your Grace Period
- Read Your Mortgage Agreement Carefully: Understand the precise terms and conditions of your mortgage, including the length of your grace period.
- Set Up Automatic Payments: Automate your mortgage payments to avoid forgetting due dates.
- Create a Realistic Budget: Track income and expenses meticulously to ensure sufficient funds for your mortgage payment.
- Build an Emergency Fund: Having savings readily available mitigates financial emergencies that could lead to late payments.
- Contact Your Lender: If you anticipate difficulty making a payment, contact your lender proactively to explore potential solutions.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
Understanding your mortgage grace period is crucial for responsible homeownership. While it provides a safety net for minor delays, proactive financial planning significantly reduces the reliance on it. By establishing a robust budget, maintaining an emergency fund, and utilizing automatic payments, you can minimize the risk of late payments, protect your credit score, and secure your financial future. Remember, responsible financial management is the best way to ensure long-term homeownership success.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Minimum Payment Credit Card Rbc
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is Minimum Payment For 10000 Credit Card
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Minimum Payment For A Visa Credit Card
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Minimum Payment For A 1000 Credit Card
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Minimum Payment For A Discover Credit Card
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Grace Period To Pay Your Mortgage . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.