What Is Bank Frauds Examples
adminse
Apr 01, 2025 · 8 min read
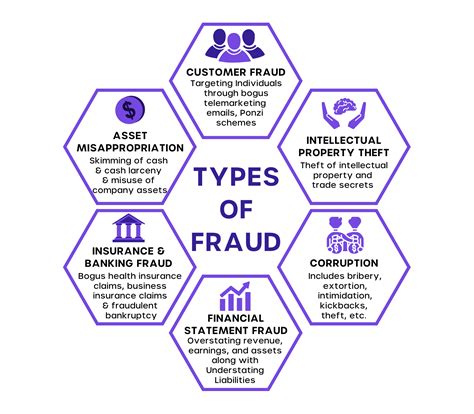
Table of Contents
Unmasking Bank Fraud: Types, Examples, and Prevention
What if the seemingly impenetrable fortress of modern banking is vulnerable to sophisticated schemes that drain millions? Bank fraud, a pervasive threat, undermines financial stability and erodes public trust, demanding a comprehensive understanding of its various forms and preventative measures.
Editor’s Note: This article on bank fraud provides a current overview of common types of bank fraud, real-world examples, and strategies for prevention. The information presented is for educational purposes and should not be considered legal or financial advice.
Why Bank Fraud Matters:
Bank fraud poses a significant threat to individuals, businesses, and the global financial system. The losses incurred are substantial, impacting not only the targeted institutions but also the broader economy through decreased consumer confidence and increased transaction costs. Understanding the various types of bank fraud and their prevention is critical for safeguarding personal finances, protecting businesses, and maintaining the integrity of the banking sector. The implications extend beyond monetary loss; reputation damage, legal battles, and even systemic instability can result from undetected and unmitigated fraud.
Overview: What This Article Covers:
This article will delve into the diverse world of bank fraud, exploring its various forms, providing real-world examples to illustrate the methods employed, and offering practical insights into prevention and detection. We will examine the roles of technology, human error, and regulatory frameworks in contributing to or mitigating the risk of bank fraud. The article also investigates specific fraud types like check fraud, credit card fraud, wire fraud, and insider fraud, providing detailed explanations and case studies.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights:
This article is the result of extensive research, drawing upon reports from regulatory bodies like the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), and the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), as well as academic studies and news reports documenting significant fraud cases. The information presented reflects a careful analysis of current trends and methodologies used in bank fraud schemes.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: A clear definition of bank fraud, encompassing its various forms and underlying motivations.
- Types of Bank Fraud: Detailed explanations of common types of bank fraud, including check fraud, credit card fraud, wire fraud, loan fraud, and insider fraud.
- Real-World Examples: Case studies illustrating the methods and consequences of various bank fraud schemes.
- Prevention and Detection Strategies: Practical strategies for individuals, businesses, and financial institutions to prevent and detect bank fraud.
- The Role of Technology: How technology both facilitates and combats bank fraud.
- Regulatory Landscape: An overview of the regulatory framework designed to combat bank fraud.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
Having established the significance of bank fraud, let's now explore its diverse forms, drawing upon real-world examples to illustrate the complexities and challenges involved in its prevention and detection.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Bank Fraud:
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
Bank fraud is any illegal activity involving deception to obtain money, property, or services from a financial institution. This broad definition encompasses a wide range of activities, from relatively simple schemes targeting individuals to sophisticated, large-scale operations that impact entire institutions. The common thread is the fraudulent misrepresentation or concealment of facts to induce a financial institution to act in a way that results in a financial loss.
2. Types of Bank Fraud:
- Check Fraud: This involves forging, altering, or stealing checks to gain unauthorized access to funds. Methods include counterfeiting checks, creating altered checks with increased amounts, or using stolen check information to create fraudulent checks.
- Credit Card Fraud: This encompasses unauthorized use of credit cards, including stolen cards, card cloning, and fraudulent applications. Phishing, skimming, and online scams are common methods used to obtain credit card information.
- Wire Fraud: This involves using electronic fund transfers to fraudulently transfer money from one account to another. Often involves phishing or social engineering to obtain banking information.
- Loan Fraud: This involves providing false information on loan applications to obtain loans that would otherwise not be approved. This can include falsifying income, assets, or credit history.
- Insider Fraud: This involves employees or insiders of a financial institution using their privileged access to commit fraud. This can involve embezzlement, manipulating accounts, or approving fraudulent loans.
- Identity Theft: Often used as a precursor to other types of bank fraud, identity theft involves stealing an individual's personal information to open fraudulent accounts or obtain loans in their name.
- Account Takeover Fraud: This involves gaining unauthorized access to an existing bank account and then using it to make fraudulent transactions. This can be achieved through phishing, malware, or exploiting vulnerabilities in online banking systems.
3. Real-World Examples:
- The Equity Funding Scandal (1970s): This infamous case involved the creation of fraudulent insurance policies to inflate the company's assets, resulting in massive losses for investors and creditors.
- The Madoff Ponzi Scheme (2000s): Bernard Madoff orchestrated one of the largest Ponzi schemes in history, defrauding thousands of investors of billions of dollars. While not directly targeting banks, it highlighted the vulnerability of financial institutions to sophisticated investment fraud.
- Credit Card Skimming: Retailers and restaurants have been victims of skimming devices attached to credit card readers, allowing criminals to steal card information at the point of sale. This highlights the ongoing threat of physical point-of-sale fraud.
- Nigerian Prince Scam (Ongoing): While seemingly simplistic, the persistent prevalence of email scams exploiting promises of wealth demonstrates the ongoing susceptibility of individuals to phishing and social engineering tactics.
4. Prevention and Detection Strategies:
- Strong Security Measures: Implementing robust security protocols, including multi-factor authentication, encryption, and regular security audits.
- Employee Training: Educating employees on recognizing and reporting suspicious activities.
- Fraud Detection Systems: Utilizing advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to detect anomalous transactions.
- Regular Account Monitoring: Individuals should regularly review their bank statements for unauthorized transactions.
- Strong Password Practices: Using strong, unique passwords for online banking accounts.
- Anti-Phishing Software: Installing and regularly updating anti-phishing software to protect against email and website scams.
- Shredding Sensitive Documents: Properly disposing of documents containing sensitive financial information.
- Reporting Suspicious Activity: Reporting any suspicious transactions or activities to the bank immediately.
5. The Role of Technology:
Technology plays a dual role in bank fraud. It can facilitate fraud through sophisticated hacking techniques and data breaches, but it also provides powerful tools for fraud detection and prevention, such as biometric authentication, anomaly detection algorithms, and blockchain technology.
6. Regulatory Landscape:
Various regulatory bodies, such as the OCC, FinCEN, and the Federal Reserve, play a crucial role in setting standards and enforcing regulations to combat bank fraud. These regulations aim to improve security practices, enhance fraud detection capabilities, and increase transparency within the financial industry.
Exploring the Connection Between Technology and Bank Fraud:
The relationship between technology and bank fraud is complex and dynamic. While technology offers powerful tools for preventing and detecting fraud, it also presents new opportunities for criminals to perpetrate sophisticated schemes.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Roles and Real-World Examples: Technology, such as malware and phishing techniques, has enabled large-scale data breaches, leading to identity theft and account takeover fraud. Simultaneously, technologies like AI-powered fraud detection systems help identify suspicious patterns and prevent fraud.
- Risks and Mitigations: The rapid evolution of technology requires continuous adaptation in security measures. Regular software updates, strong cybersecurity practices, and employee training are crucial to mitigating the risks.
- Impact and Implications: The increasing reliance on technology in banking necessitates a proactive approach to cybersecurity. Failure to address technological vulnerabilities can result in substantial financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection:
The interplay between technology and bank fraud underscores the need for a multifaceted approach to combating this pervasive threat. By proactively addressing technological vulnerabilities and leveraging advanced technologies for fraud detection, financial institutions can better protect themselves and their customers.
Further Analysis: Examining the Role of Human Error in Bank Fraud:
While technology plays a significant role, human error remains a contributing factor to bank fraud. Negligence in security practices, inadequate employee training, and social engineering tactics exploiting human psychology can all create vulnerabilities.
FAQ Section:
- What is the most common type of bank fraud? Check fraud and credit card fraud remain prevalent, although the specific methods and targets constantly evolve.
- How can I protect myself from bank fraud? Regularly monitor your accounts, use strong passwords, be cautious of phishing emails, and report any suspicious activity immediately.
- What should I do if I suspect I am a victim of bank fraud? Contact your bank immediately, report the fraud to the authorities, and take steps to secure your accounts.
Practical Tips:
- Enable two-factor authentication: This adds an extra layer of security to your online banking accounts.
- Review your bank statements regularly: Look for any unauthorized transactions or unusual activity.
- Be cautious of unsolicited emails or phone calls: Do not click on links or provide personal information unless you are certain of the source's legitimacy.
- Keep your antivirus software updated: This helps protect your computer from malware that can steal your banking information.
Final Conclusion:
Bank fraud remains a persistent threat to the financial system. Understanding the various types of bank fraud, their methods, and prevention strategies is essential for both individuals and financial institutions. By combining robust security measures, advanced technology, and vigilant awareness, we can collectively work towards mitigating this risk and maintaining the integrity of our financial system. The ongoing evolution of fraud techniques necessitates a constant adaptation and vigilance in our approach to security.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Does Td Charge A Maintenance Fee
Apr 03, 2025
-
Why Does Td Bank Charge A Maintenance Fee
Apr 03, 2025
-
Why Is Td Bank Charging Me A Maintenance Fee
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Fees Are Charged If You Are Late On A Payment
Apr 03, 2025
-
When Will I Be Charged
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Bank Frauds Examples . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.