What Does Credit Transfer Mean
adminse
Mar 31, 2025 · 9 min read
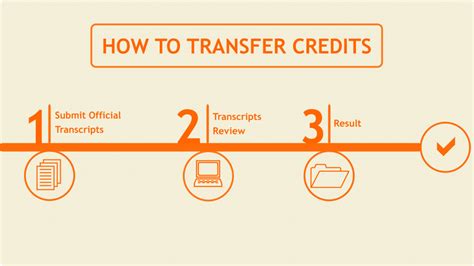
Table of Contents
What if unlocking your educational potential hinged on understanding credit transfer?
This powerful academic tool can significantly impact your academic journey and career prospects.
Editor’s Note: This article on credit transfer was published today, providing readers with up-to-date information and insights into navigating this complex yet rewarding academic process.
Why Credit Transfer Matters: Relevance, Practical Applications, and Industry Significance
Credit transfer, the process of moving earned academic credit from one institution to another, is far more than a simple administrative procedure. It's a powerful tool that can reshape educational pathways, accelerate degree completion, and significantly impact both personal and professional development. For students, it offers flexibility, cost savings, and the ability to pursue educational goals previously deemed unattainable. For institutions, it fosters collaboration, enhances student enrollment, and contributes to a more fluid and accessible higher education system. Its relevance extends to the broader societal context, by promoting lifelong learning and supporting individuals in achieving their career aspirations. The impact is felt across diverse sectors, influencing workforce skills, economic competitiveness, and individual well-being.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This comprehensive article explores the multifaceted world of credit transfer, covering its definition, types, eligibility criteria, the process involved, potential challenges, and strategies for successful navigation. Readers will gain a thorough understanding of how credit transfer works, its benefits, and how to maximize its potential to achieve academic and career goals.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article is the result of extensive research, drawing upon official guidelines from various accreditation bodies, institutional policies from diverse colleges and universities, and firsthand accounts from students and academic advisors. Credible sources, including government reports and academic journals, have been meticulously referenced to ensure accuracy and provide a balanced perspective on the complexities of credit transfer.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: A detailed explanation of credit transfer, its various forms, and the underlying principles governing its application.
- Eligibility and Requirements: A breakdown of the factors influencing credit transfer eligibility, including course content, grading systems, and institutional policies.
- The Transfer Process: A step-by-step guide outlining the procedures involved in initiating, processing, and finalizing a credit transfer request.
- Potential Challenges and Solutions: An identification of common obstacles encountered during credit transfer and practical strategies to overcome them.
- Maximizing the Benefits: Strategies for successfully navigating the credit transfer process and leveraging its advantages for accelerated degree completion and cost savings.
- Future Trends: Exploring evolving trends in credit transfer, including the influence of technology and the growing emphasis on flexible and accessible learning pathways.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion
Having established the importance and scope of credit transfer, let’s delve into its core aspects, exploring its mechanics, practical applications, and the strategic considerations involved in its successful implementation.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Credit Transfer
Definition and Core Concepts: Credit transfer involves the acceptance of previously earned academic credit from one institution (the sending institution) by another (the receiving institution) towards the completion of a degree or certificate program. This credit may be earned through various pathways, including coursework completed at another college or university, prior learning assessment (PLA) such as CLEP or DSST exams, or through military training or professional certifications. The transferred credits are incorporated into the student's academic transcript at the receiving institution, reducing the overall number of courses required to graduate.
Types of Credit Transfer: Several types of credit transfer exist, each with its own set of rules and considerations:
- Internal Transfer: Transferring credits between different departments or colleges within the same university. This process is generally simpler than external transfers.
- External Transfer: Transferring credits from one institution to another, which often requires more complex evaluation and documentation.
- Articulation Agreements: Formal agreements between institutions outlining specific pathways for credit transfer, simplifying the process and guaranteeing credit acceptance for particular courses or programs.
- Course-by-Course Transfer: Evaluating each individual course for credit equivalence at the receiving institution. This method is more common in external transfers and may result in varying levels of credit acceptance.
- Program-to-Program Transfer: Transferring credits based on the overall program completed at the sending institution. This is often streamlined through articulation agreements.
Eligibility and Requirements: Eligibility for credit transfer varies considerably depending on several factors:
- Accreditation: Both the sending and receiving institutions must be properly accredited. The accreditation status of the sending institution significantly influences the acceptability of the transferred credits.
- Course Content: The content of the transferred courses must align substantially with the corresponding courses required in the receiving institution's program.
- Grades Earned: Most institutions have minimum grade requirements for transferred courses, typically a "C" or equivalent.
- Course Equivalency: The receiving institution's academic department evaluates the transferred course to ensure it meets their standards and curriculum objectives.
- Time Limits: Some institutions impose time limits on how old the transferred credits can be.
- Institutional Policies: Each institution has its own specific policies and procedures regarding credit transfer, which must be carefully reviewed.
The Transfer Process: The steps involved in transferring credit typically include:
- Research: Identify potential receiving institutions and review their credit transfer policies.
- Application: Submit a formal application to the receiving institution, including transcripts from the sending institution.
- Evaluation: The receiving institution evaluates the transferred credits based on their policies and criteria.
- Acceptance: The receiving institution notifies the applicant of the accepted credits.
- Enrollment: Once the credit transfer is finalized, the student can enroll in the program at the receiving institution.
Potential Challenges and Solutions: Several challenges can arise during the credit transfer process:
- Unclear Policies: Ambiguous or inaccessible credit transfer policies can create uncertainty and frustration. Solution: Thorough research and direct communication with the receiving institution's registrar's office.
- Course Equivalency Issues: Difficulties in matching courses from the sending and receiving institutions can lead to loss of credit. Solution: Detailed course descriptions and proactive communication with academic advisors.
- Long Processing Times: Credit transfer evaluation can be time-consuming, delaying the enrollment process. Solution: Submitting applications early and following up regularly.
- Lost or Missing Documents: Misplaced or delayed transcripts can disrupt the transfer process. Solution: Maintaining meticulous records and using official transcript-sending services.
- Grade Requirements: Failure to meet the minimum grade requirement for credit transfer. Solution: Reviewing the academic performance and taking necessary steps to improve.
Maximizing the Benefits of Credit Transfer: Successful credit transfer requires proactive planning and attention to detail:
- Early Planning: Begin researching transfer options well in advance of the intended transfer date.
- Thorough Research: Carefully review the credit transfer policies of potential receiving institutions.
- Open Communication: Maintain open communication with academic advisors and registrars at both the sending and receiving institutions.
- Meticulous Documentation: Keep meticulous records of all applications, transcripts, and correspondence.
- Proactive Follow-up: Regularly follow up on the status of the credit transfer application.
Exploring the Connection Between Prior Learning Assessment (PLA) and Credit Transfer
Prior Learning Assessment (PLA) plays a significant role in credit transfer. PLA methods, such as CLEP, DSST, and Excelsior College Exams, allow students to demonstrate competency in specific subject areas through examinations, portfolio reviews, or other assessments. Credits earned through successful completion of PLA examinations can then be transferred to receiving institutions, granting students credit for knowledge acquired outside the traditional classroom setting. This is especially beneficial for individuals with prior work experience, military training, or self-directed learning experiences.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Roles and Real-World Examples: PLA provides opportunities for students to earn college credit for skills and knowledge obtained through military service, work experience, or independent study. For example, a veteran might transfer credits earned through CLEP exams for military training, while a working professional might leverage their experience to earn credits through a portfolio assessment.
- Risks and Mitigations: PLA may not always be accepted by all institutions, and the acceptance process can vary considerably. Careful research into the specific PLA methods accepted by the receiving institution is essential.
- Impact and Implications: The widespread acceptance of PLA can broaden access to higher education for individuals who haven't followed traditional educational paths, enhancing educational equity and promoting lifelong learning.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
The integration of PLA within the credit transfer process significantly expands the accessibility and inclusivity of higher education. By acknowledging and validating prior learning, PLA empowers individuals with diverse backgrounds to pursue higher education goals and advance their careers.
Further Analysis: Examining PLA in Greater Detail
A closer examination of PLA reveals its profound impact on educational attainment. Its ability to recognize prior learning experiences, regardless of their formal setting, challenges the traditional notion of exclusively classroom-based learning. It promotes a more holistic view of learning, recognizing the diverse pathways individuals take to acquire knowledge and skills.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Credit Transfer
What is credit transfer? Credit transfer is the process of moving academic credits earned at one institution to another institution to fulfill degree requirements.
How do I find out if my credits will transfer? Contact the receiving institution's registrar's office and review their credit transfer policies. Submit unofficial transcripts for a preliminary evaluation.
What types of credits can be transferred? Credits earned through coursework, prior learning assessments (PLA), military training, and professional certifications can be considered for transfer.
How long does the credit transfer process take? The processing time varies greatly depending on the institution's policies and the complexity of the evaluation. It can range from a few weeks to several months.
What happens if some of my credits don't transfer? The receiving institution will inform you of which credits have been accepted and which have not. You may need to take additional courses to fulfill degree requirements.
What if I change my major after transferring credits? Some credits may still transfer, but others may not be applicable to your new major. Consult with an academic advisor.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Credit Transfer
- Start Early: Begin researching transfer options well before you plan to transfer.
- Understand Policies: Thoroughly review the credit transfer policies of your target institutions.
- Communicate Effectively: Maintain open communication with academic advisors and registrars.
- Organize Documents: Keep all your transcripts and supporting documentation in order.
- Follow Up Regularly: Check the status of your application periodically.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
Credit transfer, coupled with Prior Learning Assessment, represents a powerful tool for students seeking flexibility, efficiency, and cost savings in their educational pursuits. By understanding the intricacies of the credit transfer process and leveraging available resources, individuals can effectively navigate this system and unlock their full academic potential. The ability to transfer credits not only accelerates degree completion but also fosters a more inclusive and accessible higher education landscape, empowering individuals to pursue their educational and career goals with greater ease and efficiency.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Pass The Property And Casualty Insurance Exam
Apr 29, 2025
-
How To Record Insurance Proceeds For Property Damage
Apr 29, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Can Lower The Property Insurance Premium
Apr 29, 2025
-
How Hard Is The Property And Casualty Insurance License Exam
Apr 29, 2025
-
Property Insurance Definition And How Coverage Works
Apr 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Does Credit Transfer Mean . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.