What Does 25 Basis Points In Interest Rates Mean
adminse
Mar 25, 2025 · 7 min read
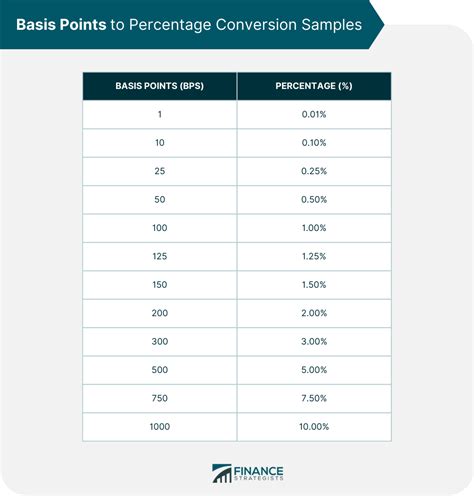
Table of Contents
Decoding 25 Basis Points: A Deep Dive into Interest Rate Changes
What if even a seemingly small adjustment in interest rates, like 25 basis points, could significantly impact your finances and the global economy? This seemingly minor fluctuation holds considerable power, affecting everything from mortgages to national debt.
Editor’s Note: This article on the meaning and impact of 25 basis points in interest rates was published today, offering up-to-date analysis and insights into this crucial economic indicator.
Why 25 Basis Points Matters: Relevance, Practical Applications, and Industry Significance
Understanding the significance of 25 basis points requires grasping the fundamental concept of basis points themselves. A basis point (bp) is one-hundredth of one percentage point, or 0.01%. Therefore, 25 basis points represent a 0.25% change in an interest rate. While seemingly small, this seemingly insignificant alteration can have substantial ripple effects across various sectors. It impacts borrowing costs for individuals and businesses, influencing investment decisions, inflation rates, and the overall economic climate. For instance, a 25-basis-point increase in the federal funds rate (the target rate the Federal Reserve sets for overnight lending between banks) can affect mortgage rates, credit card interest, and the cost of corporate loans, ultimately impacting consumer spending and business investment.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This article provides a comprehensive exploration of 25 basis points, examining its meaning, practical applications, and implications across diverse financial landscapes. We will delve into the reasons behind these adjustments, their effects on various economic actors, and the broader consequences for global markets. Readers will gain a clearer understanding of how these changes impact their personal finances and the overall economic health.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article is based on extensive research drawing from reputable sources, including reports from central banks (like the Federal Reserve and the European Central Bank), academic publications, financial news outlets, and analyses from leading economists. The analysis presented incorporates various economic models and real-world examples to illustrate the effects of 25-basis-point changes in interest rates.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: A precise definition of basis points and their role in expressing interest rate changes.
- Practical Applications: How 25-basis-point changes are used by central banks and their consequences for different sectors.
- Challenges and Solutions: Understanding the complexities and potential downsides of interest rate adjustments.
- Future Implications: Forecasting the potential long-term effects of interest rate fluctuations on the economy.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion
Having established the importance of understanding 25 basis points, let's now delve into the intricacies of how this seemingly small shift influences the financial landscape.
Exploring the Key Aspects of 25 Basis Points
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
As mentioned earlier, a basis point is 0.01% of a percentage point. A change of 25 basis points, therefore, is equivalent to a 0.25% increase or decrease. Interest rates are the price of borrowing money. They represent the percentage charged by lenders for the use of their funds. These rates influence various financial instruments, including loans, mortgages, bonds, and savings accounts. Central banks use interest rate adjustments as a primary tool for monetary policy, aiming to control inflation, stimulate economic growth, or stabilize financial markets.
2. Applications Across Industries:
-
Mortgages: A 25-basis-point increase in the benchmark interest rate can lead to a noticeable rise in mortgage rates, making homeownership more expensive for potential buyers. Conversely, a decrease can make mortgages more affordable. This impacts housing demand and the overall real estate market.
-
Consumer Loans: Credit cards, auto loans, and personal loans are all directly affected by changes in interest rates. Higher rates increase the cost of borrowing, potentially reducing consumer spending.
-
Corporate Debt: Businesses rely heavily on borrowing for expansion and operations. Interest rate changes significantly affect their financing costs. Higher rates can lead to reduced investment and slower economic growth.
-
Government Debt: Governments manage substantial debt. Changes in interest rates directly impact the cost of servicing this debt. Higher rates increase the burden on taxpayers.
-
Savings Accounts and Investments: Interest rate increases can boost returns on savings accounts and certain investments, while decreases can lower them.
3. Challenges and Solutions:
One primary challenge with interest rate adjustments is their delayed impact. It can take months, even years, for the full effect of a rate change to be felt across the economy. This lag makes precise policy adjustments difficult. Another challenge is predicting the precise response of various sectors to interest rate changes. Consumer and business behavior can be unpredictable, complicating the effectiveness of monetary policy. Careful analysis of economic data and simulations are crucial in mitigating these challenges.
4. Impact on Innovation:
While not directly influencing innovation, interest rates play a crucial role in shaping the investment climate. Lower rates encourage investment in new technologies and ventures, promoting innovation. Higher rates can curb riskier investments, slowing down innovation in some sectors.
Closing Insights: Summarizing the Core Discussion
A 25-basis-point change in interest rates, although seemingly small, is a significant tool for managing the economy. Its effects ripple through various sectors, influencing borrowing costs, investment decisions, and consumer spending. Understanding its implications is crucial for individuals, businesses, and policymakers alike.
Exploring the Connection Between Inflation and 25 Basis Points
The relationship between inflation and 25 basis points is paramount. Central banks often use interest rate increases to combat inflation. Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, reducing consumer spending and investment, thus cooling down an overheated economy and curbing inflationary pressures. A 25-basis-point hike is a relatively moderate step in this process, often part of a series of adjustments aimed at achieving price stability.
Key Factors to Consider:
-
Roles and Real-World Examples: The 2008 financial crisis saw aggressive interest rate cuts to stimulate the economy, while more recent periods of inflation have involved interest rate hikes to control price increases. These real-world examples illustrate the dynamic interplay between interest rates and inflation.
-
Risks and Mitigations: Raising interest rates too aggressively can slow economic growth too much, potentially leading to recession. Central banks try to balance inflation control with maintaining economic stability.
-
Impact and Implications: The impact of a 25-basis-point change on inflation can vary depending on various economic factors, including consumer confidence, global events, and the overall health of the economy.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
The connection between inflation and 25 basis points is critical. Central banks carefully consider the inflationary environment when adjusting interest rates, balancing the need to control inflation with the risk of hindering economic growth.
Further Analysis: Examining Inflation in Greater Detail
Inflation is a general increase in the prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time. When inflation rises too quickly, it erodes the purchasing power of money and can destabilize the economy. Various factors contribute to inflation, including supply chain disruptions, increased demand, and monetary policy decisions. Central banks monitor inflation rates closely, using tools like interest rate adjustments to maintain price stability.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About 25 Basis Points
-
Q: What is the impact of a 25-basis-point increase on my mortgage payment? A: The impact will depend on your mortgage amount, term, and the specific lender's adjustment. It will usually result in a slightly higher monthly payment.
-
Q: How does a 25-basis-point change affect the stock market? A: The stock market's reaction can be complex and depends on various factors. Higher rates can initially cause a decline in stock prices, but the long-term effect can vary.
-
Q: Who benefits from a 25-basis-point increase in interest rates? A: Lenders and savers generally benefit from higher interest rates as they receive a better return on their funds.
-
Q: Who is negatively affected by a 25-basis-point increase? A: Borrowers, businesses with significant debt, and those reliant on affordable credit are negatively impacted by higher rates.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Understanding 25 Basis Points
-
Understand the Basics: Grasp the definition and implications of basis points to interpret financial news and understand policy decisions.
-
Follow Economic Indicators: Track inflation rates, interest rate announcements, and other economic data to anticipate potential impacts on your finances.
-
Review Your Financial Plans: Regularly assess your debts and savings plans in light of interest rate changes, adjusting accordingly.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
Understanding the meaning and implications of a 25-basis-point change in interest rates is crucial for navigating the financial world. This seemingly small adjustment carries significant weight, impacting personal finances, business operations, and the overall economic landscape. By staying informed and adapting financial strategies proactively, individuals and businesses can better navigate the complexities of interest rate fluctuations. The seemingly minor change of 25 basis points is, in reality, a powerful lever shaping the economic machinery of the world.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Does 25 Basis Points In Interest Rates Mean . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.