What Are Types Of Costing
adminse
Mar 28, 2025 · 8 min read
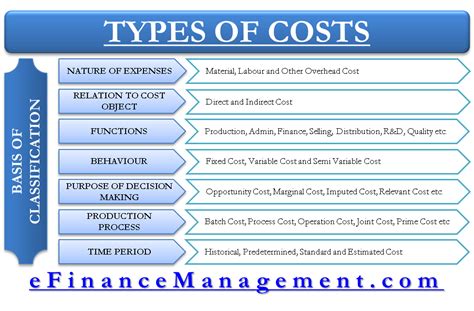
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Multifaceted World of Costing: A Comprehensive Guide to Costing Types
What if accurate cost accounting is the bedrock of a thriving business? Understanding the various types of costing is crucial for making informed decisions, optimizing operations, and ultimately achieving profitability.
Editor’s Note: This article on types of costing provides a comprehensive overview of the various methods used to determine the cost of goods or services. It explores the nuances of each method and offers practical insights into their applications. This updated guide is designed to equip both students and business professionals with a thorough understanding of this critical aspect of accounting and management.
Why Costing Matters: Relevance, Practical Applications, and Industry Significance
Costing, the systematic process of determining the cost of producing goods or services, is fundamental to successful business operations. It's not merely an accounting exercise; it's a vital tool for pricing strategies, performance evaluation, decision-making, and overall profitability. Whether a business is manufacturing automobiles, providing software solutions, or offering consulting services, understanding its costs is paramount. Accurate costing allows businesses to:
- Set competitive prices: Knowing the true cost of production ensures businesses can price their goods or services competitively while maintaining profitability.
- Control costs: By tracking and analyzing costs, businesses can identify areas of inefficiency and implement measures to reduce expenses.
- Make informed decisions: Accurate cost data is critical for decisions related to product development, pricing, investment, and resource allocation.
- Improve profitability: By optimizing cost structures, businesses can enhance their profit margins and overall financial performance.
- Evaluate performance: Cost accounting data provides insights into the efficiency and effectiveness of different processes and departments.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This article provides a detailed exploration of various costing methods, including:
- Absorption Costing (Full Costing): A detailed breakdown of absorption costing, its components, and practical applications.
- Variable Costing (Marginal Costing): A contrasting approach that focuses on variable costs and its implications for decision-making.
- Job Order Costing: How it tracks costs for individual projects or jobs.
- Process Costing: Ideal for mass production environments with uniform products.
- Activity-Based Costing (ABC): A more sophisticated method that allocates overhead costs based on activities.
- Lean Accounting: Integrating lean principles into cost accounting for efficiency improvements.
- Throughput Accounting: Focusing on throughput, operational expenses, and inventory.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article draws upon extensive research, including academic texts, industry publications, and practical case studies. The information presented is grounded in established accounting principles and aims to offer a clear and accurate portrayal of different costing methods.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: Understanding the fundamentals of different costing methods and their underlying principles.
- Practical Applications: Exploring the contexts in which each costing method is most effectively applied.
- Advantages and Disadvantages: Weighing the pros and cons of each method to determine suitability for specific situations.
- Comparative Analysis: Understanding the key differences between various costing methods and choosing the appropriate method based on business needs.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
Having established the importance of accurate costing, let's delve into the specifics of the various methods available, exploring their unique characteristics and applications.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Costing Methods
1. Absorption Costing (Full Costing):
Absorption costing, also known as full costing, allocates all manufacturing costs – direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead – to the cost of goods sold. It's the most commonly used method for external financial reporting, as it complies with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
- Components: Direct materials, direct labor, variable manufacturing overhead, and fixed manufacturing overhead are all included in the cost of goods sold.
- Advantages: Provides a complete picture of product costs, compliant with GAAP, facilitates inventory valuation.
- Disadvantages: Can be complex, fixed overhead allocation can be arbitrary, may not be suitable for short-term decision-making.
2. Variable Costing (Marginal Costing):
Variable costing only includes variable manufacturing costs (direct materials, direct labor, and variable manufacturing overhead) in the cost of goods sold. Fixed manufacturing overhead is treated as a period cost and expensed in the period it's incurred.
- Components: Direct materials, direct labor, and variable manufacturing overhead.
- Advantages: Simpler to understand and implement, useful for short-term decision-making, clearly separates fixed and variable costs.
- Disadvantages: Not compliant with GAAP for external reporting, doesn't provide a complete picture of product costs.
3. Job Order Costing:
This method is used when producing unique or customized products, such as construction projects or bespoke furniture. Costs are tracked for each individual job or order.
- Components: Direct materials, direct labor, and overhead costs are assigned to each specific job.
- Advantages: Provides accurate costs for individual jobs, allows for better pricing and profitability analysis on specific projects.
- Disadvantages: Can be labor-intensive, requires detailed record-keeping.
4. Process Costing:
Process costing is suitable for mass production environments where identical or similar products are manufactured in large quantities. Costs are averaged across all units produced.
- Components: Direct materials, direct labor, and overhead costs are averaged over the total number of units produced.
- Advantages: Relatively simple and cost-effective, suitable for high-volume production.
- Disadvantages: May not be accurate for products with significant variations in cost, less detailed cost information for individual units.
5. Activity-Based Costing (ABC):
ABC assigns overhead costs based on the activities that consume those costs. It's a more sophisticated approach that provides a more accurate cost allocation compared to traditional methods that use simple allocation bases like direct labor hours.
- Components: Identifies cost pools and cost drivers for various activities, allocates overhead costs based on the consumption of activities.
- Advantages: More accurate cost allocation, particularly for complex products with multiple activities, helps in identifying cost drivers and areas for improvement.
- Disadvantages: More complex and costly to implement than traditional methods, requires detailed data collection and analysis.
6. Lean Accounting:
Lean accounting integrates lean manufacturing principles into cost accounting, focusing on eliminating waste and improving efficiency. It emphasizes value-added activities and aims to provide real-time cost data.
- Components: Value stream costing, continuous improvement, waste reduction.
- Advantages: Focuses on value creation, improves efficiency, enhances operational decision-making.
- Disadvantages: Requires a change in organizational culture, implementation can be challenging.
7. Throughput Accounting:
Throughput accounting focuses on throughput (revenue generated from sales), operational expenses (all costs except direct materials), and inventory. It emphasizes maximizing throughput while minimizing operational expenses and inventory.
- Components: Throughput, operational expenses, inventory.
- Advantages: Simplifies cost analysis, emphasizes operational efficiency, suitable for manufacturing environments.
- Disadvantages: Oversimplifies cost structure, may not be suitable for all industries.
Closing Insights: Summarizing the Core Discussion
The choice of costing method depends on several factors, including the nature of the business, the complexity of its products, and the information needed for decision-making. While absorption costing is common for external reporting, variable costing offers valuable insights for internal decision-making. Job order costing suits unique projects, while process costing is ideal for mass production. ABC provides a more precise cost allocation, while lean accounting emphasizes efficiency. Throughput accounting focuses on maximizing revenue. Understanding these methods is key to effective cost management and profitability.
Exploring the Connection Between Technology and Costing
The relationship between technology and costing is increasingly important. Modern software solutions automate many aspects of cost accounting, improving accuracy, efficiency, and the timeliness of data. These systems can integrate with ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems, providing real-time cost information across the entire organization. Advanced analytics capabilities also enable more sophisticated cost analysis and predictive modeling.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Roles and Real-World Examples: ERP systems, cloud-based accounting software, data analytics tools are all transforming how businesses manage costs.
- Risks and Mitigations: Data security, system integration challenges, potential for inaccurate data.
- Impact and Implications: Improved accuracy, faster decision-making, better cost control, enhanced profitability.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
Technology is revolutionizing the way costing is performed. By embracing these advancements, businesses can gain valuable insights into their cost structures, leading to improved efficiency, greater profitability, and a competitive edge in today's dynamic marketplace.
Further Analysis: Examining Technology in Greater Detail
The use of AI and machine learning in cost accounting is a rapidly evolving area. These technologies can automate complex calculations, predict future costs, and identify anomalies in cost data. The integration of blockchain technology also offers potential benefits, such as improved transparency and traceability in supply chains.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Costing Types
- What is the difference between absorption and variable costing? Absorption costing includes all manufacturing costs, while variable costing only includes variable manufacturing costs.
- Which costing method is best for my business? The optimal method depends on the specific needs of your business and the nature of your products or services.
- How can I improve the accuracy of my costing system? Implement robust data collection processes, use appropriate technology, and regularly review and refine your costing methods.
- What are the ethical considerations in costing? Ensure transparency, accuracy, and consistency in cost reporting.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Costing
- Regularly review and update your costing system: Ensure it accurately reflects your current operations.
- Use appropriate technology to automate processes: This increases efficiency and reduces errors.
- Train your staff on proper costing techniques: Accurate data collection is crucial.
- Analyze your cost data regularly to identify areas for improvement: This allows for proactive cost management.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
Understanding the different types of costing is critical for effective business management. By carefully selecting the most appropriate method and leveraging technology, organizations can gain valuable insights into their cost structures, optimize operations, and ultimately achieve sustainable profitability. The journey to mastering costing is an ongoing process of refinement, adaptation, and continuous improvement.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Inside Sales Definition How It Works And Advantages
Apr 24, 2025
-
Inside Quote Definition
Apr 24, 2025
-
Inside Days Definition Trading Strategy Examples Vs Outside
Apr 24, 2025
-
Input Output Analysis Definition Main Features And Types
Apr 24, 2025
-
Inorganic Growth Definition How It Arises Methods And Example
Apr 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are Types Of Costing . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.