Surplus Value Of Labor Definition
adminse
Mar 28, 2025 · 9 min read
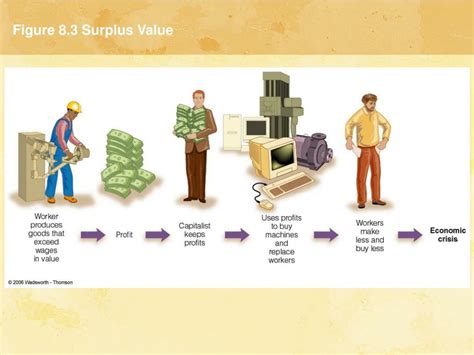
Table of Contents
Unlocking the Secrets of Surplus Value of Labor: A Deep Dive into Marx's Theory
What if understanding the surplus value of labor unlocks the key to comprehending economic inequality and power dynamics? This foundational concept, central to Marxist economics, remains profoundly relevant in analyzing modern capitalism and its inherent contradictions.
Editor’s Note: This article provides a comprehensive overview of the surplus value of labor, exploring its definition, implications, and ongoing relevance in contemporary economic discourse. We delve into the intricacies of Marx's theory, examining both its strengths and criticisms, to offer a balanced and nuanced perspective.
Why Surplus Value of Labor Matters:
The concept of surplus value of labor lies at the heart of Karl Marx's critique of capitalism. It explains how profit is generated within the capitalist system and, more importantly, how this process inherently leads to exploitation. Understanding surplus value is crucial for analyzing income inequality, class struggle, and the dynamics of power within capitalist economies. It provides a framework for understanding not just historical economic trends, but also contemporary issues such as wealth disparity and worker exploitation in various industries. The concept impacts discussions on fair wages, labor rights, and the overall distribution of wealth within society.
Overview: What This Article Covers:
This article will delve into the core aspects of surplus value of labor. We will begin by defining the concept and exploring its underlying principles. We will then examine its practical applications, analyzing how it manifests in different industries and economic contexts. Further, we will discuss the key criticisms leveled against the theory and explore its ongoing relevance in contemporary economic debates. Finally, we'll offer a concluding perspective on the enduring significance of surplus value as a tool for economic analysis.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights:
This article is the result of extensive research, drawing upon Marx's original works, including Das Kapital, along with secondary scholarly sources that offer both supporting and critical perspectives on the theory of surplus value. The analysis presented here strives for objectivity, acknowledging the complexities and nuances inherent in this multifaceted concept.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: A detailed explanation of surplus value, including the concepts of labor power, necessary labor, and surplus labor.
- Practical Applications: Real-world examples illustrating the generation of surplus value across various industries.
- Criticisms and Counterarguments: An examination of the major criticisms of the theory and responses to these critiques.
- Contemporary Relevance: An analysis of the continuing relevance of surplus value in understanding modern capitalist economies.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
Having established the importance and scope of this topic, let's now delve into the core elements of Marx's theory of surplus value.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Surplus Value of Labor:
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
Marx's theory of surplus value centers on the distinction between the value of labor and the value of labor power. Labor power refers to the worker's capacity to work – their skills, abilities, and physical strength. The value of labor power, like any other commodity, is determined by the socially necessary labor time required to produce and reproduce it – meaning the time and resources needed to sustain the worker and their family. This includes food, shelter, clothing, and other necessities.
Necessary labor is the portion of the working day that a worker spends producing enough value to cover the cost of their labor power. This generates enough value to reproduce the worker and meet the basic needs of their survival.
Surplus labor, on the other hand, is the portion of the working day that a worker spends producing value beyond what is necessary to reproduce their labor power. This surplus value is appropriated by the capitalist as profit. The rate of surplus value (or rate of exploitation) is calculated as surplus labor divided by necessary labor.
2. Applications Across Industries:
The concept of surplus value isn't abstract; it manifests concretely across various industries. Consider a factory worker producing shoes. The worker's wage covers the cost of their labor power (food, housing, etc.). However, the worker spends a significant portion of their workday producing value beyond what is needed to cover their wage. This extra value, the surplus value, is the profit the factory owner realizes. This same principle operates in service industries, agriculture, and all other sectors of a capitalist economy. The greater the difference between the value produced and the wages paid, the higher the surplus value extracted by the capitalist.
3. Challenges and Solutions (from a Marxist perspective):
A central challenge within Marx's framework is the inherent conflict between capitalists seeking to maximize surplus value and workers aiming to secure better wages and working conditions. Marx argued this conflict is inherent to capitalism and would inevitably lead to class struggle. Solutions, from a Marxist perspective, involve empowering workers through collective bargaining, unionization, and ultimately, the overthrow of the capitalist system and the establishment of a socialist or communist mode of production where the means of production are collectively owned and surplus value is distributed more equitably.
4. Impact on Innovation:
While often overlooked, Marx recognized that capitalism's drive for surplus value could be a catalyst for innovation. The relentless pursuit of profit incentivizes capitalists to invest in new technologies and methods of production to increase productivity and, consequently, surplus value. However, this innovation is often at the expense of workers, as automation and efficiency improvements can lead to job displacement and increased exploitation.
Closing Insights: Summarizing the Core Discussion:
Surplus value is not simply a theoretical construct; it's a fundamental mechanism driving the capitalist system. Understanding this mechanism illuminates the inherent power dynamics and inequalities inherent within capitalism. The extraction of surplus value is the engine of profit, and its distribution directly impacts societal wealth disparity and worker well-being.
Exploring the Connection Between Technological Advancements and Surplus Value:
Technological advancements play a significant role in shaping the generation and distribution of surplus value. This relationship is multifaceted and complex, impacting both the rate of surplus value and the very nature of labor itself.
Roles and Real-World Examples:
Technological advancements can increase productivity, leading to a higher rate of surplus value. For instance, the introduction of automation in manufacturing significantly boosts output per worker, allowing capitalists to extract more surplus value from the same amount of labor. Conversely, technology can also create new jobs and industries, altering the landscape of labor and its associated value. The rise of the internet, for example, spawned entirely new sectors, requiring different skills and generating different forms of surplus value.
Risks and Mitigations:
The increased productivity resulting from technology can lead to job displacement, exacerbating existing inequalities. Workers may find their skills rendered obsolete, leading to unemployment and reduced bargaining power. Mitigation strategies include investments in worker retraining and education, social safety nets, and policies that ensure a fair distribution of the benefits of technological progress.
Impact and Implications:
The ongoing technological revolution is reshaping the relationship between capital and labor, potentially impacting the very nature of work and the distribution of surplus value. The rise of the gig economy, for example, presents a new paradigm where traditional employment structures are challenged, leading to questions about worker rights, benefits, and the extraction of surplus value in this more fragmented labor market.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection:
The relationship between technological advancements and surplus value is dynamic and complex. While technology can increase productivity and lead to higher profit margins, it also carries the risk of exacerbating inequality and displacement if not managed thoughtfully. Addressing these risks through proactive policies and social safety nets is crucial for ensuring that technological progress benefits all members of society, not just the owners of capital.
Further Analysis: Examining Technological Unemployment in Greater Detail:
Technological unemployment, the displacement of workers due to automation and technological advancements, is a significant consequence of the pursuit of surplus value. The automation of tasks previously performed by human workers reduces the need for labor, directly impacting the workforce and potentially leading to long-term unemployment for those lacking the skills for new roles. This necessitates retraining programs, social support systems, and a broader societal discussion about the ethical implications of unchecked technological advancement.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Surplus Value of Labor:
What is surplus value?
Surplus value is the difference between the value a worker produces and the value they receive in wages. It's the profit extracted by the capitalist.
How is surplus value calculated?
Surplus value isn't directly calculated in monetary terms but rather as a ratio of surplus labor to necessary labor. It's a measure of the extent of exploitation within the capitalist mode of production.
Is surplus value exploitation?
From a Marxist perspective, the extraction of surplus value is inherently exploitative. Capitalists profit from the unpaid labor of workers, creating a fundamental imbalance of power and wealth within the system.
Is surplus value relevant today?
Absolutely. The pursuit of profit maximization and the extraction of surplus value remain central drivers of modern capitalist economies. Understanding surplus value provides a crucial lens for analyzing economic inequality, labor relations, and the dynamics of power in contemporary society.
Practical Tips: Maximizing Understanding of Surplus Value:
-
Understand the Basics: Begin by clearly grasping the definitions of labor power, necessary labor, and surplus labor.
-
Analyze Specific Industries: Apply the concept to real-world industries to see how surplus value is generated and distributed.
-
Consider the Broader Context: Analyze the societal implications of surplus value extraction, focusing on its impact on income inequality and worker welfare.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights:
The concept of surplus value, while originating in 19th-century economic theory, remains profoundly relevant in understanding the dynamics of modern capitalism. It illuminates the inherent tensions between capital and labor, the mechanisms of profit generation, and the structural inequalities embedded within the system. By critically analyzing the generation and distribution of surplus value, we can gain a deeper understanding of economic power structures and the persistent challenges of ensuring economic justice in the 21st century. The ongoing debate surrounding surplus value highlights its enduring power as a tool for economic analysis and its crucial role in informing discussions about fair wages, labor rights, and a more equitable distribution of wealth.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Letter To Credit Card Company To Remove Late Payment
Apr 03, 2025
-
How To Complain About Credit Card Charges
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Is The Maximum Late Fee Allowed By Law In Indiana
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Is The Maximum Late Fee Allowed By Law In Virginia
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Is The Maximum Late Fee Allowed By Law In Illinois
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Surplus Value Of Labor Definition . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.