Student Loan Interest Rate
adminse
Mar 28, 2025 · 10 min read
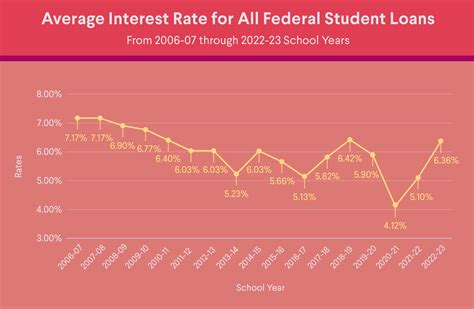
Table of Contents
Decoding the Student Loan Interest Rate: A Comprehensive Guide
What if the financial burden of higher education could be significantly eased by understanding the intricacies of student loan interest rates? Navigating this complex landscape is crucial for graduates to achieve financial freedom and avoid crippling debt.
Editor’s Note: This article on student loan interest rates was published today, offering the most up-to-date information and insights to help students and recent graduates make informed decisions about their loan repayments.
Why Student Loan Interest Rates Matter:
Student loan interest rates are a cornerstone of higher education financing. Understanding them is not merely an academic exercise; it directly impacts the total cost of a college education and dictates the long-term financial health of borrowers. Higher interest rates translate to larger repayment amounts over time, potentially delaying major life milestones like homeownership or starting a family. Conversely, understanding how to secure lower interest rates can save borrowers thousands, if not tens of thousands, of dollars. This knowledge is vital for both current students planning their financing and graduates already navigating their loan repayment plans. The impact extends beyond individual finances, affecting the overall economy through its influence on consumer spending and economic growth.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This article provides a comprehensive exploration of student loan interest rates. We will define key terms, delve into the different types of student loans and their associated interest rates, explore factors influencing interest rate determination, discuss strategies for securing lower rates, and offer actionable advice for managing student loan debt effectively. Readers will gain a clear understanding of this complex financial landscape, empowering them to make informed decisions about their educational financing and future financial well-being.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article is the culmination of extensive research, drawing upon data from the U.S. Department of Education, reputable financial institutions, and peer-reviewed academic studies. Information on current interest rates is cross-referenced with multiple sources to ensure accuracy and timeliness. The analysis presented is designed to be clear, accessible, and relevant to the average student or graduate seeking to understand their student loan repayment obligations.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: A clear explanation of student loan interest rates, principal, amortization, and other relevant terminology.
- Types of Student Loans and Interest Rates: A detailed comparison of federal and private student loans, including their varying interest rate structures.
- Factors Influencing Interest Rates: An in-depth analysis of the elements that determine student loan interest rates, such as credit score, loan type, and market conditions.
- Strategies for Securing Lower Interest Rates: Actionable tips and strategies for obtaining the most favorable interest rates on student loans.
- Managing Student Loan Debt Effectively: Practical advice on repayment strategies, including refinancing and consolidation options.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
Now that the importance of understanding student loan interest rates is established, let's delve into the specifics. We'll begin by defining key terms and exploring the different types of student loans available.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Student Loan Interest Rates:
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
A student loan interest rate is the annual percentage charged on the principal amount borrowed. The principal is the original amount of the loan. Interest accrues over time, meaning the amount owed increases as time passes. Amortization is the process of repaying a loan over time through scheduled payments that include both principal and interest. Understanding these concepts is crucial for accurately calculating total loan costs and developing an effective repayment plan.
2. Types of Student Loans and Interest Rates:
Student loans are broadly categorized into federal and private loans.
-
Federal Student Loans: These loans are offered by the U.S. government and typically have fixed interest rates, meaning the rate remains the same for the life of the loan. Interest rates for federal student loans are set annually by Congress and are generally lower than private loan rates. Several types exist, including subsidized and unsubsidized loans, which differ in terms of interest accrual during the grace period (the period after graduation before repayment begins). Federal loans often come with borrower protections, such as income-driven repayment plans and loan forgiveness programs for specific professions.
-
Private Student Loans: These loans are offered by banks, credit unions, and other private lenders. Private loan interest rates are variable, meaning they can fluctuate based on market conditions, or fixed, depending on the loan terms. Interest rates are generally higher than federal loan rates and are determined based on the borrower’s creditworthiness, income, and the loan's terms. While private loans can offer flexibility, they often lack the borrower protections of federal loans.
3. Factors Influencing Interest Rates:
Several factors contribute to the determination of student loan interest rates:
- Credit Score: For private loans, a higher credit score generally results in a lower interest rate. Lenders view a good credit score as an indicator of responsible financial behavior, making borrowers less risky.
- Loan Type: Federal student loans usually have lower interest rates than private loans due to government backing. The type of federal loan (e.g., subsidized vs. unsubsidized) can also impact the interest rate.
- Market Conditions: Interest rates are influenced by broader economic factors such as inflation and central bank policies. Higher inflation often leads to higher interest rates.
- Loan Term: Longer loan terms typically result in lower monthly payments but higher total interest paid over the life of the loan. Shorter terms lead to higher monthly payments but less overall interest.
- Co-signer: Having a co-signer with good credit can help secure a lower interest rate, particularly for borrowers with limited or poor credit history.
4. Strategies for Securing Lower Interest Rates:
Securing a lower student loan interest rate can significantly reduce the overall cost of borrowing. Strategies include:
- Maintain a Good Credit Score: Before applying for private student loans, work towards improving your credit score by paying bills on time, keeping credit utilization low, and avoiding new credit applications.
- Explore Federal Loan Options First: Federal student loans generally have lower interest rates and more borrower protections than private loans. Maximize your eligibility for federal loans before considering private options.
- Shop Around for Private Loans: Compare interest rates and terms from multiple private lenders to find the best deal.
- Consider a Co-signer: If your credit score is low, having a co-signer with a good credit history can significantly improve your chances of securing a lower interest rate.
- Negotiate with Lenders: Don't be afraid to negotiate with lenders for a lower interest rate. Highlight your positive financial history and responsible borrowing behavior.
5. Managing Student Loan Debt Effectively:
Once you've secured your loans, effective management is crucial. This includes:
- Understanding Your Repayment Options: Familiarize yourself with various repayment plans, including standard, graduated, extended, and income-driven repayment options. Choose a plan that fits your budget and financial goals.
- Making Timely Payments: Making on-time payments helps build a positive credit history and avoids late payment fees and penalties.
- Exploring Refinancing Options: Refinancing your student loans can potentially lower your interest rate, resulting in significant long-term savings. However, carefully compare offers before refinancing, as some options might have limitations.
- Considering Loan Consolidation: Combining multiple student loans into a single loan can simplify repayment and potentially lower your monthly payments. However, consolidation may also lead to a higher overall interest paid.
Closing Insights: Summarizing the Core Discussion
Understanding student loan interest rates is paramount for navigating the complexities of higher education financing. By carefully considering the various loan options, understanding the factors influencing interest rates, and implementing effective management strategies, borrowers can minimize their debt burden and pave the way for a brighter financial future.
Exploring the Connection Between Credit Score and Student Loan Interest Rates
The relationship between credit score and student loan interest rates, especially for private loans, is direct and significant. A higher credit score acts as a strong indicator of a borrower's financial responsibility to lenders. This perception translates into lower interest rates, reducing the overall cost of borrowing. Conversely, a lower credit score can lead to significantly higher interest rates, increasing the total cost of repayment.
Key Factors to Consider:
-
Roles and Real-World Examples: A borrower with a credit score of 750 might qualify for a private student loan with an interest rate of 6%, while a borrower with a 600 credit score might face an interest rate of 12% or higher, dramatically increasing the total amount they’ll repay.
-
Risks and Mitigations: Borrowers with low credit scores face the risk of higher interest rates, increased overall loan costs, and potentially difficulty securing a loan without a co-signer. Mitigation strategies include improving their credit scores before applying for loans, exploring federal loan options first, and seeking a co-signer.
-
Impact and Implications: The long-term impact of a high interest rate due to a poor credit score can be substantial, potentially delaying significant financial milestones and impacting overall financial well-being. The difference in interest rates can accumulate to tens of thousands of dollars over the life of the loan.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
The strong correlation between credit score and student loan interest rates underscores the importance of responsible financial management. By actively working to improve their credit scores, borrowers can significantly reduce their borrowing costs and secure more favorable loan terms.
Further Analysis: Examining Credit Score in Greater Detail
Credit scores are calculated based on several factors, including payment history, amounts owed, length of credit history, credit mix, and new credit. Improving a credit score takes time and effort but involves consistently demonstrating responsible financial behavior. Strategies include paying bills on time, maintaining low credit utilization, and avoiding unnecessary credit applications.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Student Loan Interest Rates
-
What is a student loan interest rate? A student loan interest rate is the annual percentage charged on the amount borrowed.
-
How are student loan interest rates determined? Factors include credit score (for private loans), loan type, market conditions, and loan term.
-
What are the different types of student loans? Federal and private student loans exist, with varying interest rates and repayment options.
-
How can I get a lower interest rate on my student loans? Maintain a good credit score, explore federal loans, shop around for private loans, consider a co-signer, and negotiate with lenders.
-
What happens if I don't make my student loan payments? Failure to make payments can lead to delinquency, damage to your credit score, and potential legal action.
-
Can I refinance my student loans? Yes, refinancing can potentially lower your interest rate, but it's crucial to compare offers and understand the terms.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Understanding Student Loan Interest Rates
-
Understand the Basics: Thoroughly research and understand the different types of student loans and the factors that influence their interest rates.
-
Check Your Credit Score: Monitor your credit score regularly and take steps to improve it if necessary.
-
Compare Loan Offers: Shop around for loans and compare interest rates, terms, and fees before making a decision.
-
Create a Realistic Repayment Plan: Develop a budget and create a repayment plan that aligns with your financial capabilities.
-
Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date on changes in interest rates and repayment options.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
Understanding student loan interest rates is not just about numbers; it’s about financial empowerment. By acquiring this knowledge and employing the strategies outlined above, students and graduates can make informed decisions, minimize their debt burden, and pave the way for a more secure and prosperous financial future. The impact of informed choices about student loan interest rates can reverberate throughout a borrower's life, affecting major financial decisions and overall well-being.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Index Hugger Definition
Apr 24, 2025
-
What Are Index Futures Definition Types And How To Profit
Apr 24, 2025
-
Index Etf Definition Types Advantages And Risks
Apr 24, 2025
-
Index Amortizing Swap Ias Definition
Apr 24, 2025
-
Index Amortizing Note Ian Definition
Apr 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Student Loan Interest Rate . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.