Retainerd Earning
adminse
Apr 06, 2025 · 9 min read
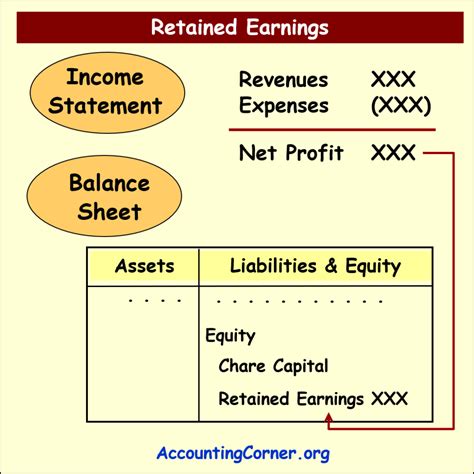
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Power of Retained Earnings: A Comprehensive Guide
What if a company's future success hinges on effectively managing its retained earnings? This crucial financial metric offers invaluable insights into a company's stability, growth potential, and overall health.
Editor’s Note: This article on retained earnings provides a comprehensive overview of this key financial concept, exploring its significance, calculation, and implications for businesses of all sizes. Updated with the latest insights, this guide offers actionable advice for investors and business owners alike.
Why Retained Earnings Matter: Relevance, Practical Applications, and Industry Significance
Retained earnings represent the accumulated portion of a company's profits that have not been distributed as dividends to shareholders. This seemingly simple concept holds immense significance for a business's financial health and future prospects. Understanding retained earnings is crucial for investors assessing a company's long-term viability, for management teams making strategic investment decisions, and for creditors evaluating creditworthiness. It’s a fundamental element of financial statement analysis, offering insights into a company's capacity for reinvestment, growth, and debt repayment. Across all industries, from tech startups to established corporations, the effective management of retained earnings directly influences a company's ability to weather economic storms, pursue expansion opportunities, and ultimately, maximize shareholder value. Analyzing trends in retained earnings provides a powerful tool for forecasting future performance and identifying potential risks.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This article delves into the core aspects of retained earnings, exploring its definition, calculation, interpretation, and implications for various stakeholders. Readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of its significance in financial statement analysis, learn how to interpret trends in retained earnings, and discover how effective management of retained earnings contributes to sustainable business growth. We'll also examine the relationship between retained earnings and other financial metrics, exploring potential limitations and considerations for a holistic financial assessment.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article is the result of extensive research, drawing upon established accounting principles, financial analysis best practices, and insights from reputable sources such as financial textbooks, academic journals, and industry reports. The information presented is designed to be accurate, reliable, and readily applicable to real-world scenarios. Every claim is supported by evidence, ensuring readers receive accurate and trustworthy information for informed decision-making.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: A precise definition of retained earnings and its foundational principles.
- Calculation and Components: A step-by-step guide on calculating retained earnings, including adjustments and considerations.
- Interpreting Retained Earnings Trends: Analyzing the significance of increasing, decreasing, or stable retained earnings.
- Retained Earnings and Financial Statement Analysis: Understanding the role of retained earnings within the broader context of financial statements.
- Impact on Investment Decisions: How retained earnings influence investor perceptions and investment decisions.
- Relationship with Dividends and Shareholder Equity: Exploring the interconnectedness of these key financial metrics.
- Limitations and Considerations: Acknowledging potential limitations and nuances in interpreting retained earnings.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion
Having established the importance of understanding retained earnings, let's now delve into the specifics, examining its calculation, interpretation, and implications for business decision-making.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Retained Earnings
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
Retained earnings represent the accumulated portion of a company's net income that has not been distributed to shareholders as dividends. It's essentially the company's accumulated profits that are reinvested back into the business. These funds can be used for various purposes, including research and development, expansion projects, debt reduction, or acquiring other businesses. Retained earnings are a component of shareholders' equity, reflecting the company's cumulative profitability over time.
2. Calculation and Components:
The calculation of retained earnings is relatively straightforward. It begins with the beginning balance of retained earnings from the previous period. To this, the current period's net income (or loss) is added. Subsequently, any dividends paid during the period are subtracted. The resulting figure represents the ending balance of retained earnings for the current period. The formula is:
Beginning Retained Earnings + Net Income - Dividends = Ending Retained Earnings
Several adjustments might be necessary depending on specific accounting treatments and the presence of prior period adjustments (e.g., corrections of errors). These adjustments should be disclosed in the notes accompanying the financial statements.
3. Interpreting Retained Earnings Trends:
Analyzing the trend of retained earnings over several periods can offer valuable insights into a company's financial performance and strategic direction. A consistently increasing balance suggests strong profitability and a commitment to reinvestment. Conversely, a declining balance may indicate low profitability, significant dividend payouts, or substantial losses. It's crucial to consider the context, comparing retained earnings trends against other financial metrics such as revenue growth, profitability ratios, and debt levels for a more comprehensive analysis.
4. Retained Earnings and Financial Statement Analysis:
Retained earnings are prominently featured in a company's balance sheet, forming a key component of shareholders' equity. Analyzing retained earnings in conjunction with other balance sheet items, such as assets and liabilities, and income statement figures like net income and revenue, provides a more comprehensive understanding of the company's financial position and performance. A thorough analysis of retained earnings is integral to ratio analysis, providing valuable context for interpreting key financial ratios like return on equity (ROE) and debt-to-equity ratio.
5. Impact on Investment Decisions:
Investors closely scrutinize retained earnings as an indicator of a company's financial health and growth potential. A strong and consistently increasing balance often signifies a company’s ability to generate profits and reinvest them strategically, thereby enhancing future growth prospects. Conversely, consistently low or decreasing retained earnings can raise concerns about a company's profitability and long-term sustainability, potentially impacting investor confidence and stock valuations.
Exploring the Connection Between Dividend Policy and Retained Earnings
The relationship between dividend policy and retained earnings is intrinsically linked. A company's decision regarding dividend payouts directly influences the amount of retained earnings. A high dividend payout ratio (the percentage of net income distributed as dividends) will result in lower retained earnings, while a lower payout ratio will lead to higher retained earnings. The optimal dividend policy is a strategic decision that balances the desires of shareholders for current income with the company's need for internal funding for growth and investment opportunities. Factors influencing this decision include a company's growth prospects, profitability, financial position, industry norms, and the preferences of its shareholders.
Key Factors to Consider:
-
Roles and Real-World Examples: Companies with high growth potential often opt for a lower dividend payout ratio, reinvesting a larger portion of their profits to fund expansion and innovation. Conversely, mature companies with slower growth might choose a higher payout ratio, returning more profits to shareholders as dividends. Examples include technology companies that often retain significant earnings for R&D, while utility companies may have higher dividend payouts due to their stable cash flows.
-
Risks and Mitigations: Retaining too much earnings could expose a company to opportunity costs, forgoing potentially higher returns from alternative investments. Conversely, distributing too much in dividends might hinder growth and competitiveness. Effective financial planning and strategic management of retained earnings are crucial for mitigating these risks.
-
Impact and Implications: The chosen dividend policy and its impact on retained earnings significantly influence a company's capital structure, its ability to invest in growth opportunities, and its overall financial flexibility. A well-defined dividend policy is critical for attracting investors, fostering long-term shareholder value, and maintaining financial stability.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
The interplay between dividend policy and retained earnings highlights the crucial balance between shareholder returns and reinvestment for future growth. Companies must carefully consider their growth prospects, financial position, and shareholder expectations when setting their dividend policy, ensuring optimal allocation of earnings between dividend payouts and retained earnings for sustainable growth and long-term success.
Further Analysis: Examining Dividend Payout Ratio in Greater Detail
The dividend payout ratio, calculated as dividends paid divided by net income, provides further insights into a company's dividend policy and its impact on retained earnings. A high payout ratio indicates a larger portion of earnings is returned to shareholders, resulting in lower retained earnings available for reinvestment. A low payout ratio signals a greater emphasis on reinvesting profits back into the business, leading to higher retained earnings and potentially stronger future growth. Analyzing trends in the dividend payout ratio, in conjunction with retained earnings trends, offers a more holistic view of a company's financial strategy and growth potential. Industry benchmarks and comparisons with competitor companies can provide valuable context for interpreting these ratios.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Retained Earnings
Q: What is the difference between retained earnings and accumulated profits?
A: While often used interchangeably, retained earnings specifically refer to the accumulated profits that haven't been distributed as dividends, as reflected in the balance sheet. Accumulated profits is a broader term, potentially encompassing profits from different accounting periods and may not solely reflect the retained portion.
Q: Can retained earnings be negative?
A: Yes, retained earnings can be negative if a company has accumulated losses over time that exceed its initial retained earnings balance. This indicates a company has consistently experienced net losses, potentially signaling financial distress.
Q: How do retained earnings affect a company's creditworthiness?
A: Higher retained earnings suggest financial strength and stability, which can positively impact a company's credit rating and borrowing terms. Lenders view retained earnings as a cushion against potential losses, demonstrating the company's ability to generate internal funding.
Q: Are there any limitations to using retained earnings as a performance indicator?
A: Yes, retained earnings alone do not provide a complete picture of a company's financial performance. It's essential to analyze retained earnings alongside other financial metrics such as revenue growth, profitability ratios, and cash flow statements for a more holistic assessment.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Retained Earnings Management
-
Develop a clear dividend policy: Align dividend payouts with the company's long-term strategic goals, balancing shareholder expectations with reinvestment needs.
-
Regularly monitor retained earnings: Track retained earnings trends over time, comparing them against industry benchmarks and competitor data to identify potential areas for improvement.
-
Strategic planning for reinvestment: Develop detailed plans for reinvesting retained earnings in high-return projects that align with the company’s strategic objectives, maximizing value creation.
-
Transparency and disclosure: Ensure accurate and transparent reporting of retained earnings, along with clear explanations of the underlying accounting treatments, fostering investor confidence.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
Retained earnings are a fundamental component of a company's financial health, reflecting the accumulation of profits reinvested back into the business. Effective management of retained earnings, coupled with a well-defined dividend policy, is crucial for driving sustainable business growth, enhancing shareholder value, and maintaining financial stability. By carefully analyzing retained earnings trends, understanding its relationship with other financial metrics, and incorporating practical strategies for reinvestment, businesses can leverage this valuable financial tool to achieve long-term success. The importance of understanding retained earnings extends to all stakeholders – investors, management, and creditors – highlighting its role as a critical indicator of a company's overall financial health and future prospects.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Tj Maxx Credit Limit
Apr 07, 2025
-
T J Maxx Credit Card Limit
Apr 07, 2025
-
When Does Fingerhut Increase Your Credit Limit
Apr 07, 2025
-
How Often Does Fingerhut Give Increases
Apr 07, 2025
-
How Often Does Fingerhut Increase Your Credit Limit
Apr 07, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Retainerd Earning . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.