Is There A Grace Period For Filing Taxes
adminse
Apr 02, 2025 · 8 min read
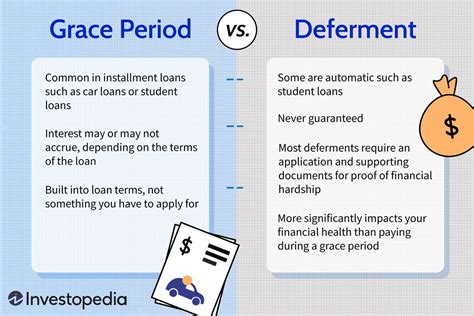
Table of Contents
Is there a grace period for filing taxes, and what happens if you miss it?
Missing the tax deadline can have serious consequences, but understanding the rules and available options can help mitigate potential penalties.
Editor’s Note: This article on tax filing grace periods was published [Date] and provides up-to-date information on the subject. However, tax laws are complex and subject to change. It's crucial to consult with a qualified tax professional for personalized advice.
Why Tax Filing Deadlines Matter: Relevance, Practical Applications, and Industry Significance
Tax deadlines are not arbitrary; they are critical for the smooth functioning of a nation's economy. The timely filing of tax returns allows governments to accurately project revenue, fund essential public services, and maintain financial stability. For individuals and businesses, meeting these deadlines is crucial for avoiding penalties, maintaining a positive credit history, and preventing potential legal repercussions. The timely submission of tax information also allows for efficient processing of refunds and credits, ensuring taxpayers receive the money they are owed promptly. The consequences of missing these deadlines can range from financial penalties and interest charges to legal action in extreme cases.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This article explores the concept of a "grace period" for tax filing, clarifying misconceptions and providing a comprehensive overview of the rules and regulations surrounding tax deadlines. It delves into the various situations where extensions might be granted, the penalties for late filing and late payment, and steps taxpayers can take to avoid or mitigate these consequences. We will examine the differences in regulations for various types of taxes and explore resources available to taxpayers who need assistance.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article is the result of extensive research, drawing from official IRS publications, legal documents, and reputable financial sources. The information presented reflects the current tax laws and regulations in the United States. Every effort has been made to ensure accuracy and provide readers with trustworthy and reliable information. However, due to the complexity of tax law, individual situations may vary, and professional consultation is always recommended.
Key Takeaways: Summarize the Most Essential Insights
- Definition of Tax Filing Deadlines: Understanding the specific dates for various tax forms.
- Automatic Extensions vs. Granted Extensions: The difference between automatic extensions for filing and the requirements for obtaining extensions for paying taxes.
- Penalties for Late Filing and Late Payment: A detailed breakdown of potential penalties and interest charges.
- Situations Warranting Extensions: Exploring specific circumstances that may qualify for an extension.
- Resources for Taxpayers: Identifying available support and assistance options.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion
While the term "grace period" might be colloquially used, it's crucial to understand that there isn't a universally defined grace period for filing taxes. Instead, the system offers avenues for extensions and considers various factors when assessing penalties. Let's examine these aspects in detail.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Tax Filing Deadlines
Definition and Core Concepts: The primary tax filing deadline in the United States is typically April 15th. However, this date may shift if the 15th falls on a weekend or holiday. Different tax forms have different deadlines, and certain individuals and businesses may qualify for automatic extensions. These extensions typically provide more time to file the tax return, not necessarily more time to pay the taxes owed. The distinction is crucial.
Applications Across Industries: The tax filing deadlines apply across all industries, encompassing individuals, small businesses, corporations, and non-profit organizations. Each entity has specific requirements and forms to complete, but the fundamental principle of timely filing remains consistent. Failure to comply can lead to significant penalties irrespective of the industry.
Challenges and Solutions: A common challenge is misunderstanding the tax laws and deadlines. Taxpayers often struggle to navigate the complex regulations, leading to missed deadlines or inaccurate filings. Solutions include utilizing IRS resources, seeking professional tax advice, and utilizing tax preparation software. Proactive planning, diligent record-keeping, and seeking assistance when needed are crucial in avoiding problems.
Impact on Innovation: While not directly impacting technological innovation, the timely filing of taxes facilitates the smooth flow of capital in the economy, indirectly supporting innovation by ensuring adequate funding for research and development, public infrastructure, and other initiatives.
Closing Insights: Summarizing the Core Discussion
Tax deadlines are not merely administrative requirements; they are the foundation of a stable tax system. Understanding the rules, seeking help when needed, and prioritizing timely filing are essential for individuals and businesses alike. Failure to comply can have severe financial and legal ramifications.
Exploring the Connection Between Automatic Extensions and Tax Filing Deadlines
The IRS offers an automatic extension for filing individual income tax returns (Form 1040). This extension typically grants taxpayers an additional six months – until October 15th – to file their return. However, it's crucial to understand that this extension only applies to filing the return; it does not extend the deadline for paying taxes owed. Taxes are still due on April 15th (or the adjusted date if it falls on a weekend or holiday). Failure to pay by the original deadline will result in penalties and interest, even if a filing extension has been granted.
Key Factors to Consider
Roles and Real-World Examples: Many taxpayers use the automatic extension to avoid last-minute rush and ensure accuracy in their filings. However, it's crucial to remember that interest and penalties accrue on unpaid taxes. A real-world example is a self-employed individual who needs more time to gather all necessary documents for accurate reporting. They file for an extension, but still make estimated tax payments to avoid penalties.
Risks and Mitigations: The primary risk associated with the automatic extension is the misconception that it extends the payment deadline as well. Mitigation involves clearly understanding the distinction between filing and payment deadlines and proactively planning for tax payments, even if filing is extended. Using tax preparation software or consulting a tax professional can help avoid this pitfall.
Impact and Implications: The automatic extension aims to reduce the burden on taxpayers and allow for more accurate filing. However, the failure to pay taxes on time, even with an extension, can significantly impact taxpayers' financial health through penalties and interest. This underscores the importance of responsible financial planning and tax management.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
The automatic extension for filing is a valuable tool for taxpayers, but it’s vital to understand its limitations. Failing to pay taxes on time, even with an extended filing deadline, will lead to penalties. Responsible financial planning and a clear understanding of tax laws are essential to avoid negative consequences.
Further Analysis: Examining Penalties for Late Filing and Payment in Greater Detail
The IRS imposes penalties for both late filing and late payment. Penalties for late filing are typically calculated as a percentage of the unpaid taxes, increasing over time. Late payment penalties also accrue interest on the unpaid amount. The exact percentages and calculation methods vary depending on the length of the delay and the taxpayer's circumstances. There are exceptions for taxpayers who can demonstrate reasonable cause for the delay, but this requires substantial documentation and justification.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Tax Filing Deadlines
What is the deadline for filing my taxes? The usual deadline for filing individual income tax returns is April 15th, but this may change depending on the day of the week.
What happens if I miss the tax filing deadline? You will be subject to penalties for late filing, calculated as a percentage of the unpaid taxes. Late payment penalties also apply.
Can I get an extension to file my taxes? Yes, you can request an automatic six-month extension for filing, but this does not extend the deadline for paying your taxes.
How do I request an extension? You can usually file Form 4868 for an automatic extension.
What are the penalties for late payment? Late payment penalties involve interest charges on the unpaid tax balance.
What constitutes reasonable cause for late filing? Reasonable cause is determined on a case-by-case basis and requires substantial documentation justifying the delay. Examples could include a serious illness or a natural disaster.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Understanding Tax Deadlines
- Mark the Deadline: Use a calendar reminder or set alerts to ensure you don't miss the deadline.
- Gather Documents Early: Start collecting all necessary documents well in advance of the tax season.
- Use Tax Software or Hire a Professional: Utilize tax preparation software or consult a tax professional to ensure accuracy and avoid errors.
- Plan for Tax Payments: Even if you obtain a filing extension, pay your taxes on time to avoid penalties.
- Understand Your Tax Obligations: Familiarize yourself with the tax laws that apply to your specific circumstances.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
While there is no formal “grace period” for filing taxes, the IRS provides mechanisms for extensions to mitigate the impact of unforeseen circumstances. However, these extensions only address the filing aspect; paying taxes on time remains a critical responsibility. Understanding the complexities of tax deadlines and proactively managing tax obligations is crucial for every taxpayer. Proactive planning, diligent record-keeping, and seeking professional advice when necessary are key to avoiding penalties and ensuring compliance with tax laws.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Penalty For Late Payment Of Electricity Bill In Ap
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Penalty For Late Payment Of Electricity Bill In Up
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Penalty For Late Electricity Bill Payment
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Grace Period For Electric Bill
Apr 04, 2025
-
Apa Itu Liquidity Pool
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is There A Grace Period For Filing Taxes . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.