How To Take Out A Private Student Loan
adminse
Mar 28, 2025 · 8 min read
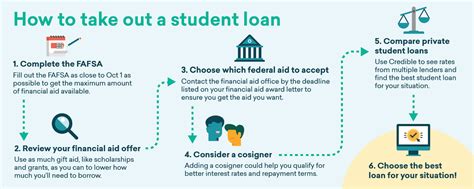
Table of Contents
Unlocking Educational Opportunities: Your Guide to Navigating Private Student Loans
Is securing a private student loan the right choice for your higher education journey? Understanding the intricacies of private student loans empowers you to make informed decisions and achieve your academic aspirations.
Editor’s Note: This comprehensive guide to private student loans was updated today to reflect current lending practices and regulations. We aim to provide readers with the most up-to-date and accurate information available.
Why Private Student Loans Matter: Relevance, Practical Applications, and Industry Significance
Private student loans serve as a crucial financial tool for many aspiring students, filling the gap left by federal aid. They provide access to higher education for individuals who may not qualify for or receive sufficient federal funding. The impact extends beyond individual students, affecting the overall economy by supporting educational attainment and future workforce contributions. Understanding the intricacies of these loans is vital for responsible borrowing and long-term financial well-being.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This article delves into the complexities of private student loans, offering a step-by-step guide to the application process. We’ll explore eligibility criteria, interest rates, repayment options, and the importance of comparing lenders. Readers will gain the knowledge to navigate this financial landscape effectively and make well-informed borrowing decisions.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article is the product of extensive research, drawing on information from reputable sources such as the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), the Federal Reserve, and leading financial institutions specializing in student lending. Data analysis and expert insights ensure that the information provided is accurate, reliable, and relevant to the current lending environment.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding Eligibility: Learn the factors lenders consider when assessing loan applications.
- Interest Rates and Fees: Decipher the complexities of interest rates, fees, and their impact on repayment.
- The Application Process: Follow a step-by-step guide to submitting a successful loan application.
- Choosing the Right Lender: Compare lenders and select the option that best suits your financial needs.
- Repayment Strategies: Explore different repayment plans and strategies to manage your debt effectively.
- Avoiding Loan Traps: Learn to identify potential pitfalls and make responsible borrowing choices.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
With a foundation laid on the significance of private student loans, let's proceed to a detailed examination of the process, from determining eligibility to securing the best loan terms.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Obtaining a Private Student Loan
1. Determining Your Eligibility:
Before embarking on the loan application process, assessing your eligibility is paramount. Lenders typically examine several key factors:
- Credit History: A strong credit history significantly improves your chances of approval and securing favorable interest rates. Those with limited or poor credit might face higher rates or even rejection. Co-signers can often mitigate this risk.
- Income: Lenders assess your income to gauge your ability to repay the loan. A stable income stream increases your eligibility and prospects for favorable terms.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio: The ratio of your existing debt to your income is a critical factor. A high debt-to-income ratio may reduce your chances of approval.
- Enrollment Status: Proof of enrollment in an eligible educational program is mandatory.
- School Accreditation: Lenders often require that your chosen institution be accredited.
2. Understanding Interest Rates and Fees:
Private student loan interest rates are variable, meaning they fluctuate based on market conditions. They are typically higher than federal student loan rates. Understanding the interest rate type (fixed or variable) is critical for long-term financial planning. Additionally, lenders charge various fees, including origination fees, late payment fees, and potentially prepayment penalties. These fees can add significantly to the overall cost of borrowing.
3. The Application Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
The application process for a private student loan typically involves these steps:
- Research and Compare Lenders: Begin by comparing offers from multiple lenders to find the best rates and terms.
- Pre-qualification: Many lenders offer pre-qualification, allowing you to check your eligibility without impacting your credit score.
- Complete the Application: Once you've chosen a lender, fill out the online application, providing accurate and complete information.
- Provide Documentation: You'll likely need to provide supporting documents such as proof of enrollment, transcripts, and tax returns.
- Credit Check: The lender will perform a credit check to assess your creditworthiness.
- Loan Approval and Disbursement: Upon approval, the funds will be disbursed directly to your educational institution or to you (depending on the lender's policy).
4. Choosing the Right Lender:
Selecting the appropriate lender is crucial. Consider these factors:
- Interest Rates: Compare interest rates across different lenders.
- Fees: Examine the various fees associated with each loan.
- Repayment Options: Evaluate the available repayment plans and their flexibility.
- Customer Service: Choose a lender with a reputation for excellent customer service and responsiveness.
- Financial Stability: Ensure the lender is financially sound and reputable.
5. Repayment Strategies and Debt Management:
Once your education is complete, understanding your repayment options is paramount. Common repayment plans include:
- Standard Repayment: Fixed monthly payments over a set period.
- Graduated Repayment: Payments start low and gradually increase.
- Extended Repayment: Longer repayment period, resulting in lower monthly payments but higher overall interest.
- Income-Driven Repayment (IDR): Some private lenders offer IDR plans, though they are less common than with federal loans. These plans adjust your monthly payment based on your income.
6. Avoiding Loan Traps: Responsible Borrowing Practices
Avoid falling into potential traps by practicing responsible borrowing:
- Borrow Only What You Need: Avoid taking out more than you need for tuition, fees, and living expenses.
- Understand the Terms: Carefully read and understand all loan documents before signing.
- Budget Effectively: Create a realistic budget to manage your loan repayments.
- Monitor Your Credit Score: Regularly check your credit score and report any errors.
- Seek Financial Counseling: If you're struggling to manage your loan repayments, seek professional financial counseling.
Exploring the Connection Between Credit Scores and Private Student Loans
Credit scores play a pivotal role in determining eligibility and securing favorable loan terms for private student loans. A higher credit score often translates to lower interest rates and improved chances of approval. Individuals with poor credit might require a co-signer to qualify. Understanding your credit score is crucial for optimizing your chances of securing a favorable loan.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Roles and Real-World Examples: A high credit score (700 or above) typically leads to the lowest interest rates, whereas a low score (below 600) can result in significantly higher rates or rejection.
- Risks and Mitigations: Individuals with poor credit can mitigate the risk by improving their credit score before applying or finding a co-signer with good credit.
- Impact and Implications: A strong credit score significantly reduces the overall cost of borrowing, while a poor score can lead to substantial additional costs over the loan's life.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
The inextricable link between credit scores and private student loans underscores the importance of responsible financial management. By maintaining a strong credit history, individuals can improve their chances of securing favorable loan terms and minimize the overall cost of their education.
Further Analysis: Examining Credit Repair in Greater Detail
Improving a poor credit score takes time and effort, but it's possible. Strategies include:
- Paying Bills on Time: Consistent on-time payments are crucial for building credit.
- Reducing Debt: Lowering your debt-to-income ratio strengthens your credit profile.
- Monitoring Your Credit Report: Regularly review your credit report for errors and inaccuracies.
- Utilizing Credit-Builder Tools: Consider credit-builder loans or secured credit cards to improve your credit history.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Private Student Loans
-
Q: What is a private student loan?
- A: A private student loan is a loan from a private lender, such as a bank or credit union, used to finance education expenses. Unlike federal student loans, they are not backed by the government.
-
Q: How do private student loans differ from federal student loans?
- A: Private loans have variable interest rates, often higher than federal loans. They may also have stricter eligibility requirements and fewer repayment options.
-
Q: What if I don't qualify for a private student loan?
- A: Explore alternative financing options, such as scholarships, grants, or work-study programs. Consider improving your credit score before reapplying.
-
Q: What happens if I default on a private student loan?
- A: Defaulting on a private student loan can severely damage your credit score and potentially lead to legal action from the lender.
-
Q: Can I refinance my private student loan?
- A: Yes, refinancing can potentially lower your interest rate and monthly payments. However, be sure to compare offers carefully.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Private Student Loans
- Shop Around: Compare offers from multiple lenders before making a decision.
- Understand the Terms: Thoroughly review the loan agreement before signing.
- Budget Wisely: Create a budget to manage your loan repayments effectively.
- Consider a Co-signer: If you have poor credit, a co-signer can improve your chances of approval.
- Explore Repayment Options: Understand your available repayment plans and choose one that fits your financial situation.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
Securing a private student loan can be a complex process, but with careful planning and a thorough understanding of the involved factors, it can provide the necessary financial resources to achieve educational goals. Responsible borrowing practices, diligent research, and proactive debt management are key to maximizing the benefits and minimizing the potential risks associated with private student loans. Remember that securing a loan is only the first step; careful planning for repayment and responsible financial management throughout the loan repayment period are crucial.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Irs Publication 516 Definition
Apr 25, 2025
-
Irs Publication 503 Child And Dependent Care Expenses Definition
Apr 25, 2025
-
Irs Publication 509 Tax Calendars Definition
Apr 25, 2025
-
Irs Publication 501 Definition
Apr 25, 2025
-
Irs Publication 5 Definition
Apr 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Take Out A Private Student Loan . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.