How Does Mobile Pay Work
adminse
Apr 06, 2025 · 9 min read
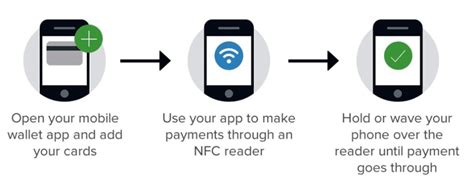
Table of Contents
Unlocking the Mobile Wallet: How Mobile Pay Works
What if the future of commerce is entirely cashless and frictionless? Mobile payment systems are rapidly transforming how we transact, offering unparalleled convenience and security.
Editor’s Note: This article on how mobile pay works was published today, providing readers with up-to-date information on this rapidly evolving technology. We’ve examined the technical aspects, security measures, and future trends to give you a comprehensive understanding.
Why Mobile Pay Matters:
Mobile payment systems are revolutionizing the way businesses and consumers conduct transactions. From the everyday coffee purchase to large online purchases, the speed, convenience, and often enhanced security offered by mobile pay are driving its widespread adoption. Its influence spans various sectors, including retail, hospitality, transportation, and even charitable giving. Understanding how mobile pay works is crucial for anyone navigating the modern digital economy. This technology impacts not only individual consumers but also shapes business strategies, influences financial innovation, and has implications for data privacy and security.
Overview: What This Article Covers:
This article delves into the core mechanics of mobile payment systems, covering their technological underpinnings, security protocols, different payment methods, and the various players involved in the ecosystem. We'll explore the benefits and challenges, examining real-world applications and future trends in mobile payments.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights:
This comprehensive analysis incorporates research from reputable sources, including industry reports from companies like Gartner and Forrester, technical white papers from leading payment processors, and news articles from trusted financial publications. The information presented is based on a structured approach, ensuring accuracy and providing readers with reliable and current insights.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: Understanding the fundamental principles of mobile payment technologies, including NFC, QR codes, and online payment gateways.
- Types of Mobile Payment Systems: Exploring the various systems available, such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, Samsung Pay, and others. Comparing their features, benefits, and limitations.
- The Technology Behind the Transaction: A deep dive into the technical processes involved in a mobile payment, from tokenization to authentication.
- Security Measures: Analyzing the security protocols implemented to protect user data and prevent fraud.
- Challenges and Future Trends: Examining current limitations and exploring potential future developments in the field of mobile payment.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
With a grasp of the overall importance of mobile payment, let's explore its inner workings in detail.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Mobile Pay:
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
Mobile payment, or mobile pay, refers to the use of mobile devices like smartphones and smartwatches to make electronic payments. This differs from traditional methods such as cash, checks, or credit/debit cards, leveraging technology to process transactions securely and efficiently. Several core concepts underpin these systems:
- Near Field Communication (NFC): NFC is a short-range wireless technology enabling communication between two devices in close proximity. Many mobile payment systems utilize NFC to transmit payment information to a point-of-sale (POS) terminal. The user simply holds their phone near the terminal to complete the transaction.
- QR Codes: Quick Response (QR) codes are two-dimensional barcodes that can store information, including payment details. Scannable by a smartphone camera, they facilitate payments by linking to a payment processor. This method is particularly popular in regions where NFC adoption is lower.
- Online Payment Gateways: For online purchases, mobile pay often relies on secure online payment gateways. These act as intermediaries, encrypting payment information and securely transmitting it between the buyer, seller, and payment processor. Examples include PayPal, Stripe, and Square.
- Tokenization: To enhance security, mobile pay utilizes tokenization. This replaces sensitive payment information (card number, expiry date, CVV) with a unique token. The token is used for transactions, while the actual card details remain securely stored on a server. This minimizes the risk of data breaches.
2. Types of Mobile Payment Systems:
The mobile payment landscape is diverse, with several prominent players offering distinct services:
- Apple Pay: A proprietary mobile payment system developed by Apple, integrated into iPhones, iPads, and Apple Watches. It utilizes NFC technology and is linked to credit, debit, and prepaid cards.
- Google Pay: Developed by Google, Google Pay is compatible with a wide range of Android devices and offers similar functionality to Apple Pay, supporting NFC payments and online transactions.
- Samsung Pay: Samsung's mobile payment platform, also NFC-based, works with Samsung Galaxy devices and boasts compatibility with a broader range of POS terminals than Apple Pay.
- PayPal: While not strictly a mobile-only system, PayPal is a widely used online payment platform accessible through mobile apps. It offers peer-to-peer payments, online shopping capabilities, and integration with various merchant services.
- Venmo: A popular peer-to-peer payment app owned by PayPal, Venmo allows users to easily send and request money from friends and family.
3. The Technology Behind the Transaction:
A typical mobile payment transaction unfolds as follows:
- Initiation: The user selects the mobile payment option at the checkout.
- Authentication: The user authenticates the transaction, typically through biometric verification (fingerprint, facial recognition) or a PIN.
- Tokenization: The payment system replaces the actual card details with a unique token.
- Transmission: The token is transmitted wirelessly (via NFC) or through a secure online connection.
- Authorization: The payment processor verifies the transaction with the issuing bank.
- Confirmation: The user receives confirmation of the successful transaction.
4. Security Measures:
Security is paramount in mobile payments. Several measures are implemented to mitigate risks:
- Encryption: All data transmitted during a transaction is encrypted to prevent interception.
- Tokenization: As mentioned, tokenization significantly reduces the risk of data breaches.
- Biometric Authentication: Utilizing biometric methods like fingerprint or facial recognition adds an extra layer of security.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Many systems incorporate 2FA, requiring verification through a second method (e.g., a code sent to the user's email or phone).
- Fraud Detection: Payment processors employ sophisticated fraud detection algorithms to identify and prevent fraudulent transactions.
5. Challenges and Future Trends:
While mobile pay offers numerous benefits, challenges remain:
- Security Concerns: Despite robust security measures, vulnerabilities always exist. Cybersecurity threats continue to evolve, requiring constant vigilance.
- Infrastructure Limitations: The widespread adoption of mobile pay hinges on the availability of compatible POS terminals and reliable internet connectivity.
- Digital Literacy: Not everyone is comfortable with digital technologies, potentially hindering broader adoption.
- Interoperability: Lack of interoperability between different mobile payment systems can create friction for users.
Future trends suggest:
- Increased Integration: Mobile payments will become more seamlessly integrated into other aspects of our lives, such as loyalty programs and transit systems.
- Biometric Advancements: More advanced and secure biometric authentication methods will be implemented.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain's decentralized nature could enhance security and transparency in mobile payments.
- Expansion into Emerging Markets: Mobile pay will continue to expand into regions with limited access to traditional banking services.
Exploring the Connection Between Security and Mobile Pay:
The relationship between security and mobile pay is undeniably pivotal. Without robust security measures, the entire system would be vulnerable to fraud and data breaches, undermining consumer confidence and stifling adoption.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Roles and Real-World Examples: Security breaches in mobile payment systems, although rare, highlight the importance of robust security protocols. Companies like Apple and Google invest heavily in security research and development to protect user data.
- Risks and Mitigations: Potential risks include phishing attacks, malware infections, and compromised devices. Mitigation strategies include strong passwords, regular software updates, and caution when using public Wi-Fi.
- Impact and Implications: Security breaches can damage a company’s reputation, lead to financial losses, and erode consumer trust. Strong security is essential for the long-term success of mobile payment systems.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection:
The security of mobile payment systems is not just a technical challenge; it's the foundation upon which trust and widespread adoption are built. By continually investing in advanced security technologies and educating users about potential risks, the mobile payment industry can ensure a secure and reliable future for digital transactions.
Further Analysis: Examining Security Protocols in Greater Detail:
A deeper dive into security protocols reveals a multifaceted approach, including encryption algorithms like AES-256, secure tokenization methods, and real-time fraud detection systems. Understanding these protocols is crucial for appreciating the complexity and sophistication of modern mobile payment security. For example, analyzing the security architecture of Apple Pay reveals its reliance on a secure element within the device, protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Mobile Pay:
Q: What is mobile pay?
A: Mobile pay is a system that allows users to make electronic payments using their smartphones or other mobile devices.
Q: Is mobile pay safe?
A: Mobile payment systems employ various security measures, including encryption and tokenization, to protect user data and prevent fraud. However, users should still practice good security habits.
Q: What are the benefits of using mobile pay?
A: Mobile pay offers convenience, speed, and often enhanced security compared to traditional payment methods.
Q: How do I set up mobile pay?
A: The setup process varies depending on the specific system (Apple Pay, Google Pay, etc.). Generally, it involves linking your credit/debit cards to the mobile payment app.
Q: What if my phone is lost or stolen?
A: Most mobile payment systems offer ways to remotely disable the payment function on your lost or stolen device.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Mobile Pay:
- Choose a Reputable Provider: Opt for well-established mobile payment systems with a proven track record of security.
- Enable Biometric Authentication: Use fingerprint or facial recognition for added security.
- Keep Your Software Updated: Regularly update your device's operating system and payment apps.
- Be Cautious of Phishing Attempts: Avoid clicking on suspicious links or providing personal information to untrusted sources.
- Monitor Your Transactions: Regularly check your transaction history for any unauthorized activity.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights:
Mobile pay is transforming the way we transact, offering convenience, efficiency, and enhanced security. While challenges remain, the ongoing advancements in security and technology promise a future where mobile payments are seamlessly integrated into our daily lives, making commerce faster, safer, and more accessible than ever before. Understanding its mechanics and adhering to best security practices are crucial for harnessing the full potential of this revolutionary technology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Add Primary Tradelines To Your Credit Report
Apr 07, 2025
-
How To Add Tradelines To Your Credit Report Yourself
Apr 07, 2025
-
What Does Your Credit Score Need To Be For Chase Sapphire Reserve
Apr 07, 2025
-
What Credit Score Do You Need To Get A Chase Sapphire Reserve Card
Apr 07, 2025
-
What Credit Bureau Does Chase Sapphire Reserve Use
Apr 07, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Does Mobile Pay Work . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.