Decentralized Market Definition
adminse
Mar 25, 2025 · 8 min read
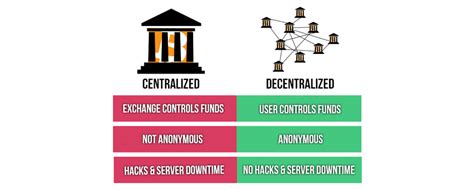
Table of Contents
Decentralized Market: A New Era of Exchange
What if the future of commerce relies on eliminating centralized control points? Decentralized markets, powered by blockchain technology and other innovative systems, are poised to revolutionize how we exchange goods, services, and value.
Editor’s Note: This article on decentralized markets provides a comprehensive overview of this rapidly evolving field, offering insights into its core principles, applications, challenges, and future implications. The information presented here reflects current understanding and is intended to be a valuable resource for anyone seeking to understand this transformative concept.
Why Decentralized Markets Matter:
Decentralized markets represent a fundamental shift away from traditional, centralized systems dominated by intermediaries like banks, payment processors, and marketplaces. These intermediaries often control access, charge fees, and exert significant influence over market dynamics. Decentralized markets aim to disintermediate these processes, offering several key advantages:
- Increased Transparency and Trust: Transactions are recorded on a public, immutable ledger (like a blockchain), enhancing transparency and accountability. This reduces the risk of fraud and manipulation.
- Enhanced Security: Decentralized systems are inherently more resistant to single points of failure and cyberattacks. The distributed nature of the network makes it harder for malicious actors to compromise the entire system.
- Greater Efficiency and Lower Costs: By removing intermediaries, decentralized markets can reduce transaction fees and processing times, making them more efficient and cost-effective.
- Improved Accessibility: Decentralized systems can provide access to markets for individuals and businesses who may be excluded from traditional financial systems due to geographical location, lack of credit history, or other factors.
- Increased Resilience: Decentralized markets are less vulnerable to censorship and regulatory capture, offering greater resilience against external pressures.
Overview: What This Article Covers:
This article explores the core concepts of decentralized markets, analyzing their underlying technologies, real-world applications, challenges, and future potential. We will examine different types of decentralized markets, discuss their impact on various industries, and investigate the key factors that will shape their future development. Readers will gain a clear understanding of this transformative concept and its implications for the future of commerce.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights:
This article is based on extensive research, drawing upon academic literature, industry reports, case studies, and analysis of existing decentralized market platforms. Information is cross-referenced to ensure accuracy and reliability. The goal is to provide readers with a balanced and well-informed perspective on this complex and rapidly evolving field.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: A thorough explanation of decentralized markets, their fundamental principles, and differentiating characteristics.
- Technological Foundations: An exploration of the technologies underpinning decentralized markets, including blockchain, smart contracts, and distributed ledger technologies (DLT).
- Applications Across Industries: Real-world examples of how decentralized markets are being implemented across various sectors.
- Challenges and Solutions: Identification of key obstacles facing decentralized markets and potential solutions.
- Future Implications: An analysis of the potential long-term impact of decentralized markets on global commerce and economic systems.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
Having established the importance and scope of decentralized markets, let's delve into a detailed exploration of their key aspects.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Decentralized Markets:
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
A decentralized market is a system for exchanging goods, services, or digital assets without relying on a central authority or intermediary to facilitate transactions. Instead, it leverages distributed ledger technology (DLT), often a blockchain, to record and verify transactions, ensuring transparency and security. Participants interact directly with each other, bypassing traditional gatekeepers. This fosters greater autonomy, reduces reliance on trusted third parties, and potentially leads to more efficient and inclusive marketplaces. Key characteristics include distributed trust, cryptographic security, and immutability of transaction records.
2. Technological Foundations:
Blockchain technology is the most prominent foundation for decentralized markets. Its distributed, immutable ledger ensures transparency and security. Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, automate transaction processes and eliminate the need for intermediaries. Other DLTs, while not as widely used, also play a role, offering different trade-offs in terms of scalability, security, and performance. These technologies are critical for enabling trustless and secure transactions in a decentralized environment.
3. Applications Across Industries:
Decentralized markets are finding applications in a wide range of industries:
- Finance: Decentralized finance (DeFi) is rapidly growing, offering decentralized lending, borrowing, trading, and other financial services. Stablecoins, cryptocurrencies pegged to fiat currencies, are also integral to this ecosystem.
- Supply Chain Management: Tracking goods and materials across the supply chain using blockchain can enhance transparency and traceability, reducing counterfeiting and improving efficiency.
- Digital Asset Trading: Cryptocurrency exchanges and non-fungible token (NFT) marketplaces are prime examples of decentralized markets for digital assets.
- Data Markets: Decentralized data marketplaces allow individuals and organizations to buy and sell data securely and transparently, while maintaining control over their data privacy.
- Gaming and Metaverse: Decentralized platforms are enabling new forms of gaming and virtual worlds where players own and trade in-game assets.
4. Challenges and Solutions:
While the potential benefits are substantial, decentralized markets face significant challenges:
- Scalability: Many blockchain networks struggle to handle large transaction volumes, leading to slow processing speeds and high fees. Layer-2 scaling solutions and alternative DLTs are being developed to address this.
- Regulation: The regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies and decentralized markets is still evolving, creating uncertainty and hindering wider adoption. Clearer regulatory frameworks are needed to foster innovation while mitigating risks.
- Security: Although decentralized systems are inherently more secure than centralized ones, they are still vulnerable to various attacks, including smart contract vulnerabilities and 51% attacks. Robust security audits and best practices are crucial.
- User Experience: The technical complexity of interacting with decentralized markets can be a barrier for many users. Improved user interfaces and simpler onboarding processes are needed to broaden adoption.
- Interoperability: Different blockchain networks often lack interoperability, limiting the seamless exchange of assets and data across platforms. Cross-chain solutions are essential for creating a more unified decentralized ecosystem.
5. Impact on Innovation:
Decentralized markets are fostering innovation in several ways:
- New Business Models: They are enabling new business models that are more efficient, transparent, and customer-centric.
- Enhanced Competition: By reducing barriers to entry, they encourage greater competition and innovation.
- Open Source Development: Many decentralized platforms are built on open-source technology, fostering collaboration and community-driven development.
Closing Insights: Summarizing the Core Discussion:
Decentralized markets represent a paradigm shift in how goods, services, and value are exchanged. While challenges remain, the potential benefits – increased transparency, enhanced security, improved efficiency, and greater accessibility – are substantial. The continued development of underlying technologies and regulatory clarity will be crucial in determining their widespread adoption.
Exploring the Connection Between Regulatory Frameworks and Decentralized Markets:
The relationship between regulatory frameworks and decentralized markets is complex and crucial. Effective regulation is necessary to mitigate risks, protect consumers, and prevent illicit activities while fostering innovation and preventing stifling the growth of this nascent industry.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Roles and Real-World Examples: Different jurisdictions are adopting varying approaches to regulating cryptocurrencies and decentralized markets, ranging from outright bans to more permissive frameworks. Examples include Singapore's progressive approach and China's stricter stance.
- Risks and Mitigations: Unregulated decentralized markets can be vulnerable to fraud, money laundering, and other illicit activities. Robust regulatory frameworks can help mitigate these risks while supporting innovation.
- Impact and Implications: Effective regulation can foster public trust, attract investment, and encourage wider adoption of decentralized technologies. Conversely, overly restrictive regulations can stifle innovation and limit the potential benefits of these systems.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection:
The interaction between regulatory frameworks and decentralized markets will be a key determinant of their future success. A balanced approach that fosters innovation while mitigating risks is essential to unlock the full potential of these transformative technologies.
Further Analysis: Examining Regulatory Challenges in Greater Detail:
The key challenge lies in balancing the need for consumer protection and preventing illicit activities with the desire to foster innovation and competition in the decentralized market space. This necessitates international collaboration to develop consistent and effective regulatory frameworks that can adapt to the rapidly evolving nature of these technologies.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Decentralized Markets:
-
What is a decentralized market? A decentralized market is a system for exchanging goods, services, or digital assets without relying on a central authority or intermediary.
-
How do decentralized markets work? They typically use distributed ledger technology, like blockchain, to record and verify transactions.
-
What are the benefits of decentralized markets? Increased transparency, security, efficiency, and accessibility are key benefits.
-
What are the challenges facing decentralized markets? Scalability, regulation, security, user experience, and interoperability are major challenges.
-
What is the future of decentralized markets? The future likely involves greater adoption across various industries, further technological advancements, and clearer regulatory frameworks.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Decentralized Markets:
- Understand the Technology: Educate yourself about blockchain, smart contracts, and other relevant technologies.
- Identify Relevant Applications: Explore how decentralized markets can address specific challenges or create opportunities within your industry or context.
- Assess Risks and Mitigations: Carefully evaluate the risks associated with participating in decentralized markets and implement appropriate security measures.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of the latest developments in the field, including technological advancements and regulatory changes.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights:
Decentralized markets represent a fundamental shift in how value is exchanged. While significant challenges remain, their potential to revolutionize commerce and various industries is undeniable. By navigating the challenges and leveraging the opportunities, businesses and individuals can participate in a new era of more transparent, secure, and efficient marketplaces. The future of decentralized markets is bright, promising to reshape the global economy in profound ways.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Decentralized Market Definition . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.