Decentralized Applications Dapps Definition Uses Pros And Cons
adminse
Mar 25, 2025 · 7 min read
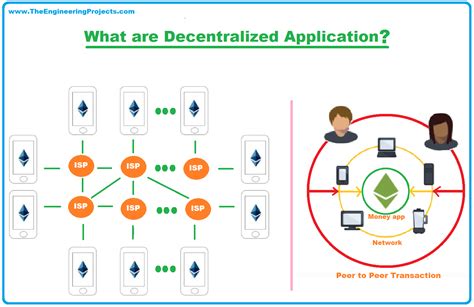
Table of Contents
Decoding Decentralized Applications (dApps): A Deep Dive into Definition, Uses, Pros, and Cons
What if the future of software lies in applications unshackled from central control? Decentralized applications (dApps) are poised to revolutionize how we interact with technology, offering unprecedented levels of security, transparency, and user autonomy.
Editor’s Note: This article on Decentralized Applications (dApps) provides a comprehensive overview of this rapidly evolving technology. The information presented is current as of October 26, 2023, and reflects the latest trends and developments in the dApp landscape.
Why dApps Matter: A New Era of Software
Decentralized applications, or dApps, represent a paradigm shift in software development. Unlike traditional applications that rely on centralized servers controlled by a single entity (like a company), dApps leverage the power of blockchain technology and distributed networks. This fundamental difference leads to several significant advantages, impacting various sectors from finance and gaming to supply chain management and healthcare. The inherent security, transparency, and censorship resistance offered by dApps are driving their increasing adoption and fueling innovation.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This article provides a comprehensive exploration of dApps, covering their core definition, diverse use cases, significant advantages, and inherent limitations. We will delve into the technological underpinnings of dApps, examine real-world examples, and analyze the factors that will shape their future development and adoption. Readers will gain a solid understanding of the potential and challenges associated with this transformative technology.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article is based on extensive research, drawing upon white papers from leading blockchain projects, peer-reviewed academic publications, industry reports, and analysis of publicly available data on dApp usage and performance. The information presented is intended to be factual, unbiased, and reflective of the current state of the dApp ecosystem.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: A precise definition of dApps and their key characteristics.
- Practical Applications: A broad overview of dApps across various industries.
- Advantages and Disadvantages: A balanced assessment of the pros and cons of dApps.
- Challenges and Future Outlook: An analysis of the obstacles facing dApp development and its future trajectory.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion
Having established the importance of dApps, let's delve into the core aspects of this technology, beginning with a clear definition and exploring its practical applications, limitations, and future potential.
Exploring the Key Aspects of dApps
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
A dApp is a decentralized application that runs on a distributed network, typically a blockchain. Key characteristics that distinguish dApps from traditional apps include:
- Open-source: The codebase is typically publicly available, allowing for community contributions and audits.
- Decentralized: The application is not controlled by a single entity, reducing censorship and single points of failure.
- Cryptographically secure: Transactions and data are secured using cryptographic methods.
- Incentivized: Often utilizes tokenized incentives to reward users and maintain network integrity.
2. Applications Across Industries:
The potential applications of dApps are vast and diverse. Some prominent examples include:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): dApps are revolutionizing the financial industry, offering services such as lending, borrowing, trading, and decentralized exchanges (DEXs) without intermediaries. Examples include Aave, Compound, and Uniswap.
- Gaming: Blockchain-based games leverage dApps to offer true ownership of in-game assets, enabling players to trade and monetize their digital possessions. Examples include Axie Infinity and Decentraland.
- Supply Chain Management: dApps can enhance transparency and traceability in supply chains, providing end-to-end visibility of product movement and origin.
- Healthcare: dApps can facilitate secure and private data sharing in healthcare, improving patient access to their medical records and streamlining healthcare processes.
- Social Media: Decentralized social media platforms aim to offer users more control over their data and reduce the power of centralized platforms. Examples include Mastodon and Diaspora*.
- Digital Identity: dApps can be used to create secure and verifiable digital identities, reducing reliance on centralized identity providers.
3. Challenges and Solutions:
Despite the potential, dApps face several challenges:
- Scalability: Many blockchains struggle to handle a high volume of transactions, limiting the scalability of dApps. Solutions include layer-2 scaling solutions and advancements in blockchain technology.
- User Experience (UX): The user experience of dApps can be challenging for non-technical users, requiring improvements in usability and accessibility.
- Security: While blockchain technology offers inherent security, vulnerabilities can still exist in the smart contracts that power dApps. Rigorous audits and security best practices are crucial.
- Regulation: The regulatory landscape for dApps is still evolving, creating uncertainty for developers and users. Clear regulatory frameworks are needed to promote innovation while mitigating risks.
4. Impact on Innovation:
dApps are driving significant innovation by fostering:
- Increased Transparency: Blockchain’s immutable ledger provides transparency in transactions and data.
- Enhanced Security: Cryptographic security measures enhance data protection and prevent unauthorized access.
- Improved Efficiency: Automation and decentralized processes streamline operations and reduce costs.
- Greater User Control: Users have more control over their data and digital assets.
Closing Insights: Summarizing the Core Discussion
dApps are not simply a technological advancement; they represent a fundamental shift in how applications are built and utilized. By leveraging the power of blockchain and distributed networks, dApps offer compelling advantages in terms of security, transparency, and user autonomy. While challenges remain, the potential of dApps to transform various industries is undeniable.
Exploring the Connection Between User Experience (UX) and dApps
The relationship between UX and dApps is critical to their widespread adoption. While the underlying technology of dApps offers numerous benefits, a poor user experience can hinder their success. A complex and unintuitive interface can deter users, especially those unfamiliar with blockchain technology.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Roles and Real-World Examples: Poor UX in dApps has led to low user adoption in certain applications. For instance, some DeFi protocols have complex interfaces that make it difficult for casual users to interact with them. Conversely, user-friendly interfaces in other DeFi projects have resulted in increased adoption.
- Risks and Mitigations: Poor UX can lead to user error, security vulnerabilities, and loss of funds. Mitigating these risks requires developers to prioritize user experience through clear instructions, intuitive designs, and robust error handling.
- Impact and Implications: Improving UX is crucial for the mass adoption of dApps. By creating user-friendly interfaces, developers can broaden the appeal of dApps beyond the tech-savvy community.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
The interplay between UX and dApps is essential for the future of decentralized applications. Addressing the challenges of UX is not just about aesthetics; it is crucial for security, accessibility, and the overall success of dApps.
Further Analysis: Examining Security in Greater Detail
Security is paramount in the context of dApps. The decentralized nature of dApps provides a certain level of security by eliminating single points of failure, but vulnerabilities can still exist within the smart contracts that govern these applications. Smart contract audits and thorough security testing are crucial steps in mitigating these risks. Furthermore, the reliance on cryptographic methods requires a high degree of expertise in cryptography to ensure the security of the dApp.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About dApps
-
What is a dApp? A dApp is a decentralized application that runs on a distributed network, typically a blockchain. It’s characterized by open-source code, decentralization, cryptographic security, and often, tokenized incentives.
-
How are dApps different from traditional apps? Traditional apps rely on centralized servers controlled by a single entity. dApps are distributed across a network, making them more resistant to censorship and single points of failure.
-
What are the benefits of using dApps? Benefits include increased security, transparency, user autonomy, and censorship resistance.
-
What are the risks associated with using dApps? Risks include smart contract vulnerabilities, scalability issues, and the complexity of the technology.
-
How can I learn more about dApps? You can explore resources like blockchain developer communities, online courses, and technical documentation.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of dApps
- Understand the Basics: Before interacting with a dApp, familiarize yourself with its functionality and the risks involved.
- Choose Reputable Platforms: Only use dApps built on well-established and secure platforms.
- Secure Your Wallet: Use a secure wallet to store your cryptocurrency and protect your assets.
- Be Aware of Scams: Be cautious of scams and phishing attempts targeting dApp users.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
Decentralized applications represent a transformative technology with the potential to reshape numerous industries. While challenges exist in terms of scalability, user experience, and regulation, the advantages offered by dApps in terms of security, transparency, and user control are undeniable. As the technology continues to mature and adoption increases, dApps are poised to play an increasingly significant role in the future of software and beyond. By understanding their potential and limitations, we can effectively harness their power to create a more decentralized and equitable digital world.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Decentralized Applications Dapps Definition Uses Pros And Cons . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.